- Putting tag in CSS class
- 3 Answers 3
- HTML Tag
- Syntax
- Example of the HTML tag:
- Result
- Example of the HTML tag placed inside an HTML tag:
- Example of the HTML tag with CSS properties:
- Attributes
- How to style tag?
- Common properties to alter the visual weight/emphasis/size of text in tag:
- Coloring text in tag:
- Text layout styles for tag:
- Other properties worth looking at for tag:
- : The Inline Code element
- Try it
- Attributes
- Examples
- Result
- Notes
- Technical summary
- Specifications
- Browser compatibility
- See also
- Found a content problem with this page?
- MDN
- Support
- Our communities
- Developers
- Css для тега code
- Кратко
- Как пишется
- Как понять
- Подсветка синтаксиса
- Тег HTML программный код
- Синтаксис
- Пример использования тега в HTML коде
- Поддержка браузерами
Putting tag in CSS class
I am new to CSS.
Is there any way to put code tag in CSS class? For displaying code, at first I was using inline style:
td.bordered . . . some codes
I was wondering whether somehow I can also put the code tag into style sheet, so I don’t need to write it every time I want to display codes.
I know this is not what you asked but you will soon find yourself using some highlight library to that code . for that you can use prettify . if you need to edit a highlighted code you can use codemirror
@LoMaPh By your question I have the feeling you’re very very very new to CSS, and perhaps HTML too. Which is perfectly fine. Everybody were once. Do you already know about external stylesheets? They will blow your mind. =P I highly recommend you take a good look at developer.mozilla.org/en-US/learn/css and developer.mozilla.org/en-US/learn/html. Hope you’ll find it all as amazing as I did when I started. Good luck!
3 Answers 3
No. You could apply styles to the table data cell that would duplicate a given browser’s default styling for a code element, and you can use ::before and ::after to generate pseudo-elements, but there is no way to apply the semantic meaning associated with an HTML element using CSS.
The CSS spec goes so far as to explicitly warn against trying to do that sort of thing:
Note. CSS gives so much power to the «class» attribute, that authors could conceivably design their own «document language» based on elements with almost no associated presentation (such as DIV and SPAN in HTML) and assigning style information through the «class» attribute. Authors should avoid this practice since the structural elements of a document language often have recognized and accepted meanings and author-defined classes may not.
On the subject of semantics, a one-by-one table suggests you are abusing it for its shrink-wrapping layout features. Use display: inline-block instead.
Thus your code should probably look like this:
what. » there is no way to apply the semantic meaning associated with an HTML element using CSS» . from where did you took this from? plz read this
@rafaelcastrocouto — I know CSS quite well, I’ve been using it for over a decade and a half. Where does that document say that you can apply semantics with CSS? (As for that statement, I wrote it myself, based on my extensive experience)
@rafaelcastrocouto — That is not what he said. «I can also put the code tag into style sheet, so I don’t need to write [the code tag] every time I want to display codes»
No. First, there are no “CSS classes”. A class is a markup language (HTML) concept. It may be referred to in CSS, using a class selector, but this is simply a way to refer to elements by their class. Second, tags are markup language concept too, and you cannot create tags or elements in CSS; in CSS, you just refer to elements by their names.
However, if we interpret the question as “can I format some elements in CSS as if they had code elements inside them”, as I think it is, then the answer is “yes, with reservations”.
For the most of it, all that code markup does is that it sets the font face to a browser-dependent monospace font and the font size to a browser-dependent reduced size, though the latter (poorly documented) applies in some contexts and some browsers only. In addition to this, it may e.g. affect automatic translation programs (like Google Translate) so that they do not translate the content, regarding it as being “not in any human language”—this is normally good, but you cannot do that in CSS. And code markup could have other effects too.
But beware that this does not necessarily produce the same effect as the use of code elements. On the other hand, this should not really be an issue: decide on the desired rendering, and implement it in CSS, instead of trying to imitate some assumed default rendering of code .
HTML Tag
The tag is used to insert variables, fragments of program code, etc. into an HTML document. In the browser, the code is displayed in a monospaced font (a font in which all characters have the same width) of the smaller size.
The tag alone represents a single code line or code phrase. It should be wrapped within a element for representing several lines of code.
You can use CSS to achieve better effects.
Syntax
The tag comes in pairs. The content is written between the opening () and closing () tags.
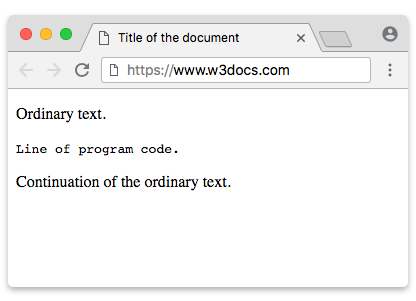
Example of the HTML tag:
html> html> head> title>Title of the document title> head> body> p>Ordinary text. p> code>Line of program code. code> p>Continuation of the ordinary text. p> body> html>Result
Example of the HTML tag placed inside an HTML tag:
html> html> head> title>Title of the document title> head> body> pre> code> body < color: yellow; font-size: 16px; line-height: 1.5; >code> pre> body> html>Example of the HTML tag with CSS properties:
html> html> head> title>Title of the document title> style> .code-style < font-size: 20px; line-height: 28px; background-color: lightblue; color: #ffffff; > style> head> body> p>Ordinary text. p> code class="code-style">Line of program code. code> p>Continuation of the ordinary text. p> body> html>Attributes
How to style tag?
Common properties to alter the visual weight/emphasis/size of text in tag:
- CSS font-style property sets the style of the font. normal | italic | oblique | initial | inherit.
- CSS font-family property specifies a prioritized list of one or more font family names and/or generic family names for the selected element.
- CSS font-size property sets the size of the font.
- CSS font-weight property defines whether the font should be bold or thick.
- CSS text-transform property controls text case and capitalization.
- CSS text-decoration property specifies the decoration added to text, and is a shorthand property for text-decoration-line, text-decoration-color, text-decoration-style.
Coloring text in tag:
- CSS color property describes the color of the text content and text decorations.
- CSS background-color property sets the background color of an element.
Text layout styles for tag:
- CSS text-indent property specifies the indentation of the first line in a text block.
- CSS text-overflow property specifies how overflowed content that is not displayed should be signalled to the user.
- CSS white-space property specifies how white-space inside an element is handled.
- CSS word-break property specifies where the lines should be broken.
Other properties worth looking at for tag:
- CSS text-shadow property adds shadow to text.
- CSS text-align-last property sets the alignment of the last line of the text.
- CSS line-height property specifies the height of a line.
- CSS letter-spacing property defines the spaces between letters/characters in a text.
- CSS word-spacing property sets the spacing between words.
: The Inline Code element
The HTML element displays its contents styled in a fashion intended to indicate that the text is a short fragment of computer code. By default, the content text is displayed using the user agent's default monospace font.
Try it
Attributes
This element only includes the global attributes.
Examples
A paragraph of text that includes :
p> The function code>selectAll()code> highlights all the text in the input field so the user can, for example, copy or delete the text. p>
Result
Notes
A CSS rule can be defined for the code selector to override the browser's default font face. Preferences set by the user might take precedence over the specified CSS.
Technical summary
| Content categories | Flow content, phrasing content, palpable content. |
|---|---|
| Permitted content | Phrasing content. |
| Tag omission | None, both the starting and ending tag are mandatory. |
| Permitted parents | Any element that accepts phrasing content. |
| Implicit ARIA role | No corresponding role |
| Permitted ARIA roles | Any |
| DOM interface | HTMLElement Up to Gecko 1.9.2 (Firefox 4) inclusive, Firefox implements the HTMLSpanElement interface for this element. |
Specifications
Browser compatibility
BCD tables only load in the browser
See also
Found a content problem with this page?
This page was last modified on Apr 13, 2023 by MDN contributors.
Your blueprint for a better internet.
MDN
Support
Our communities
Developers
Visit Mozilla Corporation’s not-for-profit parent, the Mozilla Foundation.
Portions of this content are ©1998– 2023 by individual mozilla.org contributors. Content available under a Creative Commons license.
Css для тега code
Тег для оформления программного кода.
Время чтения: меньше 5 мин
Обновлено 7 сентября 2022
Кратко
Скопировать ссылку "Кратко" Скопировано
Тег используется для вывода фрагментов программного кода.
Как пишется
Скопировать ссылку "Как пишется" Скопировано
const element = document.getElementById('#some-id');code> const element = document.getElementById('#some-id'); code>
Как понять
Скопировать ссылку "Как понять" Скопировано
используется для вывода любой информации, которая может быть обработана компьютером как программный код. Помимо непосредственно кода, сюда также относятся названия файлов, конфигурационные файлы, XML-элементы и т. д.
Тег по умолчанию строчный и браузеры не применяют к тексту внутри него никакого форматирования, кроме font - family : monospace; , и не подсвечивают синтаксис. Они не анализируют содержимое и не делают никаких предположений, на каком языке программирования написан вставленный код.
Изначально предназначен для вывода информации во фразовом контексте. Например, мы можем вставить код в середину предложения.
Пожалуй,
i— самое часто встречающееся имя переменной.p>Пожалуй, code>icode> — самое часто встречающееся имя переменной.p>
Если мы хотим вывести блок кода, то нужно дополнительно использовать тег для вывода кода с сохранением форматирования.
for(let i = 0; i < 10; i++) console.log(i) >pre>code> for(let i = 0; i < 10; i++)< console.log(i) >code>pre>Подсветка синтаксиса
Скопировать ссылку "Подсветка синтаксиса" Скопировано
Если мы хотим красивого форматирования и подсветки синтаксиса, мы должны использовать сторонние инструменты и дополнительно пометить код, например, при помощи атрибута class . Для этого обычно используются библиотеки, такие как highlight.js и prism.js.
Например, они генерируют HTML приблизительно такого вида:
const element = document . getElementById ( '#some-id' )pre class="block-code font-theme font-theme--code" data-lang="html"> code class="block-code__highlight"> span class="token keyword">constspan> element span class="token operator">=span> span class="token dom variable">documentspan> span class="token punctuation">.span> span class="token method function property-access">getElementByIdspan> span class="token punctuation">(span> span class="token string">'#some-id'span> span class="token punctuation">)span> code> pre>А пользователи его увидят вот так:
const element = document.getElementById('#some-id')const element = document.getElementById('#some-id')Тег HTML программный код
Тег в HTML используется для обозначения текста как программного кода.
Браузеры обычно отображают текст внутри HTML тега моноширинным шрифтом, однако хорошей практикой является выделение структурных частей кода с помощью стилей CSS (например, через автоматическое присвоение скриптом классов структурным элементам кода). Такой подход обеспечит более высокую читабельность выведенного кода.
Помимо тега в HTML используются другие теги логического форматирования текста, связанные с компьютерным вводом: - название клавиш на клавиатуре, - результат вывода компьютерной программы, - переменная компьютерной программы.
Все виды выделения текста описаны в статье: Теги форматирования текста в HTML.
Синтаксис
Пример использования тега в HTML коде
<style type="text/css">
.main width: 100%;
background-color: white;
font-size: 14px;
>
</style>Поддержка браузерами
| Тег | |||||
| Да | Да | Да | Да | Да |