- What is the use of ResultSetMetaData interface in Java?
- What is the use of ResultSetMetaData interface in Java?
- What is metadata in Java with example?
- Do we need to close ResultSetMetaData?
- What is DatabaseMetaData in Java?
- What happens if you close the ResultSet object?
- What happens if we don’t close prepared statement?
- How to get the resultsetmetadata object in JDBC?
- Where do I find the resultset in Java?
- Metadata in Java
- Types of Metadata
- How does Metadata work in Java?
- Examples to Implement Metadata in Java
- Example #1 – Result Set Metadata
- Example #2 – Database Metadata
- Example #3 – Database Metadata for Extracting Table Names
- Conclusion
- Recommended Articles
What is the use of ResultSetMetaData interface in Java?
What is the use of ResultSetMetaData interface in Java?
Interface ResultSetMetaData. An object that can be used to get information about the types and properties of the columns in a ResultSet object.
What is metadata in Java with example?
Metadata in Java is used to know the data about data. It means for example table field names, field data type, field data type length, database table names, number of databases that existed in the specific database, etc.
What is the different between ResultSet and ResultSetMetaData?
A ResultSet always maintains connection with the database. A RowSet can be connected, disconnected from the database. It cannot be serialized. A RowSet object can be serialized.
Do we need to close ResultSetMetaData?
You should explicitly close Statements , ResultSets , and Connections when you no longer need them, unless you declare them in a try -with-resources statement (available in JDK 7 and after). Connections to Derby are resources external to an application, and the garbage collector will not close them automatically.
What is DatabaseMetaData in Java?
Java DatabaseMetaData interface. DatabaseMetaData interface provides methods to get meta data of a database such as database product name, database product version, driver name, name of total number of tables, name of total number of views etc.
What is Type_scroll_insensitive in Java?
TYPE_SCROLL_INSENSITIVE means that the ResultSet can be navigated (scrolled) both forward and backwards. You can also jump to a position relative to the current position, or jump to an absolute position. The ResultSet is insensitive to changes in the underlying data source while the ResultSet is open.
What happens if you close the ResultSet object?
you will get a SQLException, because only Statement objects can close ResultSetsD. the ResultSet, together with the Statement which created it and the Connection from which the Statement was retrieved, will be closed and release all database and JDBC resourcesAnswer: B.
What happens if we don’t close prepared statement?
Say if you don’t close a transaction or a connection, performance issues or even stability issues will occur both on the database server side as well as on the clients side. The limits on open cursors per session can be exceeded by not closing a result set or a statement.
How is the resultsetmetadata interface useful in Java?
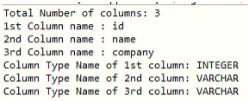
Java ResultSetMetaData Interface. The metadata means data about data i.e. we can get further information from the data. If you have to get metadata of a table like total number of column, column name, column type etc. , ResultSetMetaData interface is useful because it provides methods to get metadata from the ResultSet object.
How to get the resultsetmetadata object in JDBC?
ResultSetMetaData provides the data about the ResultSet object. It will provide all necessary information about the data available in ResultSet. We can get the ResultSetMetaData object by calling getMetadata () method on ResultSet object. Here is the complete example for ResultSetMetaData in JDBC.
Where do I find the resultset in Java?
ResultSet Interface is present in the java.sql package. It is used to store the data which are returned from the database table after the execution of the SQL statements in the Java Program. The object of ResultSet maintains cursor point at the result data. In default, the cursor positions before the first row of the result data.
What does the constant mean in resultsetmetadata Java?
The constant indicating that the nullability of a column’s values is unknown. Gets the designated column’s table’s catalog name. Returns the fully-qualified name of the Java class whose instances are manufactured if the method ResultSet.getObject is called to retrieve a value from the column.
Metadata in Java
Metadata in Java, defined as the data about the data, is called “Metadata”. Metadata is also said to be documentation about the information required by the users. This is one of the essential aspects in the case of data warehousing.
Real-Time Examples: A library catalog, the table of content, data items about person data (person weight, a person walking, etc.), etc.
Metadata Consisting of the following things:
- The description and location of the system and its components.
- It also has the Names, definitions, content, and structures of data and end-user views.
- Identification of authoritative data.
- Integration and transformation rules are used to populate data.
- Subscription information of subscribers.
- Used to analyze data usage and performance.
Why is Metadata Necessary?
It gives the Java developers information about the contents like table data, library catalog, etc., and structures.
Types of Metadata
There are 3 types of metadata:
- Operational Metadata
- Extraction and Transformation Metadata
- End-User Metadata
1. Operational Metadata: Operational metadata has all the information of the operational data sources. While selecting information from the source system for Datawarehouse, we will divide the records, combine the factors of documents from various sources, and deal with multiple coding schemes and field lengths. While we deliver the information to end-users, then we must be able to get back to source data sets.
2. Extraction and Transformation Metadata: Extraction and Transformation Metadata include data about removing data from the source systems. Those extraction methods, frequencies, and business rules for data extraction belong to Extraction and Transformation Metadata.
3. End-User Metadata: The end-user metadata is the navigational map of the data house. It enables the end-users to find the data from the data warehouse.
How does Metadata work in Java?
Java Metadata works based on data provided to it. It gives information of data about the data.
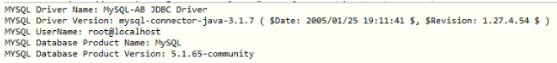
class Metadata< public static void main(String args[])< try< //load required database class //creating database metadata class DatabaseMetaData metaData=con.getMetaData(); //display the metadata of the table content System.out.println(metaData.getDriverName()); System.out.println(metaData.getDriverVersion()); System.out.println(metaData.getUserName()); System.out.println(metaData.getDatabaseProductName()); System.out.println(metaData.getDatabaseProductVersion()); con.close(); >catch(Exception e) < System.out.println(e);>> >Note: Before getting into the example, you must need MySQL database and mysql-connector jar.
Examples to Implement Metadata in Java
Below are examples of Metadata in Java:
Example #1 – Result Set Metadata
import java.sql.*;//importing sql package public class A catch (Exception e) < System.out.println(e); >> >Example #2 – Database Metadata
import java.sql.*;//importing sql package public class A catch (Exception e) < System.out.println(e); >> >Example #3 – Database Metadata for Extracting Table Names
import java.sql.*;//importing sql package public class A ; ResultSet resultSet = dbmd.getTables(null, null, null, table); // iterating number table names from database of mysql while (resultSet.next()) < System.out.println("Table name is: "+resultSet.getString(3)); >connection.close(); > catch (Exception e) < System.out.println(e); >> >Conclusion
Metadata in Java is used to know the data about data. It means, for example, table field names, field data type, field data type length, database table names, number of databases that existed in the specific database, etc.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Metadata in Java” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
89+ Hours of HD Videos
13 Courses
3 Mock Tests & Quizzes
Verifiable Certificate of Completion
Lifetime Access
4.5
97+ Hours of HD Videos
15 Courses
12 Mock Tests & Quizzes
Verifiable Certificate of Completion
Lifetime Access
4.5
JAVA Course Bundle — 78 Courses in 1 | 15 Mock Tests
416+ Hours of HD Videos
78 Courses
15 Mock Tests & Quizzes
Verifiable Certificate of Completion
Lifetime Access
4.8