- Все значения свойства display
- Значение none
- Значение block
- Значение inline
- Значение inline-block
- Значения table-*
- Вертикальное центрирование с table-cell
- Значения list-item, run-in и flex
- Html span display text
- Статьи по теме
- Типы тегов
- HTML Tag
- Syntax
- Example of the HTML tag:
- Example of the HTML tag with the class attribute:
- Attributes
- How to style tag?
- Common properties to alter the visual weight/emphasis/size of text in tag:
- Coloring text in tag:
- Text layout styles for tag:
- Other properties worth looking at for tag:
- : The Content Span element
- Try it
- Attributes
- Example
- Example 1
- HTML
- Result
- Example 2
- HTML
- CSS
- Result
- Technical summary
- Specifications
- Browser compatibility
- See also
- Found a content problem with this page?
- MDN
- Support
- Our communities
- Developers
Все значения свойства display
Свойство display имеет много разных значений. Обычно, используются только три из них: none , inline и block , потому что когда-то браузеры другие не поддерживали.
Но после ухода IE7-, стало возможным использовать и другие значения тоже. Рассмотрим здесь весь список.
Значение none
Самое простое значение. Элемент не показывается, вообще. Как будто его и нет.
Невидимый div ( ) Стоит внутри скобок Значение block
- Блочные элементы располагаются один над другим, вертикально (если нет особых свойств позиционирования, например float ).
- Блок стремится расшириться на всю доступную ширину. Можно указать ширину и высоту явно.
Это значение display многие элементы имеют по умолчанию: , заголовок , параграф
.
Блоки прилегают друг к другу вплотную, если у них нет margin .
Значение inline
- Элементы располагаются на той же строке, последовательно.
- Ширина и высота элемента определяются по содержимому. Поменять их нельзя.
Например, инлайновые элементы по умолчанию: , .
Если вы присмотритесь внимательно к примеру выше, то увидите, что между внутренними и есть пробел. Это потому, что он есть в HTML.
Если расположить элементы вплотную – его не будет:
Содержимое инлайн-элемента может переноситься на другую строку.
При этом каждая строка в смысле отображения является отдельным прямоугольником («line box»). Так что инлайн-элемент состоит из объединения прямоугольников, но в целом, в отличие от блока, прямоугольником не является.
Это проявляется, например, при назначении фона.
Например, три прямоугольника подряд:
. Ля Ля Ля Ля Ля Ля Ля Ля Ля Ля Ля Ля Ля Ля Ля Ля Ля Ля Ля Ля Ля Ля Ля Ля Ля Ля Ля Ля Ля Ля Ля Ля Ля Ля Ля Ля Ля Ля Ля Ля . Если инлайн-элемент граничит с блоком, то между ними обязательно будет перенос строки:
Значение inline-block
Это значение – означает элемент, который продолжает находиться в строке ( inline ), но при этом может иметь важные свойства блока.
Во всём остальном – это блок, то есть:
Это значение display используют, чтобы отобразить в одну строку блочные элементы, в том числе разных размеров.
Свойство vertical-align позволяет выровнять такие элементы внутри внешнего блока:
Как и в случае с инлайн-элементами, пробелы между блоками появляются из-за пробелов в HTML. Если элементы списка идут вплотную, например, генерируются в JavaScript – их не будет.
Значения table-*
Современные браузеры (IE8+) позволяют описывать таблицу любыми элементами, если поставить им соответствующие значения display .
Для таблицы целиком table , для строки – table-row , для ячейки – table-cell и т.д.
Важно то, что это действительно полноценная таблица. Используются табличные алгоритмы вычисления ширины и высоты элемента, описанные в стандарте.
Это хорошо для семантической вёрстки и позволяет избавиться от лишних тегов.
table < display: table >tr < display: table-row >thead < display: table-header-group >tbody < display: table-row-group >tfoot < display: table-footer-group >col < display: table-column >colgroup < display: table-column-group >td, th < display: table-cell >caption
Очень подробно об алгоритмах вычисления размеров и отображении таблиц рассказывает стандарт CSS 2.1 – Tables.
Вертикальное центрирование с table-cell
Внутри ячеек свойство vertical-align выравнивает содержимое по вертикали.
Это можно использовать для центрирования:
div Элемент
С неизвестной
Высотой CSS не требует, чтобы вокруг table-cell была структура таблицы: table-row и т.п. Может быть просто такой одинокий DIV , это допустимо.
При этом он ведёт себя как ячейка TD , то есть подстраивается под размер содержимого и умеет вертикально центрировать его при помощи vertical-align .
Значения list-item, run-in и flex
У свойства display есть и другие значения. Они используются реже, поэтому посмотрим на них кратко:
Этот display по умолчанию используется для элементов списка. Он добавляет к блоку с содержимым ещё и блок с номером(значком) списка, который стилизуется стандартными списочными свойствами:
Если после run-in идёт block , то run-in становится его первым инлайн-элементом, то есть отображается в начале block .
Если ваш браузер поддерживает это значение, то в примере ниже h3 , благодаря display:run-in , окажется визуально внутри div :
Про пчёл.
Пчёлы - отличные создания, они делают мёд.Если же вы видите две строки, то ваш браузер НЕ поддерживает run-in .
Вот, для примера, правильный вариант отображения run-in , оформленный другим кодом:
Про пчёл.
Пчёлы - отличные создания, они делают мёд. Если этот вариант отличается от того, что вы видите выше – ваш браузер не поддерживает run-in . На момент написания этой статьи только IE поддерживал display:run-in .
Flexbox позволяет удобно управлять дочерними и родительскими элементами на странице, располагая их в необходимом порядке. Официальная спецификация находится здесь: CSS Flexible Box Layout Module
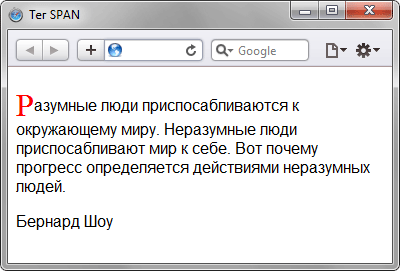
Html span display text
Бернард Шоу
Результат данного примера показан ниже.
Рис. 1. Вид текста, оформленного с помощью тега и стилей
Статьи по теме
Не выкладывайте свой код напрямую в комментариях, он отображается некорректно. Воспользуйтесь сервисом cssdeck.com или jsfiddle.net, сохраните код и в комментариях дайте на него ссылку. Так и результат сразу увидят.
Типы тегов
HTML5
Блочные элементы
Строчные элементы
Универсальные элементы
Нестандартные теги
Осуждаемые теги
Видео
Документ
Звук
Изображения
Объекты
Скрипты
Списки
Ссылки
Таблицы
Текст
Форматирование
Формы
Фреймы
HTML Tag
The HTML tag is used to define a small piece of content or text within a larger document that needs to be styled differently than the surrounding text. It is an inline element that can be used to apply styles, such as color or font, to a specific section of text.
The tag does not have any semantic meaning on its own, but it can be used in conjunction with other tags, such as or
, to give them additional styling or functionality. It is a useful tool for web designers and developers who need to make small adjustments to text without affecting the overall structure of the page.
For example, you can use the tag to highlight a specific word within a paragraph or to apply a different font size to a single character. The tag can also be used with CSS to create hover effects, animations, and other dynamic features on a web page.
The span tag is somehow similar to the div tag. But there are some differences. While the HTML tag is used to define a small piece of content or text within a larger document that needs to be styled differently than the surrounding text, the div tag is used to define a larger section or block of content that can contain other HTML elements. The div tag is a container element that is often used to group related content together and apply styling to the entire block. It is a block-level element, which means it takes up the full width of its parent container and forces a line break before and after the element.
Syntax
The tag comes in pairs. The content is written between the opening () and closing () tags.
In the example below we gave a style just inside the tag.
Example of the HTML tag:
html> html> head> title>Title of the document title> head> body> p>My cat has span style="color:#8ebf42;">green span> eyes. p> body> html>Let’s see another example where we added class attribute to the tag and gave styles to the content of the tag separately.
Example of the HTML tag with the class attribute:
html> html> head> title>Title of the document title> style> .letter < color: red; font-size: 300%; /* Font size in percents */ position: relative; /* Relative positioning */ top: 7px; /* Move from above */ > style> head> body> p> span class="letter">О span> She brought in disgusting, disturbing yellow flowers in her hands. And these flowers stood out on her black coat. p> p>Michael Bulgakov p> body> html>Attributes
Global Attributes refer to attributes that are used on any HTML element. These attributes are common for all elements in HTML.
An event occurs when a browser reacts to a particular user’s action. The user generates an event when clicking on a mouse, playing video, uploading a document or an image, or performing any other action on the website.
How to style tag?
Common properties to alter the visual weight/emphasis/size of text in tag:
- CSS font-style property sets the style of the font. normal | italic | oblique | initial | inherit.
- CSS font-family property specifies a prioritized list of one or more font family names and/or generic family names for the selected element.
- CSS font-size property sets the size of the font.
- CSS font-weight property defines whether the font should be bold or thick.
- CSS text-transform property controls text case and capitalization.
- CSS text-decoration property specifies the decoration added to text, and is a shorthand property for text-decoration-line, text-decoration-color, text-decoration-style.
Coloring text in tag:
- CSS color property describes the color of the text content and text decorations.
- CSS background-color property sets the background color of an element.
Text layout styles for tag:
- CSS text-indent property specifies the indentation of the first line in a text block.
- CSS text-overflow property specifies how overflowed content that is not displayed should be signalled to the user.
- CSS white-space property specifies how white-space inside an element is handled.
- CSS word-break property specifies where the lines should be broken.
Other properties worth looking at for tag:
- CSS text-shadow property adds shadow to text.
- CSS text-align-last property sets the alignment of the last line of the text.
- CSS line-height property specifies the height of a line.
- CSS letter-spacing property defines the spaces between letters/characters in a text.
- CSS word-spacing property sets the spacing between words.
: The Content Span element
The HTML element is a generic inline container for phrasing content, which does not inherently represent anything. It can be used to group elements for styling purposes (using the class or id attributes), or because they share attribute values, such as lang . It should be used only when no other semantic element is appropriate. is very much like a element, but is a block-level element whereas a is an inline-level element.
Try it
Attributes
This element only includes the global attributes.
Example
Example 1
HTML
Result
Example 2
HTML
li> span> a href="portfolio.html" target="_blank">See my portfolioa> span> li>
CSS
Result
Technical summary
| Content categories | Flow content, phrasing content. |
|---|---|
| Permitted content | Phrasing content. |
| Tag omission | None, both the starting and ending tag are mandatory. |
| Permitted parents | Any element that accepts phrasing content, or any element that accepts flow content. |
| Implicit ARIA role | No corresponding role |
| Permitted ARIA roles | Any |
| DOM interface | HTMLSpanElement |
Specifications
Browser compatibility
BCD tables only load in the browser
See also
Found a content problem with this page?
This page was last modified on May 10, 2023 by MDN contributors.
Your blueprint for a better internet.
MDN
Support
Our communities
Developers
Visit Mozilla Corporation’s not-for-profit parent, the Mozilla Foundation.
Portions of this content are ©1998– 2023 by individual mozilla.org contributors. Content available under a Creative Commons license.