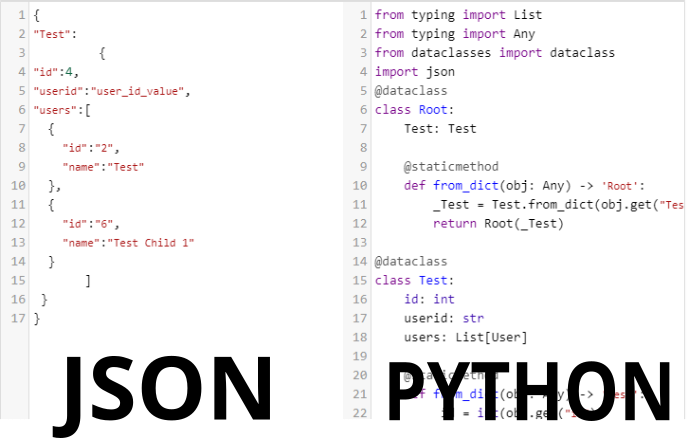
- How to create pojo classes from xsd in Java?
- Method 1: Using JAXB
- Step 1: Add JAXB dependencies to your project
- Step 2: Create XSD file
- Step 3: Generate Java classes from XSD
- Step 4: Use generated Java classes
- Method 2: Using XSD to Java code generator tool
- Step 1: Add JAXB dependencies
- Step 2: Create XSD file
- Step 3: Generate Java classes
- Step 4: Use generated Java classes
- Method 3: Manually writing POJO classes
- XML to JAVA Online Converter
- Convert any XML string to a JAVA or POJO object online. Check out the help panel below to view details on how to use this converter.
- Xsd to java object online
- Steps To Use The Tools: (Support WhatsApp No. 7439236696 )
- List of tools:
How to create pojo classes from xsd in Java?
Creating POJO (Plain Old Java Object) classes from XSD (XML Schema Definition) is a common task in Java programming. XSD defines the structure of an XML document, including the data types and elements, and is used to validate the XML document. The POJO classes are used to represent the data in a Java object, making it easier to manipulate the data in a Java program. There are several methods available to create POJO classes from XSD, and each method has its own advantages and disadvantages. The following methods can be used to generate POJO classes from XSD in Java:
Method 1: Using JAXB
JAXB is a Java API for XML binding that allows Java objects to be mapped to XML representations. It can be used to generate Java classes from an XML schema definition (XSD) file. Here are the steps to create POJO classes from XSD using JAXB:
Step 1: Add JAXB dependencies to your project
Add the following dependencies to your project’s pom.xml file:
dependency> groupId>javax.xml.bindgroupId> artifactId>jaxb-apiartifactId> version>2.3.1version> dependency> dependency> groupId>com.sun.xml.bindgroupId> artifactId>jaxb-coreartifactId> version>2.3.0.1version> dependency> dependency> groupId>com.sun.xml.bindgroupId> artifactId>jaxb-implartifactId> version>2.3.2version> dependency>Step 2: Create XSD file
Create an XSD file that describes the structure of the XML data you want to map to Java objects.
xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> xs:element name="person" type="personType"/> xs:complexType name="personType"> xs:sequence> xs:element name="name" type="xs:string"/> xs:element name="age" type="xs:int"/> xs:sequence> xs:complexType> xs:schema>Step 3: Generate Java classes from XSD
Use the xjc command-line tool provided by JAXB to generate Java classes from the XSD file. Run the following command in your project directory:
xjc -d src/main/java -p com.example.generated xsd/person.xsdThis will generate Java classes in the src/main/java/com/example/generated directory.
Step 4: Use generated Java classes
Now that you have generated Java classes from the XSD file, you can use them in your Java code to manipulate XML data. Here is an example:
import com.example.generated.Person; import javax.xml.bind.JAXBContext; import javax.xml.bind.JAXBException; import javax.xml.bind.Unmarshaller; import java.io.File; public class Main public static void main(String[] args) try File file = new File("person.xml"); JAXBContext jaxbContext = JAXBContext.newInstance(Person.class); Unmarshaller jaxbUnmarshaller = jaxbContext.createUnmarshaller(); Person person = (Person) jaxbUnmarshaller.unmarshal(file); System.out.println(person.getName()); System.out.println(person.getAge()); > catch (JAXBException e) e.printStackTrace(); > > >This code reads an XML file named person.xml and unmarshals it into a Person object. The getName() and getAge() methods can be used to retrieve the values of the name and age elements in the XML file.
That’s it! You have successfully created POJO classes from XSD using JAXB.
Method 2: Using XSD to Java code generator tool
One of the easiest ways to create POJO classes from XSD is by using a code generator tool. In Java, there are many code generator tools available, such as JAXB, Castor, and XStream. Here, we will use JAXB to generate Java classes from XSD.
Step 1: Add JAXB dependencies
First, we need to add JAXB dependencies to our project. If you are using Maven, you can add the following dependencies to your pom.xml file:
dependency> groupId>javax.xml.bindgroupId> artifactId>jaxb-apiartifactId> version>2.3.1version> dependency> dependency> groupId>org.glassfish.jaxbgroupId> artifactId>jaxb-runtimeartifactId> version>2.3.1version> dependency>Step 2: Create XSD file
Next, we need to create an XSD file. For example, let’s create a simple XSD file named person.xsd :
xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" targetNamespace="http://example.com/person" xmlns="http://example.com/person" elementFormDefault="qualified"> xs:element name="person"> xs:complexType> xs:sequence> xs:element name="name" type="xs:string"/> xs:element name="age" type="xs:int"/> xs:sequence> xs:complexType> xs:element> xs:schema>Step 3: Generate Java classes
Now, we can use the xjc tool (part of the JDK) to generate Java classes from the XSD file. Here is an example command to generate the classes:
xjc -d src/main/java -p com.example.person person.xsdThis command will generate the Java classes in the com.example.person package under the src/main/java directory.
Step 4: Use generated Java classes
Finally, we can use the generated Java classes in our code. Here is an example code snippet to create a Person object and marshal it to XML:
import com.example.person.Person; import javax.xml.bind.JAXBContext; import javax.xml.bind.JAXBException; import javax.xml.bind.Marshaller; import java.io.StringWriter; public class Main public static void main(String[] args) throws JAXBException Person person = new Person(); person.setName("John"); person.setAge(30); JAXBContext jaxbContext = JAXBContext.newInstance(Person.class); Marshaller marshaller = jaxbContext.createMarshaller(); marshaller.setProperty(Marshaller.JAXB_FORMATTED_OUTPUT, true); StringWriter writer = new StringWriter(); marshaller.marshal(person, writer); System.out.println(writer.toString()); > >This code will output the following XML:
person xmlns="http://example.com/person"> name>Johnname> age>30age> person>That’s it! We have successfully generated Java classes from XSD using the JAXB code generator tool.
Method 3: Manually writing POJO classes
To manually create POJO classes from XSD in Java, follow these steps:
- First, create a new Java package to hold your POJO classes.
- Next, create a new Java class for each complex type defined in the XSD file. The class name should match the name of the complex type, and it should have member variables for each element in the complex type.
public class MyComplexType private String element1; private int element2; public String getElement1() return element1; > public void setElement1(String element1) this.element1 = element1; > public int getElement2() return element2; > public void setElement2(int element2) this.element2 = element2; > >- If the XSD file defines any simple types, create a new Java class for each one. The class name should match the name of the simple type, and it should have a single member variable of the appropriate type.
public class MySimpleType private String value; public String getValue() return value; > public void setValue(String value) this.value = value; > >- If the XSD file defines any enumerations, create a new Java enum for each one. The enum name should match the name of the enumeration, and it should have a member for each enumeration value.
public enum MyEnum VALUE1, VALUE2, VALUE3 >- If the XSD file defines any attributes, add member variables to the appropriate classes to represent them.
public class MyComplexType private String element1; private int element2; private String attribute1; public String getElement1() return element1; > public void setElement1(String element1) this.element1 = element1; > public int getElement2() return element2; > public void setElement2(int element2) this.element2 = element2; > public String getAttribute1() return attribute1; > public void setAttribute1(String attribute1) this.attribute1 = attribute1; > >- Finally, create a new Java class to represent the root element of the XML document. This class should have member variables for each top-level element in the XSD file.
public class MyRootElement private MyComplexType complexType; private MySimpleType simpleType; private MyEnum myEnum; public MyComplexType getComplexType() return complexType; > public void setComplexType(MyComplexType complexType) this.complexType = complexType; > public MySimpleType getSimpleType() return simpleType; > public void setSimpleType(MySimpleType simpleType) this.simpleType = simpleType; > public MyEnum getMyEnum() return myEnum; > public void setMyEnum(MyEnum myEnum) this.myEnum = myEnum; > >That’s it! You’ve now manually created POJO classes to represent the elements in your XSD file. You can use these classes to parse and generate XML documents using a variety of Java libraries, such as JAXB or XMLBeans.
XML to JAVA Online Converter
Convert any XML string to a JAVA or POJO object online. Check out the help panel below to view details on how to use this converter.
➔
➔
➔
➔
➔
➔
➔
➔
➔
➔
➔
Xsd to java object online
You can request for new feature / tool based on your project needs. It will be considered with high importance and added shortly if feasible.
You can reach to us at easycodeforall@gmail.com Alternatively, please report here if you find any defect/error . It will help us to correct/fix it. If you need any enhancement, please share with us also
There is a monthly cost to run this webs site. You may support us through below UPI QR Code / through Buy Me A Coffee
—Susanta (UPI ID: susanta.ghosh@okicici)
Steps To Use The Tools: (Support WhatsApp No. 7439236696 )
List of tools:
- Generate Jav Code For XML Processing:
- Generate Java Code For JSON Processing:
- Generate XSLT Code::
- Webservice Code:
- Generate SpringBoot Code(REST):
- Generate Java Beans Code :
- Generate XSD From XML :
- XML To JSON:
- JSON To XML:
- CSV To XML:
- CSV To JSON:
- XML To Template:
- XML To Mapping Document:
- Debug/Test XSLT:
- XPath Utility:
- XML Utility:
- JSON Utility:
- String Utility:
- JavaDoc Comments:
- Replace Hard-coded String:
- Validate XSD/XML:
- XML Formatter:
- JSON Formatter:
- SQL To Java DAO Code Generator:
- URL Encoder/Decoder:
- JSON To JavaScript:
- JSON To AngularJS Code:
Gaurav Pandey (2022-04-16) :
Can you please add a tool to generate nodeJS code from JSON. Mainly the nodeJs code required to develop a REST service with mongodb.?
Reply ;
easycodeforall: (2022-04-21)
Thanks for your request! We have added it into our backlog. We will add it soon.
Devandra Malik (2022-04-16) :
Thanks easycodeforall for such developer friendly tool set. I use most your tools in our project. We need to write JUnit test cases for each of our Java Classes. Can you please add a tool to generate JUnit Test Cases for a Java Class? It would be a great help!
Reply ;
easycodeforall: (2022-04-21)
Thank you so much Devandra for your feedback. We will add a tool to generate JUNIT test cases for a Java Class.
easycodeforall: (2022-04-21)
Thanks once more for your reques! We have added JUnit test case generator and its available now online (https://www.easycodeforall.com/generate-junit.html)
easycodeforall: (2022-04-21)
Thank you so much for using easycodeforall! We would like to know if any tool did not meet the expectaion or if you need any new tool or enhancement on any existing tool !
anonymous (2022-04-16) :
If we need to define 100+ payment type in the SBC, is there any api for it? or we need to configure each payment manually only in the SBC.
Reply ;
Balaji K (2022-04-16) :
We have a business requirement where we need to identify SCAC and CarrierServiceCode for an order during scheduling itself. We are maintaining routing guide in OMS at enterprise level. We will receive an Order XML from website where we wont be having carrier and carrier service code. We will only be having LevelOfService and FreightTerms as PREPAID(in order to identify the routing guide). We have noticed in the javadocs that when we run scheduleOrder API or even findInventory API, the determineRouting API will be called internally. So during this scheduleOrder call, we thought of making use of this determineRouting API call and somehow identify SCAC and CarrierServiceCode for that order. But when we try calling scheduleOrder API, we saw that the determineRouting API is not even getting called. Is this workflow correct, will determineRouting API will be called during promising API calls or will we be missing any configurations?
The same order after shipment created moves into Awaiting routing and the ROUTE_SHIPMENT transaction is identifying the SCAC and CarrierServiceCode for that shipment. So, routing guide is working fine but need to understand if expecting it to happen during scheduleOrder or findInventory is correct or not?
Please help us in the same.
Thanks,
Balaji K
Reply ;
easycodeforall: (2022-04-21)
Thanks for your question.
I responded in the page https://www.easycodeforall.com/ibm-sterling-commerce-interview-question.html
Rahul Ghosh (2022-07-07) :
I personally know you. When ever I asked for knowledge( or help). I got it. Thank you so much Susanta da.
Reply ;