- zoom
- Syntax
- Values
- Formal definition
- How TO — Zoom on Hover
- Zoom on Hover
- How To Zoom on Hover
- Example
- COLOR PICKER
- Report Error
- Thank You For Helping Us!
- How TO — Zoom on Hover
- Zoom on Hover
- How To Zoom on Hover
- Example
- COLOR PICKER
- Report Error
- Thank You For Helping Us!
- Implement simple font zoomer in JavaScript & HTML
- JavaScript code
- Calling JavaScript from HTML
- Accessibility Page Zoom
- What
- How
- Provide enough space for key content
- Hidden icons
- No clutter
- Avoid horizontal scrolling
- Fixed width
- All content and functionality is available
- Hidden tabs
- Avoid text in images
zoom
Non-standard: This feature is non-standard and is not on a standards track. Do not use it on production sites facing the Web: it will not work for every user. There may also be large incompatibilities between implementations and the behavior may change in the future.
The non-standard zoom CSS property can be used to control the magnification level of an element. transform: scale() should be used instead of this property, if possible. However, unlike CSS Transforms, zoom affects the layout size of the element.
Syntax
/* Keyword values */ zoom: normal; zoom: reset; /* values */ zoom: 50%; zoom: 200%; /* values */ zoom: 1.1; zoom: 0.7; /* Global values */ zoom: inherit; zoom: initial; zoom: revert; zoom: revert-layer; zoom: unset;
Values
Render this element at its normal size.
Do not (de)magnify this element if the user applies non-pinch-based zooming (e.g. by pressing Ctrl — — or Ctrl + + keyboard shortcuts) to the document. Do not use this value, use the standard unset value instead.
Zoom factor. 100% is equivalent to normal . Values larger than 100% zoom in. Values smaller than 100% zoom out.
Zoom factor. Equivalent to the corresponding percentage ( 1.0 = 100% = normal ). Values larger than 1.0 zoom in. Values smaller than 1.0 zoom out.
Formal definition
How TO — Zoom on Hover
Learn how to zoom/scale an element on hover with CSS.
Zoom on Hover
How To Zoom on Hover
Example
.zoom:hover transform: scale(1.5); /* (150% zoom — Note: if the zoom is too large, it will go outside of the viewport) */
>
Tip: Go to our CSS Transform Tutorial to learn more about how to scale elements.
COLOR PICKER
Report Error
If you want to report an error, or if you want to make a suggestion, do not hesitate to send us an e-mail:
Thank You For Helping Us!
Your message has been sent to W3Schools.
Top Tutorials
Top References
Top Examples
Get Certified
W3Schools is optimized for learning and training. Examples might be simplified to improve reading and learning. Tutorials, references, and examples are constantly reviewed to avoid errors, but we cannot warrant full correctness of all content. While using W3Schools, you agree to have read and accepted our terms of use, cookie and privacy policy.
How TO — Zoom on Hover
Learn how to zoom/scale an element on hover with CSS.
Zoom on Hover
How To Zoom on Hover
Example
.zoom:hover transform: scale(1.5); /* (150% zoom — Note: if the zoom is too large, it will go outside of the viewport) */
>
Tip: Go to our CSS Transform Tutorial to learn more about how to scale elements.
COLOR PICKER
Report Error
If you want to report an error, or if you want to make a suggestion, do not hesitate to send us an e-mail:
Thank You For Helping Us!
Your message has been sent to W3Schools.
Top Tutorials
Top References
Top Examples
Get Certified
W3Schools is optimized for learning and training. Examples might be simplified to improve reading and learning. Tutorials, references, and examples are constantly reviewed to avoid errors, but we cannot warrant full correctness of all content. While using W3Schools, you agree to have read and accepted our terms of use, cookie and privacy policy.
Implement simple font zoomer in JavaScript & HTML
A lot of websites on internet provide users with an option to increase the font size of the page for better reading experience. Although nowadays almost all the web browsers supports zoom in/out functionality using mouse wheel scroll or other shortcut keys, it is sometimes a good idea to give user a way to increase/decrease the font size of web page. Let us implement a simple zoomer code in JavaScript that will increase/decrease the font size of the web page at client side without reloading the page from server. A small JavaScript snippet will be used to change the font size of the web page at client side.
JavaScript code
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)var fontSize = 1; function zoomIn( ) < fontSize += 0.1; document.body.style.fontSize = fontSize + "em"; > function zoomOut( ) < fontSize -= 0.1; document.body.style.fontSize = fontSize + "em"; >
In the above JavaScript code, a global variable fontSize is defined with value 1. This variable’s value will be changed whenever user tries to increase or decrease the font size. Then we have two functions zoomIn() and zoomOut() to perform zoom in and zoom out respectively. The font size of the web page is changed by changing the attribute fontSize in document.body.style.
Calling JavaScript from HTML
You can place simple icons to zoom in and zoom out the text and call the zoomIn() and zoomOut() methods on click event. Or can place buttons to zoom in/out.
Code language: HTML, XML (xml)input type="button" value="+" onClick="zoomIn()"/> input type="button" value="-" onClick="zoomOut()"/>
Accessibility Page Zoom
People with low vision need to zoom the content in order to use the page.
What
The big brother of text zoom is page zoom. Zoom everything! The principles are easy to understand:
- Avoid horizontal scrolling.
- All content is available.
- All functionality is available.
- Avoid text in images.
- Provide space for key content.
Available means that nothing is clipped, truncated or obscured.
Page zoom often triggers mobile view on responsive sites, which is good.
How
You will now learn five techniques to support page zoom.
Provide enough space for key content
Do not let secondary content occupy the screen.
Hidden icons
In this example from Samsung India, the page is zoomed 400 %. The content is scaling properly. No horizontal scrollbar. However, the chat button occupies a big part of the browser window. It is not easy to access the buttons for search, cart or menu. And the quality of the button graphic is low. In addition, there is a huge ad for an app.
- Add a minimize button for the chat button. Use the minimized version as the default.
- Use vector graphics like SVG instead of raster graphics like PNG.
- Show mobile ads only for mobile devices.
No clutter
In this example from Philips, the entire viewport is available for main content. The main navigation is opened, and there is no clutter. The text and graphics are scaled well.
Avoid horizontal scrolling
Scrolling in two dimensions is confusing.
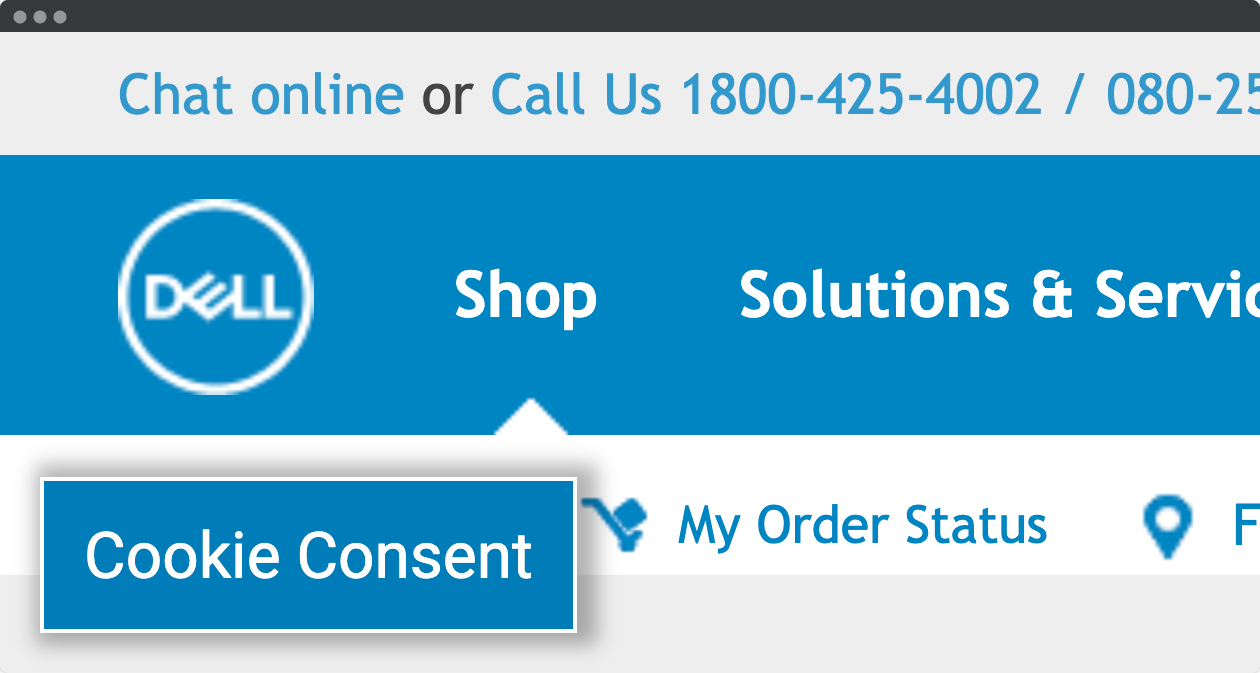
Fixed width
In this example from Dell, we can only see a small part of the header. The site does not scale when zoomed. The result is a large horizontal scroll that makes it hard to navigate the page in two dimensions.
In addition, the cookie consent button is fixed, not possible to remove even though the consent is given. The logo and the icons are low resolution PNGs that does not scale well. Viewport is not set.
- Make the site responsive.
- Add a minimize button for the cookie button. Use the minimized version as the default.
- Use vector graphics like SVG instead of raster graphics like PNG.
All content and functionality is available
No content should be hidden when zoomed.
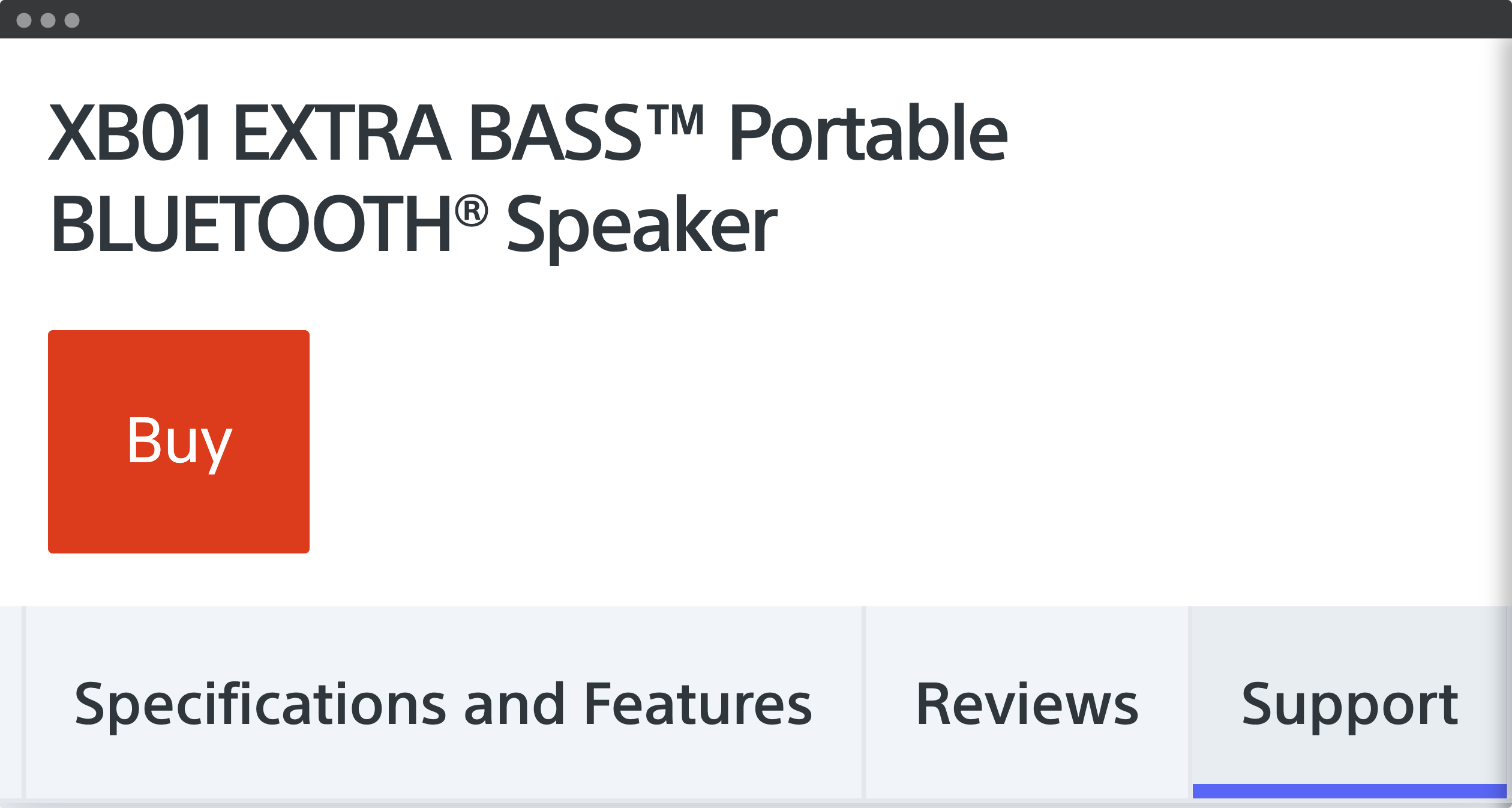
Hidden tabs
In this example from Sony, the tabs with product information is not accessible in a desktop browser with page zoom. Even if the user scrolls, the scrolling is happening outside of the browser window. All the specifications, features, reviews and support are inaccessible. The problem is that the entire section is «sticky»:
.sticky-nav position: fixed;
z-index: 1035;
top: 0;
>
This section is 159 pixels high in a mobile view. When zoomed four times, the fixed section occupies 636 pixels of the desktop view. With a browser height of 720 pixels, minus the top part of the browser, leaves not much room for the main content.
Fixed content is not necessarily inaccessible. The takeaway is that you should always test your site with page zoom in common browser sizes.
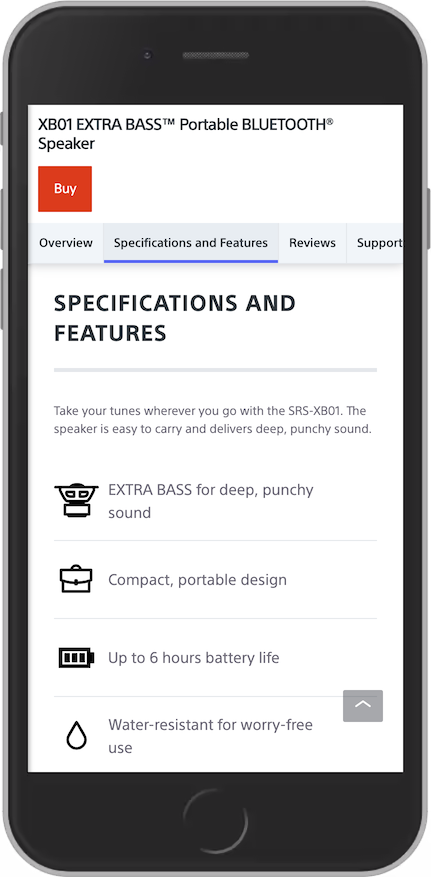
In a mobile view, the content beneath the tabs is accessible.
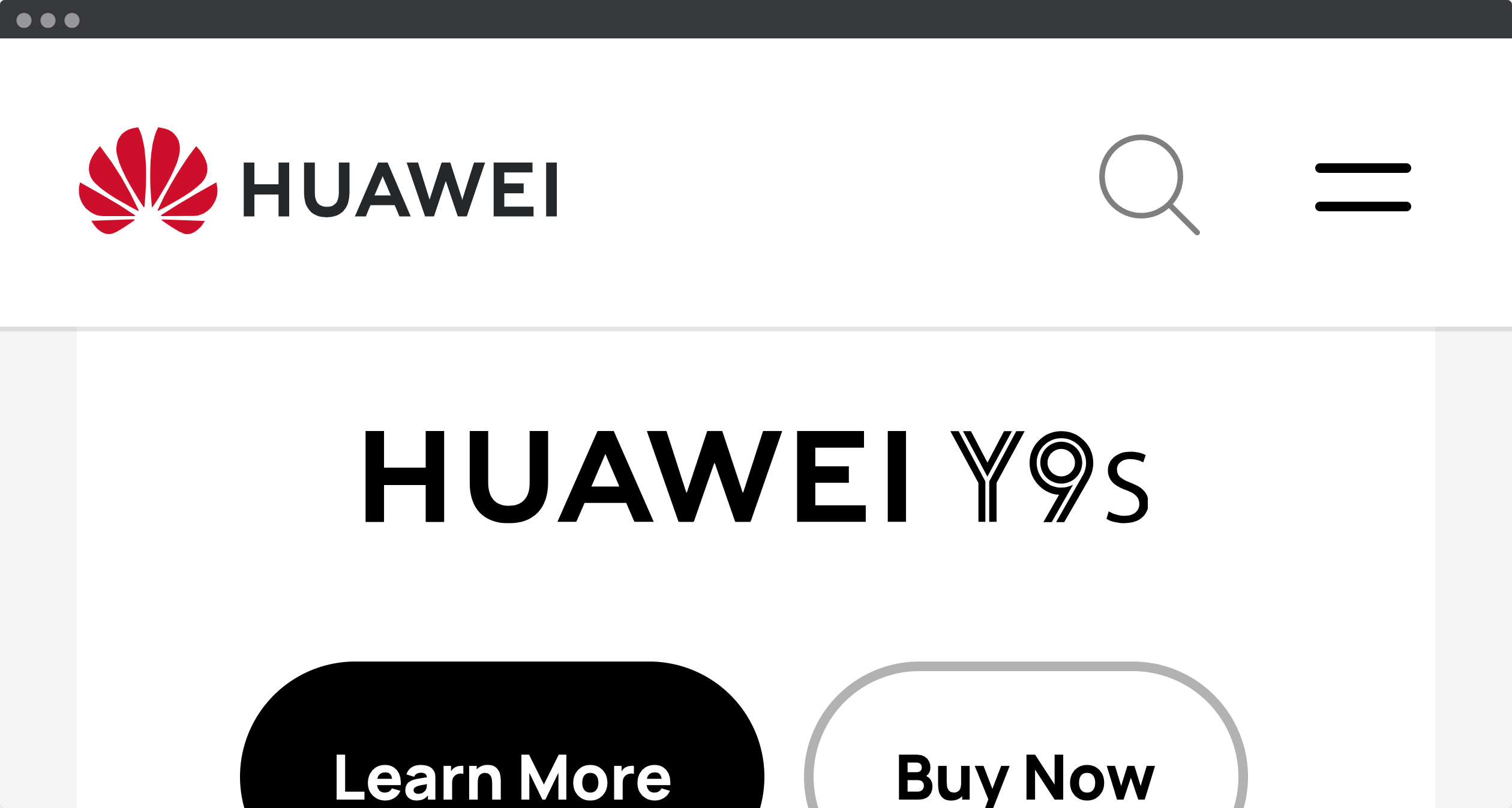
The sticky navigation from Huawei is not too high, so there are enough space for the main content.
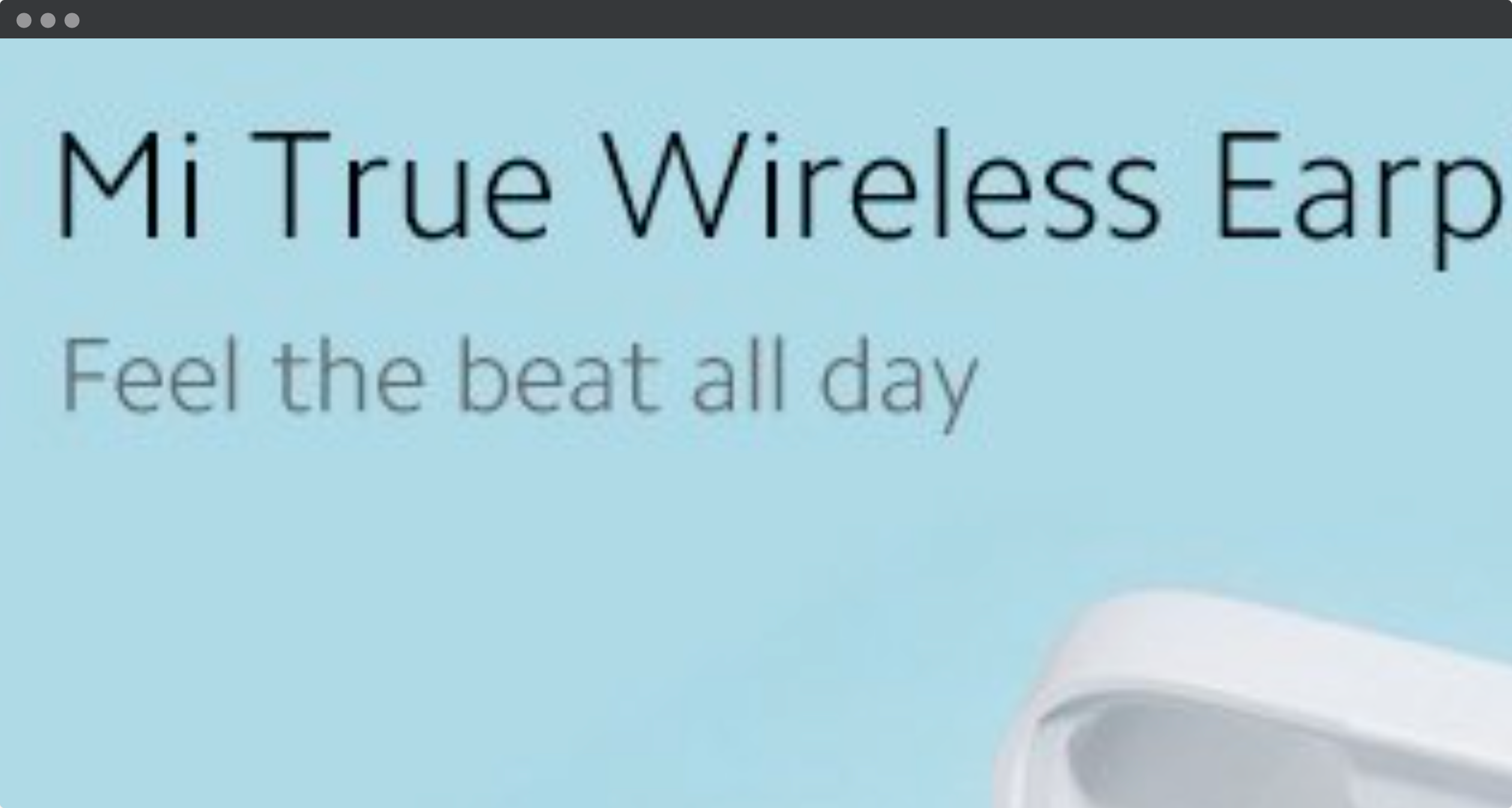
Avoid text in images
In this example from Xiaomi, the zoomed text is pixelated because it is part of the image. Parts of the text is also outside the browser window, so that the user has to scroll to read the entire product title. Displaying text with pure HTML and CSS has many benefits, in addition to be accessible: responsive, translatable and searchable.