- CSS font-size Property
- Syntax
- Example of the font-size property:
- Result
- Usage of percentage values
- Example of the font-size property specified in percentage:
- Usage of the em unit
- Example of the font-size property with the «em» value:
- Usage of the rem unit
- Example of the font-size property with the «rem» value:
- Usage of the ex unit
- Usage of viewport units
- Example of the font-size property with the «length» value:
- Example of the font-size property with the absolute-size values:
- Example of the font-size property with «smaller» and «larger» values:
- Values
- Browser support
- CSS font-size Property
- CSS Syntax
- Property Values
- Related Pages
- COLOR PICKER
- Report Error
- Thank You For Helping Us!
- CSS Font Size
- Set Font Size With Pixels
- Example
- Set Font Size With Em
- Example
- Use a Combination of Percent and Em
- Example
- Responsive Font Size
- Hello World
- Example
- Hello World Viewport is the browser window size. 1vw = 1% of viewport width. If the viewport is 50cm wide, 1vw is 0.5cm. Источник
CSS font-size Property
The font-size property defines the font size of the text.
Font size can be defined by the following ways:
Absolute font size includes the following values:
Relative font size includes the following values:
Lengths can be relative lengths (em, ex, px) and absolute lengths (in, cm, mm, pt, pc). Percentages specify an absolute font size relative to the font size of the parent element.
| Initial Value | medium |
| Applies to | All elements. It also applies to ::first-letter and ::first-line. |
| Inherited | Yes. |
| Animatable | Yes. |
| Version | CSS1 |
| DOM Syntax | object.style.fontSize = «15px»; |
Syntax
font-size: medium | xx-small | x-small | small | large | x-large | xx-large | smaller | larger | length | initial | inherit;Example of the font-size property:
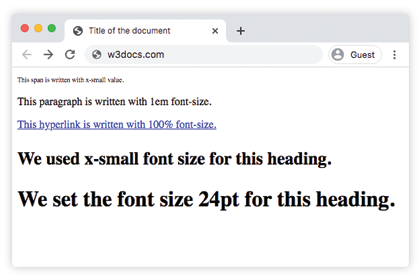
html> html> head> title>Title of the document title> style> h1 < font-size: 24pt; > h3 < font-size: 26px; > p < font-size: 1em; > a < font-size: 100%; > span < font-size: x-small; > style> head> body> span>This span is written with x-small value. span> p>This paragraph is written with 1em font-size. p> a href="https://www.w3docs.com/">This hyperlink is written with 100% font-size. a> h3>We used x-small font size for this heading. h3> h1>We set the font size 24pt for this heading. h1> body> html>Result
Usage of percentage values
Percentage values are relative to the font-size of the parent element. The code below shows its usage:
Example of the font-size property specified in percentage:
html> html> body> h3>We used x-small font size for this heading.h3> span>This span is written with x-small value.span> p>This paragraph is written with 1em font-size.p> body> html>Usage of the em unit
The em unit is considered to be a relative unit. It is based on the calculated value of its parent element’s font size. In the code below, the paragraph will be 32px, because 2×16=32, and the heading will have a font-size of 48px because 3×16=48px. This method is very useful because we can be sure that all the child elements will always be relative to each other.
Example of the font-size property with the «em» value:
html> html> head> title>Title of the document title> style> .container < font-size: 16px; > p < font-size: 2em; > h2 < font-size: 3em; > style> head> body> div class="container"> h2>Here is the heading h2> p>Here is the text. p> div> body> html>Usage of the rem unit
In the case of using the rem unit, the font-size depends on the value of the HTML element. In the example below, the rem unit is inherited from the HTML element, that’s why it is equal to 24px. So, the heading will have a font-size of 24px, because 1.5×16=24px.
Example of the font-size property with the «rem» value:
html> html> head> title>Title of the document title> style> html < font-size: 16px; > h2 < font-size: 1.5rem; > style> head> body> div class="container"> h2>Here is the heading h2> p>Here is the text. p> div> body> html>Usage of the ex unit
In the case of the ex unit, 1ex is equal to the calculated height of the HTML element’s letter x. In the code example below, the HTML element is 15px. The x-height of that particular font will determine all the other font-sizes.
Usage of viewport units
Viewport units (vw and vh) are used for setting the font-size of an element, which is relative to the size of the viewport.
Example of the font-size property with the «length» value:
html> html> head> title>Title of the document title> style> span < color: green; font-size: 2vh; > p < color: red; font-size: 1em; > .length < color: orange; font-size: 30px; > h3 < color: lightblue; font-size: 3ex; > h1 < color: purple; font-size: 24pt; > a < color: blue; font-size: 120%; > style> head> body> h2>Font-size property h2> span>This text is written with 2vh font-size. span> p>This paragraph is written with 1em font-size. p> div class="length">Example with 30px font-size length div> h3>Example with 3ex font-size length. h3> h1>We set the font size 24pt for this heading. h1> a href="https://www.w3docs.com/">This hyperlink is written with 100% font-size. a> body> html>Example of the font-size property with the absolute-size values:
html> html> head> title>Title of the document title> style> .font-xxsmall < color: grey; font-size: xx-small; > .font-xsmall < color: grey; font-size: x-small; > .font-small < color: grey; font-size: small; > .fontSize-medium < color: grey; font-size: medium; > .font-large < color: grey; font-size: large; > .font-xlarge < color: grey; font-size: x-large; > .font-xxlarge < color: grey; font-size: xx-large; > style> head> body> h1>Font-size property h1> div class="font-xxsmall">Example with font-size xx-small property div> div class="font-xsmall">Example with font-size x-small property div> div class="font-small">Example with font-size small property div> div class="font-medium">Example with font-size medium property div> div class="font-large">Example with font-size large property div> div class="font-xlarge">Example with font-size x-large property div> div class="font-xxlarge">Example with font-size xx-large property div> body> html>Example of the font-size property with «smaller» and «larger» values:
html> html> head> title>Title of the document title> style> .smaller < color: red; font-size: smaller; > .larger < color: red; font-size: larger; > style> head> body> h1>font-size property h1> div class="smaller">Example with font-size smaller property div> div class="larger">Example with font-size larger property div> body> html>Values
| Value | Description | Play it |
|---|---|---|
| medium | Sets the font-size to medium. This is the default value of this property. | Play it » |
| xx-small | Sets the font-size to xx-small. | Play it » |
| x-small | Sets the font-size to x-small. | Play it » |
| small | Sets the font-size to small. | Play it » |
| large | Sets the font-size to large. | Play it » |
| x-large | Sets the font-size to x-large. | Play it » |
| xx-large | Sets the font-size to xx-large. | Play it » |
| smaller | Smallers the font-size. | Play it » |
| larger | Largers the font-size. | Play it » |
| length | Specifies the font-size by px, em etc. | Play it » |
| % | Sets the font-size to a percent of the parent element’s font size. | Play it » |
| initial | Makes the property use its default value. | Play it » |
| inherit | Inherits the property from its parents element. |
Browser support
CSS font-size Property
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the property.
CSS Syntax
font-size:medium|xx-small|x-small|small|large|x-large|xx-large|smaller|larger|length|initial|inherit;
Property Values
| Value | Description | Demo |
|---|---|---|
| medium | Sets the font-size to a medium size. This is default | Demo ❯ |
| xx-small | Sets the font-size to an xx-small size | Demo ❯ |
| x-small | Sets the font-size to an extra small size | Demo ❯ |
| small | Sets the font-size to a small size | Demo ❯ |
| large | Sets the font-size to a large size | Demo ❯ |
| x-large | Sets the font-size to an extra large size | Demo ❯ |
| xx-large | Sets the font-size to an xx-large size | Demo ❯ |
| smaller | Sets the font-size to a smaller size than the parent element | Demo ❯ |
| larger | Sets the font-size to a larger size than the parent element | Demo ❯ |
| length | Sets the font-size to a fixed size in px, cm, etc. Read about length units | Demo ❯ |
| % | Sets the font-size to a percent of the parent element’s font size | Demo ❯ |
| initial | Sets this property to its default value. Read about initial | |
| inherit | Inherits this property from its parent element. Read about inherit |
Related Pages
COLOR PICKER
Report Error
If you want to report an error, or if you want to make a suggestion, do not hesitate to send us an e-mail:
Thank You For Helping Us!
Your message has been sent to W3Schools.
Top Tutorials
Top References
Top Examples
Get Certified
W3Schools is optimized for learning and training. Examples might be simplified to improve reading and learning. Tutorials, references, and examples are constantly reviewed to avoid errors, but we cannot warrant full correctness of all content. While using W3Schools, you agree to have read and accepted our terms of use, cookie and privacy policy.
CSS Font Size
Being able to manage the text size is important in web design. However, you should not use font size adjustments to make paragraphs look like headings, or headings look like paragraphs.
Always use the proper HTML tags, like — for headings and
for paragraphs.
The font-size value can be an absolute, or relative size.
- Sets the text to a specified size
- Does not allow a user to change the text size in all browsers (bad for accessibility reasons)
- Absolute size is useful when the physical size of the output is known
- Sets the size relative to surrounding elements
- Allows a user to change the text size in browsers
Note: If you do not specify a font size, the default size for normal text, like paragraphs, is 16px (16px=1em).
Set Font Size With Pixels
Setting the text size with pixels gives you full control over the text size:
Example
Tip: If you use pixels, you can still use the zoom tool to resize the entire page.
Set Font Size With Em
To allow users to resize the text (in the browser menu), many developers use em instead of pixels.
1em is equal to the current font size. The default text size in browsers is 16px. So, the default size of 1em is 16px.
The size can be calculated from pixels to em using this formula: pixels/16=em
Example
h2 font-size: 1.875em; /* 30px/16=1.875em */
>
p font-size: 0.875em; /* 14px/16=0.875em */
>
In the example above, the text size in em is the same as the previous example in pixels. However, with the em size, it is possible to adjust the text size in all browsers.
Unfortunately, there is still a problem with older versions of Internet Explorer. The text becomes larger than it should when made larger, and smaller than it should when made smaller.
Use a Combination of Percent and Em
The solution that works in all browsers, is to set a default font-size in percent for the element:
Example
Our code now works great! It shows the same text size in all browsers, and allows all browsers to zoom or resize the text!
Responsive Font Size
The text size can be set with a vw unit, which means the «viewport width».
That way the text size will follow the size of the browser window:
Hello World
Resize the browser window to see how the font size scales.
Example
Hello World
Viewport is the browser window size. 1vw = 1% of viewport width. If the viewport is 50cm wide, 1vw is 0.5cm.