- Приведение типов объектов в Java
- Дальнейшее чтение:
- Основы Java Generics
- Java экземпляр оператора
- 2. Примитив против Ссылка
- 3. Апкастинг
- What is Type Casting in Java? Casting one Class to other class or interface Example
- What is Type Casting in Java? Up Casting and Down Cast
- Type casting example in Java
- Class Casting in Java | Generalization, Specialization
- Generalization in Java with Example Program
- Specialization in Java with Example Program
Приведение типов объектов в Java
Система типов Java состоит из двух типов типов: примитивы и ссылки.
Мы рассмотрели примитивные преобразования вthis article, и здесь мы сосредоточимся на приведении ссылок, чтобы получить хорошее представление о том, как Java обрабатывает типы.
Дальнейшее чтение:
Основы Java Generics
Краткое введение в основы Java Generics.
Java экземпляр оператора
Узнайте об операторе instanceof в Java
2. Примитив против Ссылка
Хотя примитивные преобразования и приведение ссылочных переменных могут выглядеть одинаково, они довольноdifferent concepts.
В обоих случаях мы «превращаем» один тип в другой. Но в упрощенном виде примитивная переменная содержит свое значение, а преобразование примитивной переменной означает необратимые изменения ее значения:
double myDouble = 1.1; int myInt = (int) myDouble; assertNotEquals(myDouble, myInt);После преобразования в приведенном выше примере переменнаяmyInt равна1, и мы не можем восстановить из нее предыдущее значение1.1.
Reference variables are different; ссылочная переменная относится только к объекту, но не содержит самого объекта.
Приведение ссылочной переменной не затрагивает объект, к которому она относится, а только помечает этот объект другим способом, расширяя или сужая возможности для работы с ним. Upcasting narrows the list of methods and properties available to this object, and downcasting can extend it.с
Ссылка похожа на дистанционное управление объектом. Пульт дистанционного управления имеет больше или меньше кнопок в зависимости от его типа, а сам объект хранится в куче. Когда мы выполняем кастинг, мы меняем тип пульта дистанционного управления, но не меняем сам объект.
3. Апкастинг
Casting from a subclass to a superclass is called upcasting. Как правило, преобразование выполняется неявным образом.
Обновление тесно связано с наследованием — еще одна ключевая концепция в Java. Обычно используются ссылочные переменные для ссылки на более конкретный тип. И каждый раз, когда мы делаем это, происходит неявное обновление.
Чтобы продемонстрировать апкастинг, давайте определим классAnimal:
What is Type Casting in Java? Casting one Class to other class or interface Example
Type casting in Java is to cast one type, a class or interface, into another type i.e. another class or interface. Since Java is an Object-oriented programming language and supports b oth Inheritance and Polymorphism, It’ s easy that Super class reference variable is pointing to SubClass objects but the catch here is that there is no way for Java compiler to know that a Superclass variable is pointing to SubClass object. This means you can not call a method that is declared in the subclass. In order to do that, you first need to cast t he Object back into its original type. This is called type casting in Java. You can type cast both primitive and reference type in Java. The concept of casting will be clearer when you will see an example of type casting in the next section.
Type casting also comes with the risk of ClassCastException in Java, which is quite common with a method that accepts Object type and later types cast into more specific types.
We will see when ClassCastException comes during type casting an d How to avoid it in the coming section of this article. Another worth noting point here is that from Java 5 onwards you can use Generics to write type-safe code to r educe the amount of type casting in Java which also reduces the risk of java.lang.ClassCastException at runtime.
What is Type Casting in Java? Up Casting and Down Cast
From the first paragraph, we pretty much know What is type casting in Java. Anyway, In simple words, type casting is a process of converting on e type, whi ch cou ld be a class or interface t o another, But as per rules of Java programming language, only classes or i nterfaces (collectively known as Type) from the same type hierarchy can be cast or converted into each other.
If you try to cast two objects which don’t share same type hierarchy, i.e. there is no parent-child relationship bet ween them, y ou wil l get compile time error. On the other hand, if you typecast objects fr om same type hierarchy but the object which you are casting are not of the same type on which you are casting then it will throw ClassCastException in Java.
Some people may ask why do you need type casting? well, you need type casting to get access to fields and methods declared on the target type or class. You can not access them with any other type. Let’s see a simple example of type casting in Java with two classes Base and Derived which share the same type hierarchy.
Type casting example in Java
In this Example of type casting in Java, we have two classes, Base , and Derived . Derived class extends Base i.e. Base is a Super class and Derived is a Subclass. So their type hierarchy looks like the following tree :
Class Casting in Java | Generalization, Specialization
The process of converting a class type into another class type having the relationship between them through inheritance is called class casting in java.
We have known in the previous tutorial that a class is a referenced data type.
If classes have some relationship between them through inheritance, it is also possible to convert a class type into another class type through type casting.
For example, we can not convert a Dog class into Horse class if there is no relationship between them through inheritance.
Look at the below figure which shows the classes Department, College, and University have a relationship among them through inheritance.
From the above figure, since a College class is derived from University class through inheritance, we can convert a College class into a University class through type casting.
Similarly, we can also convert a Department class into College class, since Department is subclass of College class. These are the examples of class casting in java.
Generalization in Java with Example Program
The process of converting subclass type into superclass type is called generalization in java. This is because we are making the subclass to become more general so that its scope can be more widening.
This conversion is also called widening or upcasting in referenced data types. Let’s understand generalization by taking a realtime example.
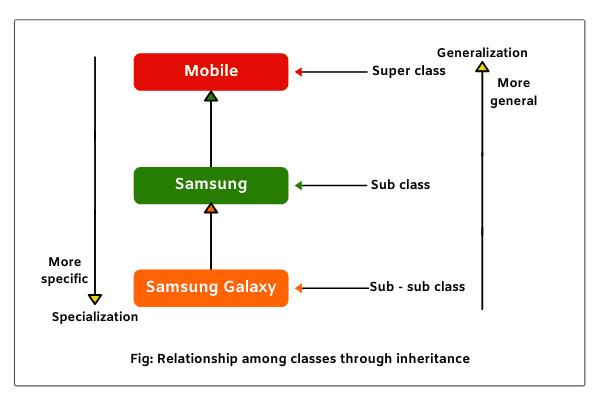
Let us consider a superclass Mobile and subclasses are Samsung and Samsung Galaxy as shown in the below figure.
When we talk about a mobile, In general, it may represent any kind of mobile. So, here, the scope is widened.
Now, suppose we talk about Samsung mobile, then we come down one step in the hierarchy of inheritance and we have eliminated any other kind of mobiles.
Thus, we are becoming more specific. When we still come down to Samsung Galaxy, we are pointing only Samsung Galaxy mobile and not any other Samsung mobile.
Thus, this is very specific. This means that when we move down from superclass to subclasses, we are becoming more and more specific.
When we go back from subclasses to superclass, we are becoming more general. This is called generalization in java. Generalization is safe because classes will be more general.
Hence, we do not need a cast operator to perform generalization. Java compiler will do the implicit casting in generalization.
Let’s take an example program to understand the widening effect where we will write superclass reference to refer to subclass object. Look at the source code to understand better.
Program code 1:
public class A < void m1()< System.out.println("Superclass method"); >> public class B extends A < void m2()< System.out.println("Subclass method"); >> public class WideningTest < public static void main(String[] args) < A a; // a is superclass reference variable. a = (A)new B(); // generalization (widening) because a is referring to subclass object. a.m1(); >> Explanation:
1. In this example program, we have used superclass reference to refer to a subclass object. So, subclass object type will be converted into superclass type, as:
2. Now you can observe that we have called the m1() method of superclass but we are unable to call m2() method of subclass. This is because if we call m2() method as a.m2();, java compiler would generate an error message during compilation time.
Suppose we override superclass method into subclass as shown in the below program 2, it is possible to access subclass method but not superclass method. Anyhow, we will get only 50% functionality of the program.
Program code 2:
public class A < void m1()< System.out.println("Superclass method"); >> public class B extends A < void m1() // Overriding superclass method. < System.out.println("Subclass method"); >> public class WideningTest < public static void main(String[] args) < A a; // a is superclass reference variable. a = (A)new B(); // generalization (widening) because a is referring to subclass object. a.m1(); >> Specialization in Java with Example Program
The conversion of a superclass type into subclass type is called specialization in java.
Specialization means going down from a more general form to a more specific form. Thus, its scope will be narrowed. Hence, this conversion is also called narrowing or down-casting in referenced data types.
Specialization is not safe because classes will be more and more specific. In this case, we will need cast operator. Java compiler will do explicit casting in the specialization.
Let’s take an example program to see the narrowing effect by taking subclass reference to refer to superclass object.
Program code 3:
public class A < void m1()< System.out.println("Superclass method"); >> public class B extends A < void m2()< System.out.println("Subclass method"); >> public class NarrowingTest < public static void main(String[] args) < B b; // b is subclass reference variable. b = (B)new A(); // specialization (narrowing) because b is referring to superclass object. a.m1(); >> Output: Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ClassCastException: inheritance.A cannot be cast to inheritance.B
Explanation:
As you observe in the above program, method call b.m1() is not executing the super class method.
Similarly, if we call subclass method m2() as b.m2(); it will give the same error message.
Hence, we cannot access any of the methods of the superclass or subclass in the specialization. We will get 0% functionality in this case.
The solution to this problem is available. We will not create an object of superclass as we did in the previous case.
This time, we will create a reference of superclass to refer to subclass object and will use narrowing (specialization) concept. Look at the below source code.
Program code 4:
public class A < void m1()< System.out.println("Superclass method"); >> public class B extends A < void m2()< System.out.println("Subclass method"); >> public class CastingTest < public static void main(String[] args) < A a; // a is superclass reference variable. a = new B(); // Superclass reference refers to subclass object. B b = (B)a; // Narrowing because we are converting class A's reference type as class B's type. b.m1(); b.m2(); >> Output: Superclass method Subclass method
1. If superclass reference refers to subclass object, all the methods of superclass is accessible but not subclass method.
2. If subclass reference refers to subclass object, all the methods of superclass and subclass are accessible because subclass objects avails a copy of superclass.
3. Generalization (widening) is performed by using subclass object, only methods of superclass are accessible. If we override methods of superclass into subclass, only subclass methods are accessible.
4. If specialization (narrowing) is performed by using superclass object, none of the superclass or subclass methods are accessible. It is useless.
5. If narrowing is performed by using subclass object, all the methods of superclass and subclasses can be accessed.
Hope that this tutorial has covered almost all important points related to class casting, generalization, and specialization in java. I hope that you will have understood the basic idea of these topics and enjoyed them.
Thanks for reading.