- Java Mapping in SAP PI
- Java Mapping within ESR
- Create Message Mapping
- Related posts:
- SAP PI Java Mapping to append File Contents
- Functionality of given SAP-PI Java map:
- Pre-requisites:
- Steps to create Java Map:
- Handling Attachments with Java Mapping – SAP PI/PO
- Use cases of Attachments in Integration Scenarios
- Attachments in SOAP messages
- Zip File Processing
- Mails with Attachments
- Java Class InputAttachments
- Method getAllContentIds
- Method areAttachmentsAvailable
- Method getAttachment
- Integration Scenario Overview
- Java Mapping to Handle Attachments in the Source Message
Java Mapping in SAP PI
This blog will cover how to do Java mapping in SAP PI. Java Mapping is always a concern for any PI consultant, so today I will try to explain the techniques which will make it interesting and easier.
In PI mapping can be done in the following ways
- Graphical Mapping – The most popular and easier way.
- Java Mapping
- XLST Mapping
- ABAP Mapping – This will not be applicable in case you have a single stack instance.
In this blog, we will cover Java Mapping in SAP PI.
Here we will focus on the 2nd option which will be easier for beginners.
For option 1 here is a good article which can be used
Java Mapping within ESR
This is good option especially for people not well versed with Java and want to write codes without bothering about eclipse configuration or loading Java libraries.
It is really cool idea and some of the advantages
- No need to install Java editor – for beginners some time it is confusing and time-consuming.
- No need to spend time looking for java libraries.
- Debugging will be easier as you can use a graphical mapping editor.
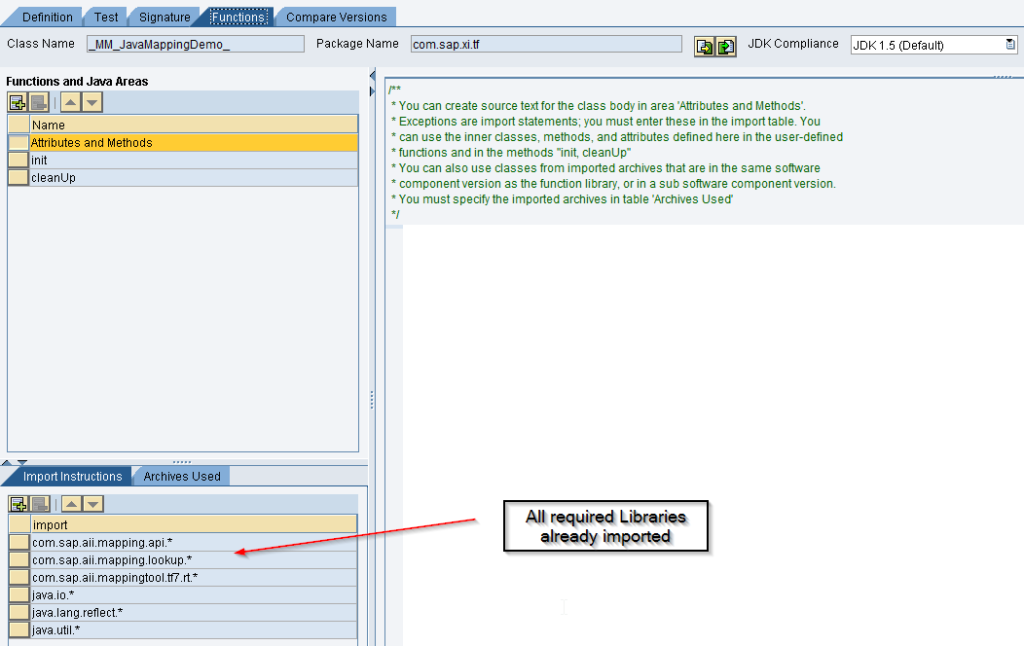
- No need of importing the jar as Imported Archive.
- For small changes no need to recompile and reimport the jar files to ESR, directly make the change in ESR.
Here are steps to follow for creating Java mapping in ESR directly.
Create Message Mapping
The first step is same as graphical mapping –create a Mapping
Select Source and Target message type
Note: As this is Java mapping these will not be validated
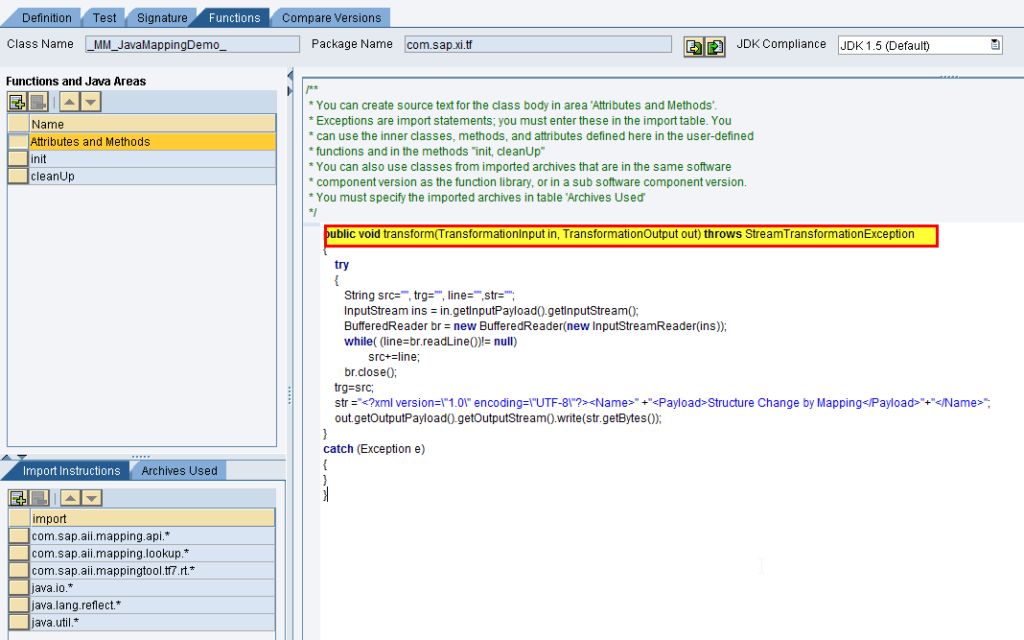
Go to Functions tab > Attributes and Methods
Example: In this example, I am changing the target structure completely.
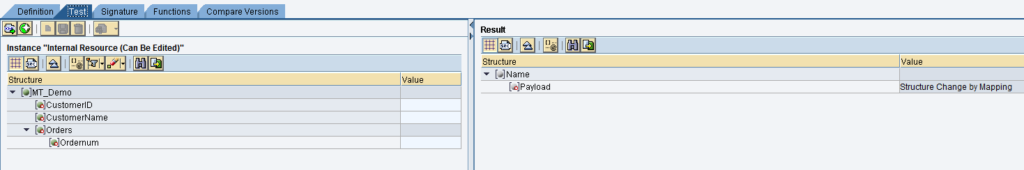
Save and test as is done for Message Mapping
if you notice the target structure is changed completely.
Related posts:
SAP PI Java Mapping to append File Contents
This SAP-PI Java map was required in below business scenario:
- One SAP-PI Soap Synchronous web-service has been hosted, where:
- In Soap-Request, client will send FileName starting key words
- and in Soap-Response message, SAP-PI has to return FileContents of one File found in SAP directory with same FileNameKey
- To achieve above, we use this example of JavaMap to populate Soap Response message.
- This Java map is been applied in Response-Tab of Operation Mapping
Functionality of given SAP-PI Java map:
- Get File-Name-Key from SoapRequest payload using Dynamic Configuration
In Request Mapping, below UDF is been used to get FileNameKey from Soap Request Dynamic Configuration variableString RequestDataStr = ""; RequestDataStr = ReqStr_FileName ; try < // set to dynamic config: DynamicConfiguration conf = (DynamicConfiguration) container .getTransformationParameters().get(StreamTransformationConstants.DYNAMIC_CONFIGURATION); DynamicConfigurationKey key = DynamicConfigurationKey.create("http://sap.com/xi/XI/System/SOAP", "FileName_StartKey" ); if ( conf != null)< conf.put(key, RequestDataStr); >> catch (Exception ex) < ; >return RequestDataStr;
Pre-requisites:
- SAP-PI 7.1
- Java Map Library (aii_map_api.jar)
- Java Eclipse (to create Java Mapping program)
- Jre 1.6
Steps to create Java Map:
- Create a Java Project in Eclipse
- Import External jar lib file ‘aii_map_api.jar‘
- Go to -> right Click on Project fodler ‘JavaMap_Example-01’ -> Bulid Path -> Configure Build Path -> Tab ‘Libraries’ -> click button ‘Add External Jars’ to import file from local desktop
- Insert Resource File ‘FolderPath_details.xml’
- Insert xml file having path information
- Create one Java Class
- ight Click on Project fodler ‘JavaMap_Example-01’ -> src -> New -> Class -> create a new Java class
- and write JavaMap Source code as given below
import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.OutputStream; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder; import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory; import javax.xml.parsers.ParserConfigurationException; import javax.xml.transform.Transformer; import javax.xml.transform.TransformerFactory; import javax.xml.transform.dom.DOMSource; import javax.xml.transform.stream.StreamResult; import org.w3c.dom.Attr; import org.w3c.dom.CDATASection; import org.w3c.dom.Document; import org.w3c.dom.Element; import org.w3c.dom.Node; import org.w3c.dom.NodeList; import org.xml.sax.SAXException; import com.sap.aii.mapping.api.AbstractTrace; import com.sap.aii.mapping.api.DynamicConfiguration; import com.sap.aii.mapping.api.DynamicConfigurationKey; import com.sap.aii.mapping.api.StreamTransformation; import com.sap.aii.mapping.api.StreamTransformationConstants; import com.sap.aii.mapping.api.StreamTransformationException; public class Example_01 implements StreamTransformation < private String ArchivalPath = ""; private String SourcePath = ""; private AbstractTrace trace = null; private Map param; public void setParameter(Map map)< param = map; if (param == null) < param = new HashMap(); >> public void execute(InputStream in, OutputStream out) throws StreamTransformationException< try< trace = (AbstractTrace) param.get(StreamTransformationConstants.MAPPING_TRACE); trace.addInfo("Starting JavaMap 'Example_01'"); //Get FileNameKey using DynamicConfig String FileNameKey = ""; FileNameKey = getFileNameKey(); trace.addInfo("FileName starting key found as: " + FileNameKey); //Get FolderPath from ResourceFile 'FolderPath_details.xml' getFolderPath(); trace.addInfo("SourcePath: " + SourcePath); trace.addInfo("ArchivalPath: " + ArchivalPath); //----Start:Read File from SAPDirectory & Append it to OutputXml ------- String FileName = ""; String FileContent = ""; String ErrorStr = ""; File theDir = new File(SourcePath); if (!theDir.exists())< //Error message 'SourcePath not found' ErrorStr = "SourcePath '" + SourcePath + "' not found"; >else< //If directory found, then check if it is empty File[] dirFileList = new File(SourcePath).listFiles(); if (dirFileList.length < 1)< //Error message 'No file found in SourcePath' ErrorStr = "No file found in SourcePath '" + SourcePath + "'"; >else < //If folder is not empty, the search for files for (int i=0; i>else < ErrorStr = "No .CSV/.csv file found"; >> > > //----End :Read File from SAPDirectory & Append it to OutputXml ------- //----Start: Create output XML Document ------------------- DocumentBuilderFactory dbFactory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance(); DocumentBuilder dbBuilder = dbFactory.newDocumentBuilder(); Document docOut = dbBuilder.newDocument(); //Create XML RootElement Element rootElmnt = docOut.createElement("ns0:MT_TargetMsg"); docOut.appendChild(rootElmnt); //Append rootElement to Output document //Set Attribute info to RootElement Attr attr = docOut.createAttribute("xmlns:ns0"); attr.setValue("http://Test-01"); rootElmnt.setAttributeNode(attr); //Create child Node Element Chld1 = docOut.createElement("Item"); rootElmnt.appendChild(Chld1); //Create sub child node Element subChld1 = docOut.createElement("FileName"); Chld1.appendChild(subChld1); Node nd1 = docOut.createTextNode(FileName); subChld1.appendChild(nd1); Element subChld2 = docOut.createElement("FileContent"); Chld1.appendChild(subChld2); CDATASection cdataFCS = docOut.createCDATASection(FileContent); subChld2.appendChild(cdataFCS); Element subChld3 = docOut.createElement("Error"); Chld1.appendChild(subChld3); Node nd3 = docOut.createTextNode(ErrorStr); subChld3.appendChild(nd3); //----End : Create output XML Document ------------------- trace.addInfo("Message: " + ErrorStr); //Transform Output Document trace.addInfo("Transforming results to output xml payload"); TransformerFactory tf = TransformerFactory.newInstance(); Transformer transform = tf.newTransformer(); transform.transform(new DOMSource(docOut), new StreamResult(out)); > catch (Exception e) < trace.addInfo(e.getMessage()); >> private void getFolderPath() throws IOException, ParserConfigurationException, SAXException < /* This function helps to get folder path details from resource 'FolderPath_details.xml' Jar file of this map will include resource file 'FolderPath_details.xml' */ //Get reference of ResourceFile 'FolderPath_details.xml' InputStream is_ShpCrd = getClass().getResourceAsStream("FolderPath_details.xml"); //Parse input to create document tree DocumentBuilderFactory dbFactory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance(); DocumentBuilder dbBuilder = dbFactory.newDocumentBuilder(); Document xmlDoc_ShpCrd = dbBuilder.parse(is_ShpCrd); //Read XmlElement tag to fetch SharePoint_Credentials NodeList ndList_1 = xmlDoc_ShpCrd.getElementsByTagName("Path"); for(int i1 = 0; i1 < ndList_1.getLength(); i1++)< Node nd_1 = ndList_1.item(i1); for(Node nd_2 = nd_1.getFirstChild(); nd_2 != null; nd_2 = nd_2.getNextSibling())< if(nd_2.getNodeName().equals("SourcePath"))< SourcePath = nd_2.getFirstChild().getNodeValue(); >if(nd_2.getNodeName().equals("ArchivalPath")) < ArchivalPath = nd_2.getFirstChild().getNodeValue(); >> > > private String getFileNameKey() throws IOException < /* This function helps to get FileName starting Key word using DynamicConfiguration variable which is set from SoapRequestPayload */ String FileNameKey = ""; try< DynamicConfiguration conf = (DynamicConfiguration)param.get("DynamicConfiguration"); DynamicConfigurationKey key = DynamicConfigurationKey.create("http://sap.com/xi/XI/System/SOAP", "FileName_StartKey"); if(conf != null)< FileNameKey = conf.get(key); >>catch(Exception e) < trace.addInfo(e.getMessage()); >return FileNameKey; > private String getFileContent(String filePath) throws IOException < /* * This Function read file content into String * */ FileInputStream fin = new FileInputStream(new File(filePath)); java.util.Scanner scanner = new java.util.Scanner(fin,"UTF-8").useDelimiter("\\A"); String theString = scanner.hasNext() ? scanner.next() : ""; scanner.close(); return theString; >/* public static void main(String[] args) < try< Example_01 myClass = new Example_01(); FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream("C:/Request_Input_2.xml"); FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("C:/Output.xml"); myClass.execute(in, out); >catch (Exception e) < e.printStackTrace(); >> */ > - right Click on Project fodler ‘JavaMap_Example-01’ -> Export -> Java -> JAR File -> Click Next -> give Jar name -> select resource -> Finish
Handling Attachments with Java Mapping – SAP PI/PO
In this article, we’ll look at how to handle attachments in incoming messages in PI/PO interfaces. We will go through use cases that involve attachments; Java class used for processing the attachments; and methods of the Java class that can be used to process attachments.
Then, we will build a Java Mapping to read and copy the attachment payload from XI message to the target. Moreover, we’ll check step-by-step how to develop and configure the end-to-end interface in ESR and ID.
Use cases of Attachments in Integration Scenarios
When it comes to system integration, a lot of protocols have the capability of sending attachments with the main message payload. Therefore, when building SAP integration scenarios via SAP PI/PO, you will come across interfaces where attachments should be processed.
Here are some examples where attachments in the messages should be managed in SAP PI/PO. Additionally, you can read about attachment handling for SAP documents using GOS in the linked article.
Attachments in SOAP messages
SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) has the capability to exchange attachments with the main message payload. When integrating SAP with SOAP services, the interface should be able to read attachment data from SOAP message or write attachments to the SOAP message.
Zip File Processing
Usually, zipped or compressed files contain multiple files inside. For example, a zip file can contain one XML as the main payload and multiple PDFs. In such cases, the PDFs will be assigned to XI payload as attachments.
This article goes hand-in-hand with my previous post on how to process zip files in PI/PO.
Mails with Attachments
In most instances, email messages contain one or more attachments. When integrating email messages via Mail adapter, the interface should be built to handle attachments in the email.
Java Class InputAttachments
We can use the Java class interface InputAttachments and its methods to read attachments in XI message. Java class can be used in User-Defined Functions (UDF) or Java Mapping programs. This class is included in source path com.sap.aii.mapping.api.
The class has three methods to handle attachments in the XI payload. They are, getAllContentIds, areAttachmentsAvailable and getAttachment.
Method getAllContentIds
This method returns all the attachment IDs of the source payload as a collection of string. Each attachment in a source payload has a unique ID called content ID. Using this method, you fetch the content IDs of all the attachments in the XI message as a collection.
Method areAttachmentsAvailable
As the method name indicates, we can use this method to check if there are attachments in the XI payload. Further, attachments in the payload can be accessed from the message mapping program.
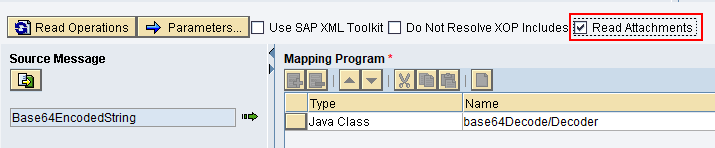
The mapping program can access the attachments in the payload only if the option “Read Attachment” is activated in the Operation Mapping.
“Read Attachments” option marked in Operation Mapping
Method getAttachment
This method returns the Attachment object of a specific content ID.
Syntax: Attachment getAttachment(String contentID)
The attachment object consists of a set of methods that can read the content of the attachment in different formats. Furthermore, it contains methods to identify the type of attachment.
Base64 schema is a great way to handle attachments.
For more information about base64, you can read previous articles,
Integration Scenario Overview
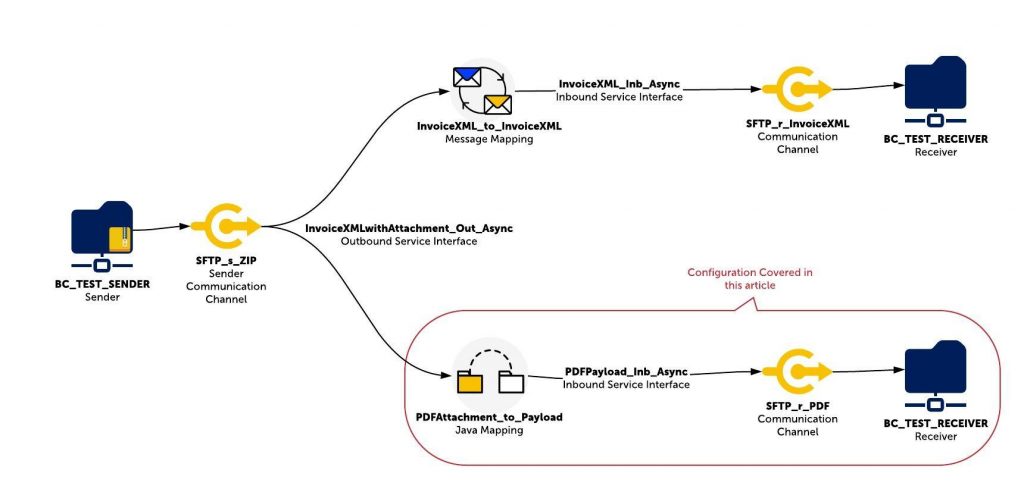
To illustrate attachment handling, let’s assume we have an SFTP server where zip files are stored. Each zip file contains an Invoice XML and the corresponding PDF file of the invoice. We want to extract the zip files and transfer the Invoice XML and PDF to two different locations in the receiver SFTP server.
Attachment Handling Demo Scenario Overview
Sender SFTP adapter reads the zip file and unzips it using the adapter module AF_Modules/PayloadZipBean. After the zip file is unzipped, the source message will include both Invoice XML and PDF.
Let’s make use of two mapping programs to handle the zip file content.
- A graphical message mapping program to map the source invoice XML to receiver invoice XML format.
- A Java Mapping program to read the PDF attachment data from the source message and copy the content to the output stream.
If you want to send the PDF to an SAP back-end system as a proxy message, one possible method is to convert the attachment content to base64 format using getBase64EncodedContent.
Java Mapping to Handle Attachments in the Source Message
Using the Java interface InputAttachment we discussed earlier in the article, the Java Mapping program reads the content of the PDF attachment and copies it to the output stream.
First, the handler for attachment is generated from the method getInputAttachments. Second, the attachment handler is looped to get content IDs of the attachments. In our scenario, there is only one attachment in the payload. Finally, the content of the attachment is read by applying the method getContent and assigned to the output.