- Python Variables with examples
- Variable name – Identifiers
- Python Variable Example
- Python multiple assignment
- Plus and concatenation operation on the variables
- Data Types
- Top Related Articles:
- About the Author
- Python Variables
- Example
- Example
- Casting
- Example
- Get the Type
- Example
- Single or Double Quotes?
- Example
- Case-Sensitive
- Example
- COLOR PICKER
- Report Error
- Thank You For Helping Us!
Python Variables with examples
Variables are used to store data, they take memory space based on the type of value we assigning to them. Creating variables in Python is simple, you just have write the variable name on the left side of = and the value on the right side, as shown below. You do not have to explicitly mention the type of the variable, python infer the type based on the value we are assigning.
num = 100 #num is of type int str = "Chaitanya" #str is of type string
Variable name – Identifiers
Variable name is known as identifier. There are few rules that you have to follow while naming the variables in Python.
1. The name of the variable must always start with either a letter or an underscore (_). For example: _str, str, num, _num are all valid name for the variables.
2. The name of the variable cannot start with a number. For example: 9num is not a valid variable name.
3. The name of the variable cannot have special characters such as %, $, # etc, they can only have alphanumeric characters and underscore (A to Z, a to z, 0-9 or _ ).
4. Variable name is case sensitive in Python which means num and NUM are two different variables in python.
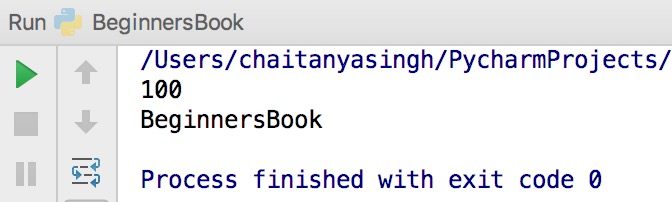
Python Variable Example
num = 100 str = "BeginnersBook" print(num) print(str)
Output:
Python multiple assignment
We can assign multiple variables in a single statement like this in Python.
x = y = z = 99 print(x) print(y) print(z)
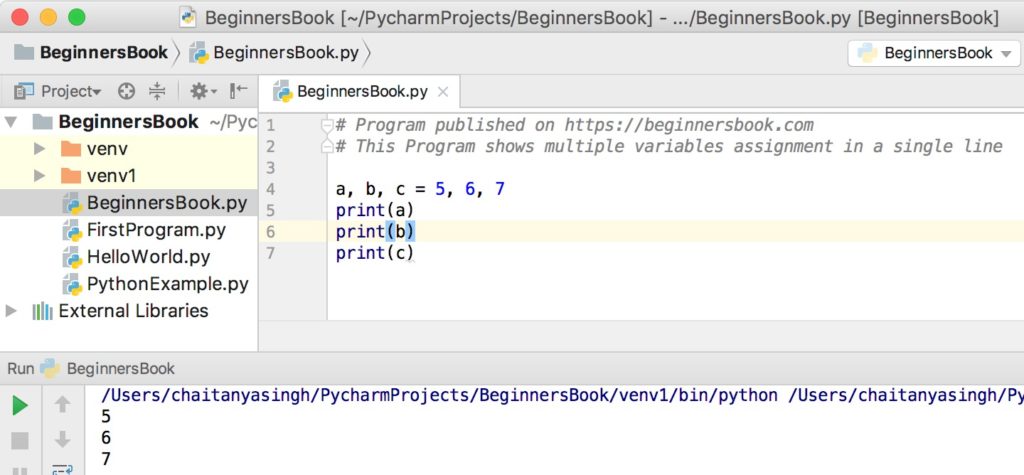
Another example of multiple assignment
a, b, c = 5, 6, 7 print(a) print(b) print(c)
Output:
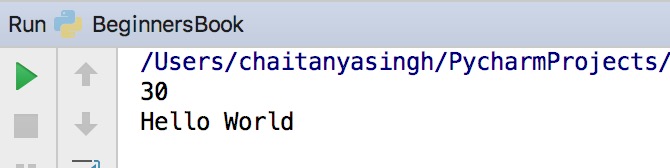
Plus and concatenation operation on the variables
x = 10 y = 20 print(x + y) p = "Hello" q = "World" print(p + " " + q)
Output:
However if you try to use the + operator with variable x and p then you will get the following error.
unsupported operand type(s) for +: 'int' and 'str'
Data Types
A data type defines the type of data, for example 123 is an integer data while “hello” is a String type of data. The data types in Python are divided in two categories:
1. Immutable data types – Values cannot be changed.
2. Mutable data types – Values can be changed
Immutable data types in Python are:
1. Numbers
2. String
3. Tuple
Mutable data types in Python are:
1. List
2. Dictionaries
3. Sets
Top Related Articles:
About the Author
I have 15 years of experience in the IT industry, working with renowned multinational corporations. Additionally, I have dedicated over a decade to teaching, allowing me to refine my skills in delivering information in a simple and easily understandable manner.
Python Variables
A variable is created the moment you first assign a value to it.
Example
Variables do not need to be declared with any particular type, and can even change type after they have been set.
Example
Casting
If you want to specify the data type of a variable, this can be done with casting.
Example
Get the Type
You can get the data type of a variable with the type() function.
Example
Single or Double Quotes?
String variables can be declared either by using single or double quotes:
Example
Case-Sensitive
Variable names are case-sensitive.
Example
This will create two variables:
COLOR PICKER
Report Error
If you want to report an error, or if you want to make a suggestion, do not hesitate to send us an e-mail:
Thank You For Helping Us!
Your message has been sent to W3Schools.
Top Tutorials
Top References
Top Examples
Get Certified
W3Schools is optimized for learning and training. Examples might be simplified to improve reading and learning. Tutorials, references, and examples are constantly reviewed to avoid errors, but we cannot warrant full correctness of all content. While using W3Schools, you agree to have read and accepted our terms of use, cookie and privacy policy.