- Python MySQL – Delete Data from a Table
- Python Delete data from MySQL Table
- Table of contents
- Prerequisites
- Python Example to Delete a Single Row from a MySQL table
- Use Python Variable in a SQL query to delete data from the table
- Python Delete Multiple Rows from a MySQL Table
- Delete All rows from a table in Python
- Delete MySQL Table and Database from Python
- Delete MySQL Table column from Python
- Next Steps
- About Vishal
- Related Tutorial Topics:
- Python Exercises and Quizzes
Python MySQL – Delete Data from a Table
Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to delete data from a table in the MySQL database using Python.
To delete data from a table from a Python program, you follow these steps:
- Connect to the database by creating a new MySQLConnection object.
- Instantiate a new cursor object and call its execute() method. To commit the changes, you should always call the commit() method of the MySQLConnection object after calling the execute() method.
- Close the cursor and database connection by calling close() method of the corresponding objects.
The following example shows you how to delete a book specified by book id:
from mysql.connector import MySQLConnection, Error from python_mysql_dbconfig import read_db_config def delete_book(book_id): db_config = read_db_config() query = "DELETE FROM books WHERE try: # connect to the database server conn = MySQLConnection(**db_config) # execute the query cursor = conn.cursor() cursor.execute(query, (book_id,)) # accept the change conn.commit() except Error as error: print(error) finally: cursor.close() conn.close() if __name__ == '__main__': delete_book(102)Code language: Python (python)Notice that we use the read_db_config() function from the python_mysql_dbconfig module.
Because we need to delete a specific row in the books table, we use a placeholder ( % ) inside the DELETE statement.
When we call the execute() method, we pass both the DELETE statement and (book_id,) tuple. The connector will translate the DELETE statement into the following form:
DELETE FROM books WHERE >102;Code language: Python (python)You should always use placeholders inside any query that you pass to the execute() method. This helps you avoid the SQL injection.
Before running the code, let’s check the books table to see the data before we delete the entry.
SELECT * FROM books WHERE id = 102;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)After running the module above, we execute the SELECT statement again. No rows returned. It means the module has deleted the entry successfully.
In this tutorial, you have learned how to delete data from a table using MySQL Connector/Python API.
Python Delete data from MySQL Table
This lesson demonstrates how to execute the SQL DELETE query from Python to delete data from a MySQL database table.
After reading this article, you will able to delete single, multiple, and all rows, as well as delete a single column and multiple columns from the MySQL table using Python
Further Reading:
Table of contents
Prerequisites
Before moving further, Please make sure you have the following in place: –
- Username and password to connect MySQL
- MySQL table name in which you want to insert data.
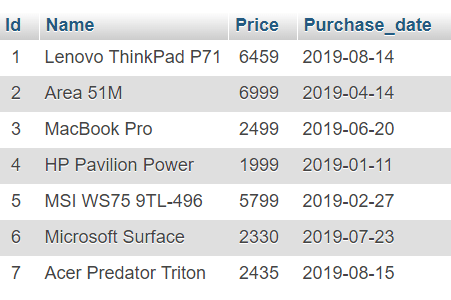
To perform a delete operation, I am using a Laptop table present in my MySQL server.
If a table is not present in your MySQL server, you can refer to our article to create a MySQL table from Python.
You can also download a SQL query file, which contains SQL queries for table creation and data so that you can use this table for your INSERT operations.
Python Example to Delete a Single Row from a MySQL table
Follow these steps: –
How to delete a row in MySQL using Python
- Connect to MySQL from Python Refer to Python MySQL database connection to connect to MySQL database from Python using MySQL Connector module
- Define a SQL Delete Query Next, prepare a SQL delete query to delete a row from a table. Delete query contains the row to be deleted based on a condition placed in where clause of a query.
For example, DELETE FROM MySQL_table WHERE > - Get Cursor Object from Connection Next, use a connection.cursor() method to create a cursor object. This method creates a new MySQLCursor object.
- Execute the delete query using execute() method Execute the delete query using the cursor.execute() method. This method executes the operation stored in the delete query.
After a successful delete operation, the execute() method returns us the number of rows affected. - Commit your changes After successfully executing a delete operation, make changes persistent into a database using the commit() of a connection class.
- Get the number of rows affected Use a cursor.rowcount method to get the number of rows affected. The count depends on how many rows you are deleting.
You can also Execute a MySQL select query from Python to Verify the result. - Close the cursor object and database connection object use cursor.clsoe() and connection.clsoe() method to close open connections after your work completes.
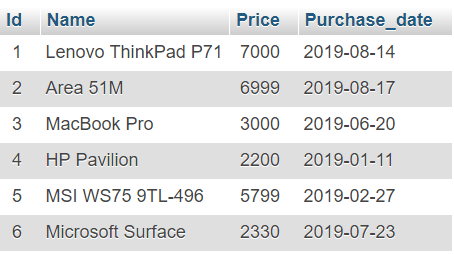
import mysql.connector try: connection = mysql.connector.connect(host='localhost', database='electronics', user='root') cursor = connection.cursor() print("Laptop table before deleting a row") sql_select_query = """select * from Laptop where cursor.execute(sql_select_query) record = cursor.fetchone() print(record) # Delete a record sql_Delete_query = """Delete from Laptop where cursor.execute(sql_Delete_query) connection.commit() print('number of rows deleted', cursor.rowcount) # Verify using select query (optional) cursor.execute(sql_select_query) records = cursor.fetchall() if len(records) == 0: print("Record Deleted successfully ") except mysql.connector.Error as error: print("Failed to delete record from table: <>".format(error)) finally: if connection.is_connected(): cursor.close() connection.close() print("MySQL connection is closed")Displaying laptop record Before Deleting it (7, 'Acer Predator Triton', 2435.0, datetime.date(2019, 8, 17)) Record Deleted successfully MySQL connection is closed
Use Python Variable in a SQL query to delete data from the table
Sometimes we need input from the user, for example, when the user is deleting their data from the web portal or any other details through User Interface. in such a scenario, it is always best practice to use a parameterized query.
A prepared statement or parameterized query uses placeholders ( %s ) inside any SQL statements that contain input from users. i.e., Using a parameterized query, we can pass Python variables as a query parameter in which placeholders ( %s ) used for parameters.
import mysql.connector try: connection = mysql.connector.connect(host='localhost', database='electronics', user='pynative', password='pynative@#29') cursor = connection.cursor() sql_Delete_query = """Delete from Laptop where # row to delete laptopId = 6 cursor.execute(sql_Delete_query, (laptopId,)) connection.commit() print("Record Deleted successfully ") except mysql.connector.Error as error: print("Failed to Delete record from table: <>".format(error)) finally: if connection.is_connected(): cursor.close() connection.close() print("MySQL connection is closed")Record Deleted successfully MySQL connection is closed
Note: We defined SQL delete query with placeholder which contains Laptop Id to delete in tuple format. Refer to Select query to fetch data from MySQL table to verify your delete operation result.
Python Delete Multiple Rows from a MySQL Table
Sometimes we need to delete an N-number of rows that match a specific condition. For example, you want to delete employee data from the employee table who left the organization. You can delete multiple rows from the MySQL table using a single delete SQL Query in Python.
import mysql.connector try: connection = mysql.connector.connect(host='localhost', database='electronics', user='pynative', password='pynative@#29') cursor = connection.cursor() sql_Delete_query = """Delete from Laptop where records_to_delete = [(6,), (5,)] cursor.executemany(sql_Delete_query, records_to_delete) connection.commit() print(cursor.rowcount, " Record Deleted successfully") except mysql.connector.Error as error: print("Failed to Delete records from MySQL table: <>".format(error)) finally: if connection.is_connected(): cursor.close() connection.close() print("MySQL connection is closed") 2 Record Deleted successfully MySQL connection is closed
Refer to Select query to fetch data from MySQL table to verify your delete operation result.
Let’s understand the above program: –
- We defined SQL delete query with placeholder which contains Laptop IDs to delete in a list format. This List contains a tuple for each row. Here we created two tuples, so we are deleting two rows.
- Next, we used the cursor’s executemany() method to delete multiple rows of a database table. Using a cursor.rowcount method, we can find how many rows were deleted successfully.
Delete All rows from a table in Python
It is possible to delete all rows from a MySQL database table using a truncate SQL query. Truncate SQL queries remove all data from a table, typically bypassing the number of integrity enforcing mechanisms.
You can refer to the Wikipedia article to read more on SQL truncate. Let’s move to python code to delete all rows from the MySQL table.
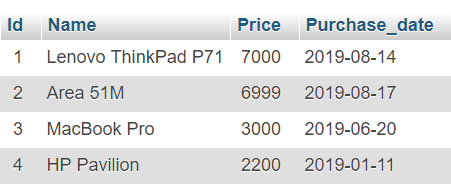
import mysql.connector try: connection = mysql.connector.connect(host='localhost', database='electronics', user='pynative', password='pynative@#29') cursor = connection.cursor() Delete_all_rows = """truncate table Laptop """ cursor.execute(Delete_all_rows) connection.commit() print("All Record Deleted successfully ") except mysql.connector.Error as error: print("Failed to Delete all records from database table: <>".format(error)) finally: if connection.is_connected(): cursor.close() connection.close() print("MySQL connection is closed") All Record Deleted successfully MySQL connection is closed
Delete MySQL Table and Database from Python
You can delete old, unused tables and temporary databases and tables using a DROP TABLE and DROP DATABASE statement. Let see the demo.
import mysql.connector try: connection = mysql.connector.connect(host='localhost', database='electronics', user='pynative', password='pynative@#29') cursor = connection.cursor() delete_table_query = """DROP TABLE Laptop""" cursor.execute(delete_table_query) delete_database_query = """DROP DATABASE Electronics""" cursor.execute(delete_database_query) connection.commit() print("Table and Database Deleted successfully ") except mysql.connector.Error as error: print("Failed to Delete table and database: <>".format(error)) finally: if connection.is_connected(): cursor.close() connection.close() print("MySQL connection is closed") Table and Database Deleted successfully MySQL connection is closed
Delete MySQL Table column from Python
Use alter table drop column command to delete a column from a MySQL table.
import mysql.connector try: connection = mysql.connector.connect(host='localhost', database='electronics', user='pynative', password='pynative@#29') cursor = connection.cursor() alter_column = """ALTER TABLE Laptop DROP COLUMN Purchase_date""" cursor.execute(alter_column) connection.commit() print("Column Deleted successfully ") except mysql.connector.Error as error: print("Failed to Delete column: <>".format(error)) finally: if connection.is_connected(): cursor.close() connection.close() print("MySQL connection is closed") Column Deleted successfully MySQL connection is closed
Next Steps
To practice what you learned in this article, Please solve a Python Database Exercise project to Practice and master the Python Database operations.
Did you find this page helpful? Let others know about it. Sharing helps me continue to create free Python resources.
About Vishal
I’m Vishal Hule, Founder of PYnative.com. I am a Python developer, and I love to write articles to help students, developers, and learners. Follow me on Twitter
Related Tutorial Topics:
Python Exercises and Quizzes
Free coding exercises and quizzes cover Python basics, data structure, data analytics, and more.
- 15+ Topic-specific Exercises and Quizzes
- Each Exercise contains 10 questions
- Each Quiz contains 12-15 MCQ