- Escape Characters in Python | Explained with Examples
- What are Escape Characters in Python?
- Example 1: Add a Single Quote in a String
- Example 2: Add a Double Quote in a String
- Example 3: Add a Backslash in a String
- Example 4: Add a New Line to a String
- Example 5: Remove Specific Characters in a String
- Example 6: Add Multiple White Spaces in a String (Tab Key)
- Example 7: Remove a Single Character in a String
- Example 8: Represent an Octal Value to its Equivalent
- Example 9: Represent a Hexa Value to its Equivalent
- Conclusion
- Python Escape Character Sequences (Examples)
- Types of Escape Sequence
- Example Usage of Various Escape Characters
- What Does “\t” Do in Python?
- When to use “\t” in Python?
- Application of built-in function Chr () and Ord ()
- Summary
Escape Characters in Python | Explained with Examples
In any programming language, we have to deal with different data types such as string, list, tuple, etc. The string is used to input any characters enclosed in double or single quotation marks.
Some special characters give errors when they are put directly into the strings. To handle such errors, the escape characters are used, which helps us to enter illegal characters inside the string. This post will provide a deep insight into the Python “Escape Characters” with the help of suitable examples.
What are Escape Characters in Python?
In Python, the backslash character “\” is an escape character. An escape character is used with the combination of backslash “\” and a special character such as for newline “\n” combination is used
Every escape character performs some specific operation when used inside the string.
We can insert single or double quotes, add new lines, add whitespaces, etc inside the string.
Let’s learn different escape characters with their example one by one:
Example 1: Add a Single Quote in a String
In Python, the preceding backslash “\” is used along with the single quote escape character to add a “single quote” inside the string or substring. If we directly put the quote character on any string, the output will give us an invalid syntax error. Let’s understand via the following example:
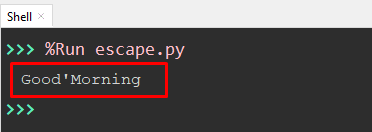
Value = 'Good\'Morning' print(Value)
In the following code, the “preceding backslash” is used to add the “single quote” in the string value stored in a variable named “value”.
The “single quote” is added at the start of the substring named “Morning”.
Example 2: Add a Double Quote in a String
The “Double Quote” is also placed inside the string using a preceding backslash. Let’s do it by the following code:
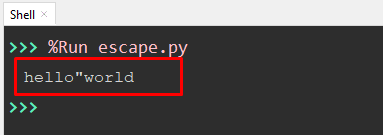
Value = "hello\"world" print(Value)
In the above code, the “preceding backslash” is used to add the “double quote” in the substring of the string value that is stored in a variable named “value”.
The substring named “world” has a “double quote” at the start.
Example 3: Add a Backslash in a String
The “backslash” is added inside the string using double backslash “\\”.Similarly, to add a double backslash we need to use three preceding backslashes “\\\” inside the string. Let’s see an example of code shown below:
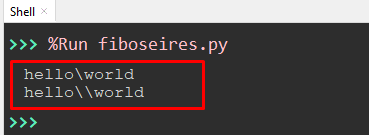
Value = 'hello\\world' Value_1 = 'hello\\\world' print(Value) print(Value_1)
In the above lines of code, the two backslashes “\\” are used inside the string value of the first variable to add one backslash “\” before the substring named “world”.simalrly three backslashes “\\\” is used to add two backslashes”\\” inside the string.
From the output, single and double backslash “\” is added before the substring “world”.
Example 4: Add a New Line to a String
The newline character “\n” is used to add the newline at any position in the string. When this character is used in the string, the sequence is terminated and shifted to the next line. Let’s see an example of code given below:
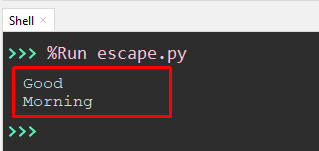
Value = 'Good\nMorning' print(Value)
In the above code, a newline character “\n” is used before the substring named “morning”. This character is added by placing the preceding backslash with the character value “n”.
The substring “Morning” is positioned at the new line.
Example 5: Remove Specific Characters in a String
The “carriage return” has a special character with preceding backslash “\r” that will return the content of the string used after the character on output. The content of the string before the escape character “\r” will be removed. Let’s understand it with the code given below:
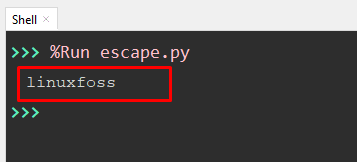
value = 'its\rlinuxfoss' print(value)
In the above code, the preceding backslash is used with the character “r” to remove all the string values before its position. Only the value after the carriage return character will be left.
The output shows that the substring “its” has been removed, and only “linuxfoss” is left.
Example 6: Add Multiple White Spaces in a String (Tab Key)
The “tab” escape gives the tab space between the string that is equal to “4” simple spaces. The tab escape is also used with preceding backslash with the special character “t”. Let’s understand via the following code:
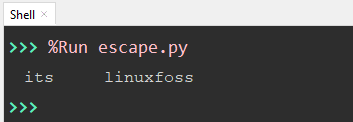
value = 'its\tlinuxfoss' print(value)
The “Tab” character is used along with preceding backslash such as “\t”. This character “\t” generates a tab space between the substring value “its” and “linuxfoss”.
The output shows the space between the two substrings.
Example 7: Remove a Single Character in a String
The “Backspace” escape deletes the previous character of the string. It only deletes one previous character at a time. The backspace escape character “b” is used along with preceding backslash like “\b”. Let’s understand it with an example of code:
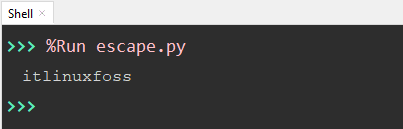
value = 'its\blinuxfoss' print(value)
In the following code, the backspace character is used along with the preceding backslash “\b”. The “\b” escape character deletes the value of its last previous character “s” from the substring.
The output shows that the character “s” is removed from the string “itslinuxfoss”.
Example 8: Represent an Octal Value to its Equivalent
Octal number system ranging from “0” to “7”. This means the value can not be more than the “7”. In Python, every octal value has a special character value; for example, character “A” is “101” in octal representation. Every character has a specific octal value that is predefined in Python. Let’s see an example of code given below:
value = '\101\102\103\104\105\106' print(value)
The octal value is used to generate the alphabetic character using the specific number. Every value has a specific octal number like the character “A” has an octal value of “101”. All octal numbers are placed inside the string using the preceding backslash.
The output shows the character values “A”,” B”, and” CDEF” on the screen.
Example 9: Represent a Hexa Value to its Equivalent
In Python, Hexadecimal values are converted into special Characters. The character value is printed on the basis of their hex value like the hex value of “A” is “x41” these are Python-defined terms that are different for each character. Let’s convert the hex value into character using the following code:
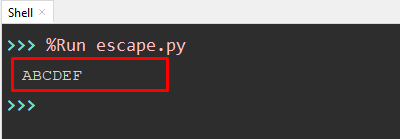
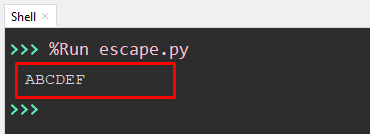
value = '\x41\x42\x43\x44\x45\x46' print(value)
In the above code, the “Hex” values are specified using the preceding backslash with the character “x” and two number digits. The “x” character is mandatory to use because it specifies the hex type value.
The character value “ABCDEF” is shown on the console screen.
That’s it from this informative guide!
Conclusion
In Python, Escape characters such as “single quote”, “double quote ”, “newline”, “carriage return”, “tab” etc are used to place characters inside the string. The escape characters are placed inside the string using preceding backslashes such as “\b” for Backspace. Every escape character inside the string has a specific purpose and to complete that purpose we have to place the escape character before or after the substring of the string. This Python guide has provided detailed working and usage of the escape characters in Python.
TUTORIALS ON LINUX, PROGRAMMING & TECHNOLOGY
Python Escape Character Sequences (Examples)
Escape characters or sequences are illegal characters for Python and never get printed as part of the output. When backslash is used in Python programming, it allows the program to escape the next characters.
Following would be the syntax for an escape sequence
Explanation:
Here, the escape character could be t, n, e, or backslash itself.
Types of Escape Sequence
Escape characters can be classified as non-printable characters when backslash precedes them. The print statements do not print escape characters.
Here is a list of Escape Characters
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| \’ | Single quotation |
| \\ | Backslash |
| \n | New Line |
| \r | Carriage return |
| \t | Tab |
| \b | Backspace |
| \f | Form feed |
| \ooo | Octal equivalent |
| \xhhh | Hexadecimal equivalent |
Example Usage of Various Escape Characters
| Escape character | Function | Example Code | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| \n | The new line character helps the programmer to insert a new line before or after a string. | txt = “Guru\n99!” print(txt) | Guru99 |
| \\ | This escape sequence allows the programmer to insert a backslash into the Python output. | txt = “Guru\\99!” print(txt) | Guru\99! |
| \xhh | Use a backslash followed by a hexadecimal number. This is done by printing in backslash with the hexadecimal equivalent in double quotes. | txt = “\x47\x75\x72\x75” + “99!” print(txt) | Guru99! |
| \ooo | To get the integer value of an octal value, provide a backslash followed by ooo or octal number in double-quotes. It is done by printing in a backslash with three octal equivalents in double quotes. | txt = ‘\107\125\122\125’+ “99!” print(txt) | GURU99! |
| \b | This escape sequence provides backspace to the Python string. It is inserted by adding a backslash followed by “b”. “b” here represents backslash. | txt = “Guru\b99!” print(txt) | Guru99! |
| \f | It helps in the interpolation of literal strings | txt = “Guru\f99!” print(txt) | Guru99! |
| \r | It helps you to create a raw string | txt = “Guru\r99!” print(txt) | Guru99! |
| \’ | It helps you to add a single quotation to string | txt = “Guru\’99!” print(txt) | Guru’99! |
What Does “\t” Do in Python?
The t alphabet in Python represents a space. It enables you to insert space or tab between strings in a code. It helps us to have space in the Python program when there is a need for it. To eliminate the usage of keyboard space, the coders utilize tab escape sequences.
Following is the syntax for a tab escape sequence.
In this example, the string used is “Guru99”. The program will put a tab or a space between Guru and 99.
Python Code:
TextExample="Guru\t99" print (TextExample)
Explanation:
In the above example, instead of adding space using a keyboard, the program helps us by putting a space or a tab between the string “Guru99”. It also provides a space at the precise location where the escape sequence is added.
When to use “\t” in Python?
The escape sequence tab is utilized to put a horizontal tab between words and hence helps manipulate python strings. However, If the escape sequence tab is not used, the programmer has to manually add a space between every word of the string.
You can transform it into a time-consuming exercise. Moreover, the space added between different keywords may or may not be precise in its placement.
Here is an example that displays the manual addition of a space between words and the use of an escape sequence between words.
Python Code:
print("Manually Added space in string Guru 99") TextExample="Use\tof\ttab\tto\tadd\tspace\tGuru\t99" print(TextExample) Manually Added space in string Guru 99 Use of tab to add space Guru 99
Explanation:
The programmer manually added space between words in the above code, so the placement was not precise. When the escape sequence tab was applied, the program automatically provided the precise location of space between words.
Application of built-in function Chr () and Ord ()
The Chr () function is a built function that takes a single argument as input. The function takes Unicode characters as an input which ranges from 0 to 1,114 and 111, respectively. The function can be used as the substitute for escape sequence “\t” to put a space between two words.
The syntax for the Chr function is represented below: –
The tab has the Unicode character 9. Use the following Python command to arrive at the Unicode character as shown below: –
Python Code:
print("Unicode character of the tab is") Ord=ord('\t') print(Ord) Unicode character of the tab is 9
Explanation:
The above code provides the Unicode character for the tab. It can be used as an input for the Chr function. Use of Chr (9) would allow us to create a substitute for a tab escape sequence.
This code is an example of how to use Chr (9), as shown below:
Python Code:
TextExample="Guru+chr(9)+99" print(TextExample)
The above function, however, is deprecated for version 3 and above.
Summary
- Backslash is also regarded as a special character.
- To create an escape sequence, begin with a backslash followed by the illegal character.
- Examples of escape sequences include “\b”, “\t”,”\n”,”\xhh” and “\ooo” respectively.
- “\t” allows inserting a space or tab between two words. It plays a similar role to the space key present on the keyboard.
- “\t” is used when the programmer wants to add space to a string at a precise location.
- Certain whitespaces help in putting a new line between python strings.
- Line feed and carriage return, vertical tab, and form feed are types of whitespaces.