- What is www and public_html directory in my folder?
- Understanding the public_html folder
- Where To Access
- Addon Domains & Subdomains
- Ideal Permissions
- What is a public_html Folder?
- Where To Find this Folder?
- Addon Domains & Subdomains
- Permissions
- Also Read
- What is public_html?
- Public_html permissions
- WordPress setup folder
- What to keep in public_html folder?
- What to keep out of public_html folder?
What is www and public_html directory in my folder?
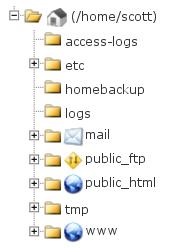
The public_html directory is the folder to place in web-readable files. This means that public_html is the folder where you put all website files which you want to appear when someone types your main domain. Files placed below the public_html folder will not be visible on the web. The www folder is what is called a symlink. This points to the public_html folder and generally is used as a shorthand is cgi scripts for the path. Instead of using the path /home/yourusername/public_html you can use /home/yourusername/www. The www directory is simply a symbolic link to the public_html directory. So anything you place in either directory will be identical when viewed from the other directory on the server. One is usually set up as an alias for the other meaning that it doesn’t matter which of the two you use because they both point to the same folder.
public_html folder
The public_html folder is the web root for your primary domain name. when someone types your domain name into their browser, whatever is in your public_html directory is what will be shown to them. We can explain this using an example: If you have a default filename like index.html or default.html inside your public_html folder, then when someone call your domain name it will display that page. If you don’t have any default file in your public_html directory, then a list of files in the public_html folder will be shown. You can create addon domains and sub domains in your account and if you have added an addon domain called myaddon.com then it will use the subfolder similar to /public_html/myaddon.com/or if you are added a sub domain called mysubdomain.com then it will use the subfolder similar to /public_html/mysubdomain.com/
In Shared hosting accounts, you will get only one cPanel account, which is why all addon domains are subfolders of the public_html folder. If you do not want the additional domains to be subfolders of the public_html, then go with the reseller, VPS or dedicated hosting is a better solution since you can put each domain in its own cPanel to keep it separate from other domains.
How to access the public_html folder?
You can access your public_html folder from your cPanel interface. Please follow the below given steps to know about how to access your public_html folder from your cPanel account.
1) Login to your cPanel account.
2) Navigate to Files >> File Manager.
3) You can see the public_html folder on your File Manager page.
The public_html folder should always have 0750 permissions. All folders inside the public_html folder should have 0755 permissions. All files inside the public_html folder should have 0644 permissions.
If you need any further help, please do reach our support department.
Understanding the public_html folder
We have discussed about what exactly is the web root. Web root is also referred to as the public_html folder.
This therefore means that p ublic_html is the folder where files for your main domain rests. You can put all website files which are a part of your main domain.
In other words, whenever someone visits your domain (say example.com), they will be able to see files in the public_html folder.
Where To Access
public_html folder is located inside your File Manager in your cPanel.
Here is a view of how your file manager folder looks like
Quite often, the main file hosted for your domain is titled as index.html (or any of the other default filenames) in the public_html folder, and it will display that page.
| Path in File Manager (or in FTP)* | Corresponding URL in a Web Browser |
|---|---|
| /public_html/ | http://www.ukhost4u.com/ |
| /public_html/pagename.html | http://www.ukhost4u.com/pagename.html |
| /public_html/folder/ | http://www.ukhost4u.com/folder/ |
| /public_html/folder/page.html | http://www.ukhost4u.com/folder/page.html |
Replace ukhost4u.com with the primary domain on your account. This would be the one that you’d have originally signed up with.
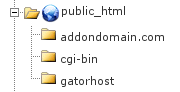
Addon Domains & Subdomains
You can also create sub-domains and add on domains. These will rest inside the public_html folder.
Examples
You can create an Addon domain called ukhost4u.com and it will use a subfolder similar to /public_html/ukhost4u.com/ (unless you specified otherwise).
Or you could create a Subdomain called ukhost4u.example.com and it would use a subfolder similar to /public_html/ukhost4u/ (unless you specified otherwise).
Here is how you can understand this entire thing using examples
| Path in File Manager (or in FTP)* | Corresponding URL in a Web Browser |
|---|---|
| /public_html/ukhost4u/ | http://ukhost4u.example.com/ |
| /public_html/ukhost4u.com/ | http://www.ukhost4u.com/ |
Replace example.com with the primary domain on your account (the one you originally signed up with, unless you changed it). Replace addondomain.com with the additional domain you added in the “addon domains” section of cPanel. Shared accounts only get one cPanel, which is why all addon domains are subfolders of the public_html folder.
Ideal Permissions
- the public_html folder should always have 0750 permissions.
- All folders inside the public_html folder should have 0755 permissions
- All files inside the public_html folder should have 0755 or 0644 permissions.
Some websites and scripts may advise you to use 777 permissions, however, 755 permission can be used for the same purpose instead, since it is more secure.
*The full path is actually /home/username/public_html/ (where username is your cPanel username) rather than /public_html/ but in most places you will see /public_html/ instead of the full path, since it assumes you know you are in your own home directory.
What is a public_html Folder?
The web root for your primary domain name is called as the public_html folder.
The public_html folder comprises of all website files which you want to be displayed when someone types your main domain (the one provided while signing up for hosting).
Or in other words, when visitors type your domain name into their browser, whatever is in the public_html folder will get displayed to them.
Where To Find this Folder?
You can find the public_html folder inside your File Manager in your cPanel.
For example, if the file named as index.html is present in the public_html folder, it will get displayed when your website is browsed.
In case there isn’t a default file in the public_html folder (such as index.html, default.html, etc.), then a list of files in the public_html folder will be displayed.
Note: Ensure to replace example.com with the primary domain on your account ( the one that you had signed up with).
Addon Domains & Subdomains
It is possible to create Addon domains and Subdomains and these will be stored in the folder inside public_html.
Suppose you create an Addon domain named as addondomain.com. It will use a subfolder same as /public_html/addondomain.com/ (unless you specify any other).
Or if create a Subdomain named as milesweb.abc.com, it will use a folder same as /public_html/milesweb/ (unless you specify any other).
Suppose milesweb.abc.com is defined as a subdomain, and addondomain.com is defined as an addon domain, then the following examples are applicable:
Note: Ensure to replace abc.com with the primary domain on your account (the one you originally signed up with and haven’t changed it). Also, replace addondomain.com with the extra domain you added in the cPanel’s “addon domains” section.
In case you don’t want the additional domains to be subfolders of public_html, then reseller, VPS or dedicated hosting is a better solution, because you can insert each domain in its own cPanel to keep it independent from other domains. With shared hosting you only get one cPanel, and therefore, all addon domains are subfolders of the public_html folder.
Permissions
It is important that public_html folder has 0750 permissions.
Check if all files within the public_html folder have 0755 or 0644 permissions.
Note: If the complete path is actually /home/username/public_html/ (where username is your cPanel username) instead of /public_html/ but in maximum places you will see /public_html/ rather than the full path, because it assumes that you know you are in your own home directory.
Hope this article has helped you to learn about public_html folder.
Also Read
Pallavi is a Digital Marketing Executive at MilesWeb and has an experience of over 4 years in content development. She is interested in writing engaging content on business, technology, web hosting and other topics related to information technology.
What is public_html?
Public_html or public html is the folder that contains all website files that will be shown to a viewer who visits your website. It is located inside your website directories. What makes this different from the rest of the files? All the files in that directory may be publicly accessible, and usually yoursite.com opens the index file in that directory. Other directories (not within the public html) are not accessible through the HTTP scheme. The directory of www. is the shortcut link to the overall public_html directory. So typing in www. is a way of accessing public_html.
Public_html permissions
Directory permissions, such as Linux permissions , are important to ensure security of your website and all connected files. While permissions may changes based on the configuration of your server, in most circumstances default permissions should be used and are as follows:
- The public_html folder should have permissions of 750. In this case the owner can read, write, and execute, whereas others cannot read, write or execute.
- Folders within the public_html folder should have 755 permissions. Owners can read, write, and execute, and others can read and execute.
- Files within the public_html folder should have 644 permissions. Owners can read and write, others can only read.
WordPress setup folder
All WordPress root directory files, such as core files and code functionalities of installed themes and plugins, should be installed/unpacked into the the public html folder.
What to keep in public_html folder?
As public_html is the folder in which all the files for your main domain are located, keep all of the website files that are part of your main domain here. Whenever a user visits a website, every page viewed loads from the public_html directory, so the folder is where you would keep all website files you want to appear when a user looks up your main domain.
What to keep out of public_html folder?
You should keep the following out of the public html folder: some PHP files, logs, emails (in the case of an email server hosted in the same place), and any other files and scripts that are for service purposes and should not be visible as a part of website content, or be executable by non-admins.
For the security purposes, it’s also always important to make sure that the files and folders outside of public html are not public and that users cannot access them from the web.
- What is a cron job?
- What is localhost?
- What is a virtual server?
- What is a physical server?
- What is domain transfer?
- What are Cache Types?
- What is MySQL?
- What is PHP?
- What are error logs?
- What are access logs?
- What is caching?
- What is Microsoft IIS?
- What is Nginx?
- What is Apache?
- What is FTP/SFTP?
- What is a staging environment?
- What is a data center?
- What is SSH?
- What is an SSD?