TypeScript — Returning a Function
Functions may also return value along with control, back to the caller. Such functions are called as returning functions.
Syntax
function function_name():return_type < //statements return value; >
- The return_type can be any valid data type.
- A returning function must end with a return statement.
- A function can return at the most one value. In other words, there can be only one return statement per function.
- The data type of the value returned must match the return type of the function.
Example
//function defined function greet():string < //the function returns a string return "Hello World" >function caller() < var msg = greet() //function greet() invoked console.log(msg) >//invoke function caller()
- The example declares a function greet(). The function’s return type is string.
- Line function returns a string value to the caller. This is achieved by the return statement.
- The function greet() returns a string, which is stored in the variable msg. This is later displayed as output.
On compiling, it will generate following JavaScript code −
//Generated by typescript 1.8.10 //function defined function greet() < return "Hello World"; >function caller() < var msg = greet(); //function greet() invoked console.log(msg); >//invoke function caller();
The output of the above code is as follows −
TypeScript function return type
Function return type in TypeScript is nothing but the value we want to return from the function. The function return type is used when we return value from the function. We can return any value or nothing from the function in TypeScript. Some return types are a string, number, object, etc. We will have an error and exception if we do not return the expected value from the function. In the coming section, we will discuss the internal working and how to implement different return types or functions in detail.
Syntax
As discussed, we can return any value from the function we write; it depends upon the requirement. But while returning, we have to return the correct value to avoid the error. Let’s have a look at its syntax for a better understanding of its usage. See below;
function function_name(val1 , val2, so on..): return type < // logic goes here .. >As you can see in the above lines of syntax, to return something from a function, we have to follow this standard defined by TypeScript, which is common in any other language. Let’s have a look at one practice syntax for beginners; see below;
function demo(vale:string ): string < // logic goes here .. >We will discuss this in detail in the coming section; for now, we just have a basic idea to define it for later use in the program.
How does the function return type work in TypeScript?
In TypeScript or any other programming language, we can return a different type of value from the function. This is important while writing good code because we may experience errors while calling the function. if we do not return anything from the function, we are not required to specify the function’s return. We can have both functions in TypeScript with or without return type like any other programming language. Let’s look closer at the function signature that needs to be followed while working with the return type in TypeScript. See below;
Method signature:
function function_name(paam ..): return_type< // body goes here return val ; >1. function_name: Here, we can assign some value to our function. This is the normal function name we can give.
2. (paam ..): This is used to pass parameters inside the function. Which can be any number; also, we can define the type of parameter being passed in the function.
3. : return_type: This is the standard the TypeScript documentation gives to define the return type in TypeScript. We have to use the ‘:’ colon symbol to make this function return any value. Immediately after this, we can specify the type we want to return from our function; it can be anything like string, number, or any.
4. return: If our function is expected to return some value, we must use the ‘return’ keyword inside the body. This keyword returns the expected result from the called function in any programming language. Suppose we do not provide this return statement inside our function body. In that case, we will have a compile-time error saying the function must include the return statement, and the return value should match the function’s return type.
Let’s have a list of what we can return from the function in TypeScript see below;
1. Number: we can return numbers from the function; we must use the ‘number’ type available in TypeScript. Let’s have a look at its implementation for a better understanding. See below;
Example:
function demo(val:number): number
2. string: we can return a string from the function; for this, we must use the ‘string’ type available in TypeScript. Let’s have a look at its implementation for a better understanding. See below;
Example:
function demo(val:string): string
3. any: we can return any from the function; for this, we must use the ‘any’ type available in TypeScript. Let’s have a look at its implementation for a better understanding. See below;
Example:
function demo(val:string): any
One advantage of using the ‘any’ type in TypeScript is that we can return anything from our function. Hence, using that, our function is not specific to return a number or string; rather, we can return anything from it. Now we will see one sample example for beginners to understand its implementation and usage. See below;
Example:
function demofunction(i: number): number < console.log("value is " + i); return i; >let returnvalue = demofunction(100);In the above code lines, we are implementing one function that returns the number type; inside this, we have used the return keyword to return the value passed to the function. On calling, it will return the result value, which we can hold in any variable and use for further requirements.
Examples
1. We are trying to return numbers from the function body in the example. Using the return statement as the sum of all parameters passed as a vale. This is a simple example for beginners to start implementing this while programming.
Example:
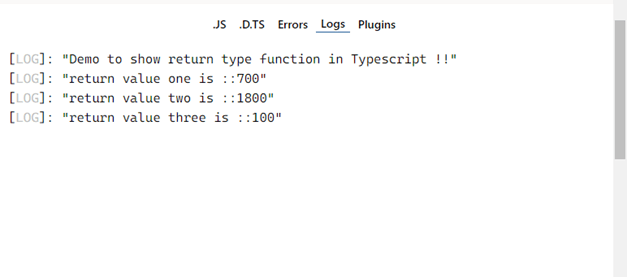
function demofunction(i: number, j: number, k: number): number < let addition = i + j+ k; return addition; >console.log("Demo to show return type function in Typescript !!"); let returnvalue1 = demofunction(100, 200, 400); console.log("return value one is ::"+ returnvalue1); let returnvalue2 = demofunction(500, 600, 700); console.log("return value two is ::"+ returnvalue2); let returnvalue3 = demofunction(20, 30, 50); console.log("return value three is ::"+ returnvalue3);Rules and regulations for function return type
There are some rules which we need to follow while working with return type in TypeScript, which are as follows see below;
- If we return any value from our function, we must use the ‘return’ statement inside our function body.
- We can return any value from the function, like string, number, any, character, etc.
- To define the return type for the function, we have to use the ‘:’ symbol just after the function’s parameter and before the function’s body in TypeScript.
- Therefore, the function body’s return value should match the function return type; otherwise, our code will have a compile-time error.
Conclusion
However, Using the return statement or return type function makes our function more standard and less error-free. This becomes more understandable by the caller what value t will return after calling.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “TypeScript function return type” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
500+ Hours of HD Videos
15 Learning Paths
120+ Courses
Verifiable Certificate of Completion
Lifetime Access
1000+ Hours of HD Videos
43 Learning Paths
250+ Courses
Verifiable Certificate of Completion
Lifetime Access
1500+ Hour of HD Videos
80 Learning Paths
360+ Courses
Verifiable Certificate of Completion
Lifetime Access
3000+ Hours of HD Videos
149 Learning Paths
600+ Courses
Verifiable Certificate of Completion
Lifetime Access
PYTHON Course Bundle — 81 Courses in 1 | 59 Mock Tests
363+ Hours of HD Videos
81 Courses
59 Mock Tests & Quizzes
Verifiable Certificate of Completion
Lifetime Access
4.8