- Static class Java Example
- 1. Example of nested classes
- 2. Download the source code
- Static class java пример
- Static Class in Java
- What is Static Class in Java?
- Syntax
- 1. Inner Class
- 2. Outer Class
- 3. Nested Class
- Example
- Why We Use Static Class in Java?
- Difference between Static and Non-static Nested Class
- Conclusion
- See More
Static class Java Example
In this example, we will discuss the purpose of a static class in Java. First of all, let’s give a short explanation of the static modifier.
For example, in Java, if a field or a method in a class has the static modifier in its declaration, then it is always associated with the class as a whole, rather than with any object of the class.
In the code below we have declared a class named Vehicle , a class field member named vehicleType and a method named getVehicleType() , both declared as static .
The static modifier allows us to access the variable vehicleType and the method getVehicleType() using the class name itself, as follows:
Something similar happens to classes that are declared static , but in order to explain this better, we must first explain the inner classes or generally, the nested classes, because ONLY nested classes can be static.
Java supports the concept of nested classes. Nested classes are classes that can be defined within the body of another class. An example of a nested class is illustrated below:
The OuterClass which contains another class can be also called top-level class.
Nested classes are further divided into two categories: static and non-static. Nested classes that are declared static are called static nested classes. Non-static nested classes are just called inner classes.
What’s the difference between nested static classes and non-static (inner) classes?
The main difference is that inner class requires the instantiation of the outer class so as to be initialized and it is always associated with an instance of the enclosing class. On the other hand, a nested static class is not associated with any instance of the enclosing class. Nested static classes are declared with the static keyword, which means than can be accessed like any other static member of class, as we shown before.
1. Example of nested classes
Create a java class named OuterClass.java with the following code:
As we can observe in the above code, we have declared a class named OuterClass which is considered to be the outer class or otherwise, the top-level class. Also, we can see that we have declared two more nested classes (they are enclosed in the outer class), one of which is static and the other one is non-static. Finally, we have declared the main method in the outer class, which is static as always (Really, why is that? The answer is that we can call it without creating an instance of a class which contains this main method). We can see that the method of the nested static class can be accessed without creating an object of the OuterClass , whereas the method of the inner class needs instantiation of the OuterClass in order to get accessed.
Method of nested static class Method of inner(non-static nested) class
2. Download the source code
This was an example of the static class in Java.
Static class java пример
В этом примере невозможно инициализировать объект List всеми начальными значениями вместе с объявлением, поэтому используется статический блок.
Код ниже демонстрирует особенность статических блоков — они выполняются раньше конструкторов и при создании нескольких объектов класса, статический блок выполняется только один раз.
public class Test < static < System.out.println("Вызов статического блока"); >Test() < System.out.println("Вызов конструктора"); >> class Main < public static void main(String[] args) < Test t1 = new Test(); Test t2 = new Test(); >> - Если для инициализации статических переменных требуется дополнительная логика, за исключением операции присваивания
- Если инициализация статических переменных подвержена ошибкам и требует обработки исключений
- У класса может быть несколько статических блоков
- Статические поля и статические блоки выполняются в том же порядке, в котором они присутствуют в классе
- Из статического блока нельзя получить доступ к не статическим членам класса
- Статический блок не может пробросить дальше перехваченные исключения, но может их выбросить. При этом всегда будет выкидываться только java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError
- Статические поля или переменные инициализируются после загрузки класса в память в том же порядке, в каком они описаны в классе
Язык программирования Java позволяет создавать классы внутри другого класса. Такой класс называется вложенным (nested). Вложенный класс группирует элементы, которые будут использоваться в одном месте, сделав тем сам код более организованным и читабельным.
- вложенные классы, объявленные статическими, называются статическими вложенными классами (static nested classes)
- вложенные классы, объявленные без static, называются внутренними классами (inner classes)
Основное различие между этими понятиями состоит в том, что внутренние классы имеют доступ ко всем членам включающего их класса (включая приватные) верхнего уровня, тогда как статические вложенные классы имеют доступ только к статическим членам внешнего класса.
Наиболее широко используемый подход для создания объектов «одиночка» (singleton) — это статический вложенный класс, поскольку он не требует никакой синхронизации, его легко изучить и реализовать:
public class Singleton < private Singleton() <>private static class SingletonHolder < private static final Singleton INSTANCE = new Singleton(); >public static Singleton getInstance() < return SingletonHolder.instance; >> - Если какой-то класс используются только в одном другом классе, то их можно сгруппировать, поместив в один общий класс. Это усиливает инкапсуляцию
- Если вложенный класс не требует какого-либо доступа к членам экземпляра его класса, то лучше объявить его как статический, потому, что таким образом он не будет связан с внешним классом и, следовательно, будет более оптимальным, поскольку ему не потребуется память в куче или в стеке
- Статические вложенные классы не имеют доступа к какому-либо члену экземпляра внешнего класса — он может получить к ним доступ только через ссылку на объект
- Статические вложенные классы могут получить доступ ко всем статическим членам внешнего класса, включая приватные
- Спецификация Java не позволяет объявлять класс верхнего уровня статическим. Только классы внутри других классов могут быть статическими
- Опять же, этот класс привязан к внешнему классу и если внешний наследуется другим классом, то этот не будет унаследован. При этом данный класс можно наследовать, как и он может наследоваться от любого другого класса и имплементировать интерфейс
- По сути статический вложенный класс ничем не отличается от любого другого внутреннего класса за исключением того, что его объект не содержит ссылку на создавший его объект внешнего класса
- Для использования статических методов/переменных/классов нам не нужно создавать объект данного класса
- Яркий пример вложенного статического класса — HashMap.Entry, который предоставляет структуру данных внутри HashMap. Стоит заметить, также как и любой другой внутренний класс, вложенные классы находятся в отдельном файле .class. Таким образом, если вы объявили пять вложенных классов в вашем главном классе, у вас будет 6 файлов с расширением .class
Говоря о ключевом слове static, нельзя не упомянуть о его применении в определении констант — переменных, которые никогда не изменяются.
В языке Java существует зарезервированное слово «const», но оно не используется, и Java не поддерживает константы на уровне языка. Выход из ситуации имеется: для определения константы необходимо добавить модификаторы «static final» к полю класса.
Константы — это статические финальные поля, содержимое которых неизменно. Это относится к примитивам, String, неизменяемым типам и неизменяемым коллекциям неизменяемых типов. Если состояние объекта может измениться, он не является константой.
Модификатор static делает переменную доступной без создания экземпляра класса, а final делает ее неизменяемой. При этом нужно помнить, что если мы сделаем переменную только static, то ее легко можно будет изменить, обратившись к ней через имя класса. Если переменная будет иметь только модификатор final, то при создании каждого экземпляра класса она может быть проинициализирована своим значением. Соответственно, используя совместно модификаторы static и final, переменная остается статической и может быть проинициализирована только один раз. В Java константой считается не та переменная, которую нельзя изменить в рамках одного объекта, а та, которую не могут изменить ни один экземпляр класса в котором она находится (такая переменная создается и инициализируется один раз для всех экземпляров, сколько бы их не было).
Static Class in Java
In Java, static is one of the most popular keywords associated with functions, variables, classes, and blocks. When any of these members are made static, we can access it without creating an instance of the class in which they are defined.
Static class in Java is a nested class and it doesn’t need the reference of the outer class. Static class can access only the static members of its outer class.
What is Static Class in Java?
We as Java programmers have come across the keyword static and it is majorly seen with the main() function in Java. But does it mean that only functions can be declared static? The answer is No. In Java, variables, blocks, methods, and classes can be declared as static .
In order to declare a member as static, we use the keyword static before the member. When we declare a certain member as static, we do not have to create an instance of the class to access it.
Syntax
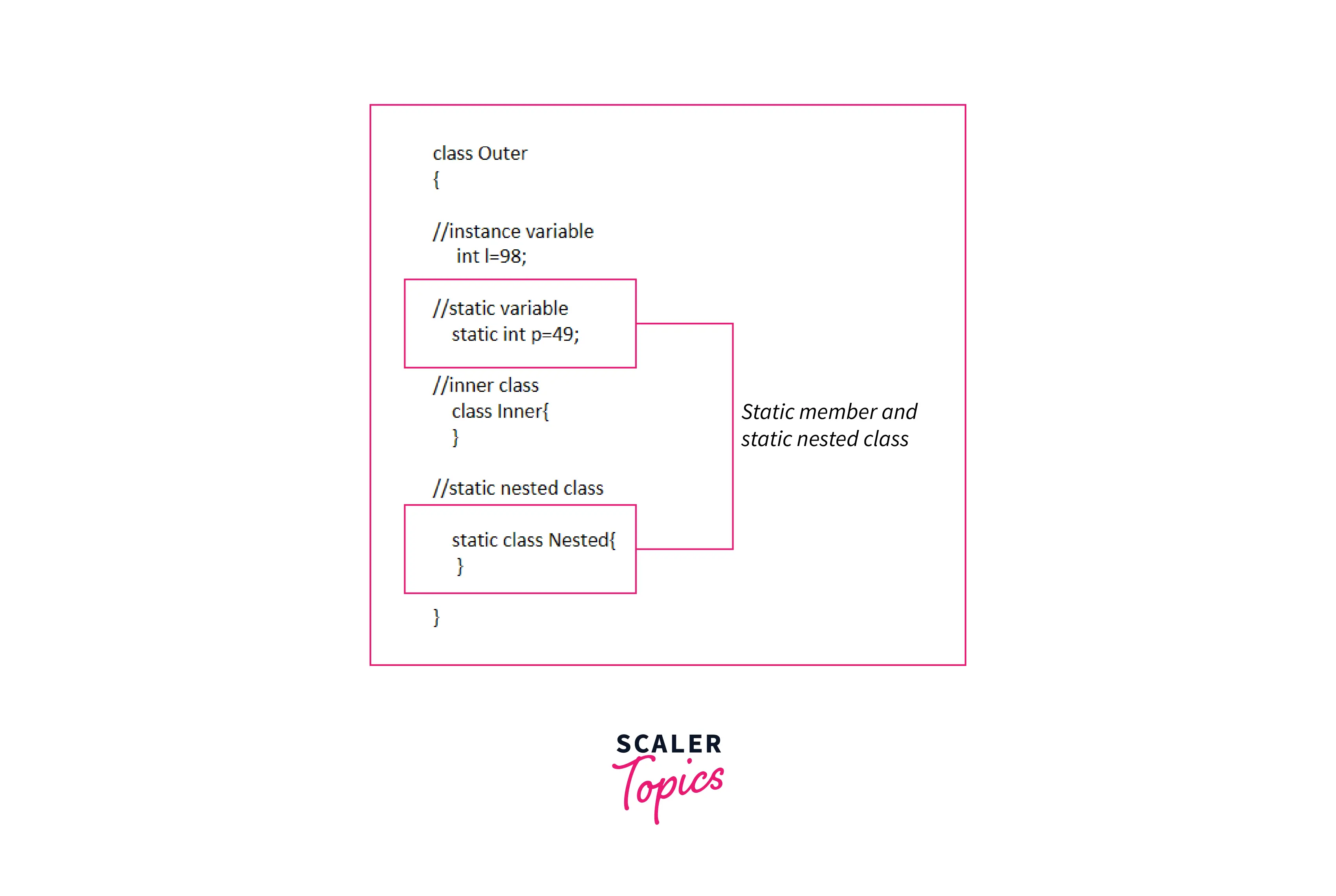
Here we have declared an Outer class and then declared a nested class.
Static classes in Java can be created only as nested classes. Let us understand the concept of inner, outer, and nested classes first.
1. Inner Class
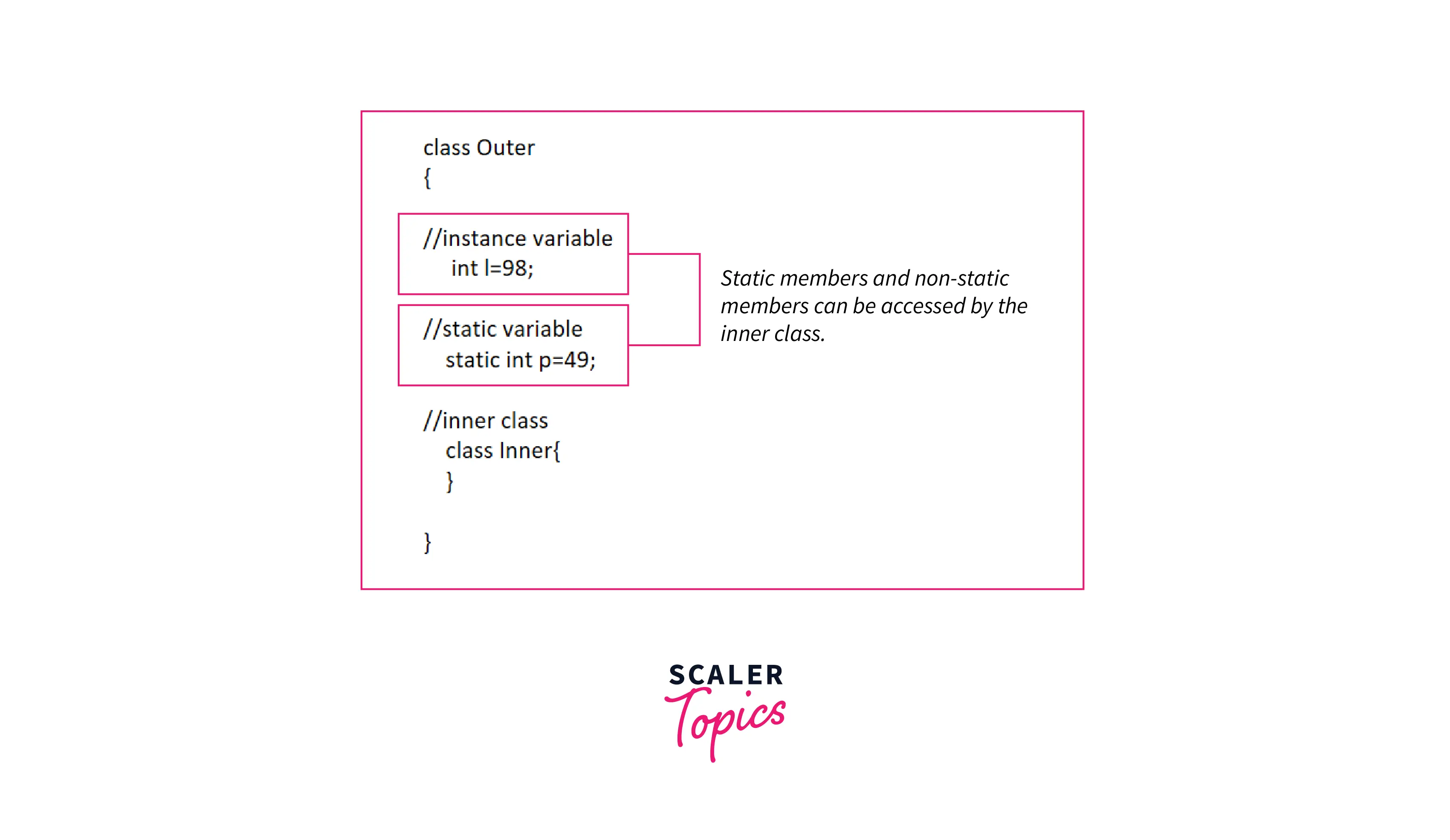
Inner classes are the classes that are non-static and nested. They are written inside an outer class. We are unable to create an instance of the inner class without creating an instance of its given outer class. This is needed when the user has to create a class but doesn’t want other classes to access it. Here we can use an inner class for that reason.
2. Outer Class
Outer classes are the classes in which nested or inner classes are defined.
3. Nested Class
Nested class can be static or non-static. The non-static nested class is known as an inner class.
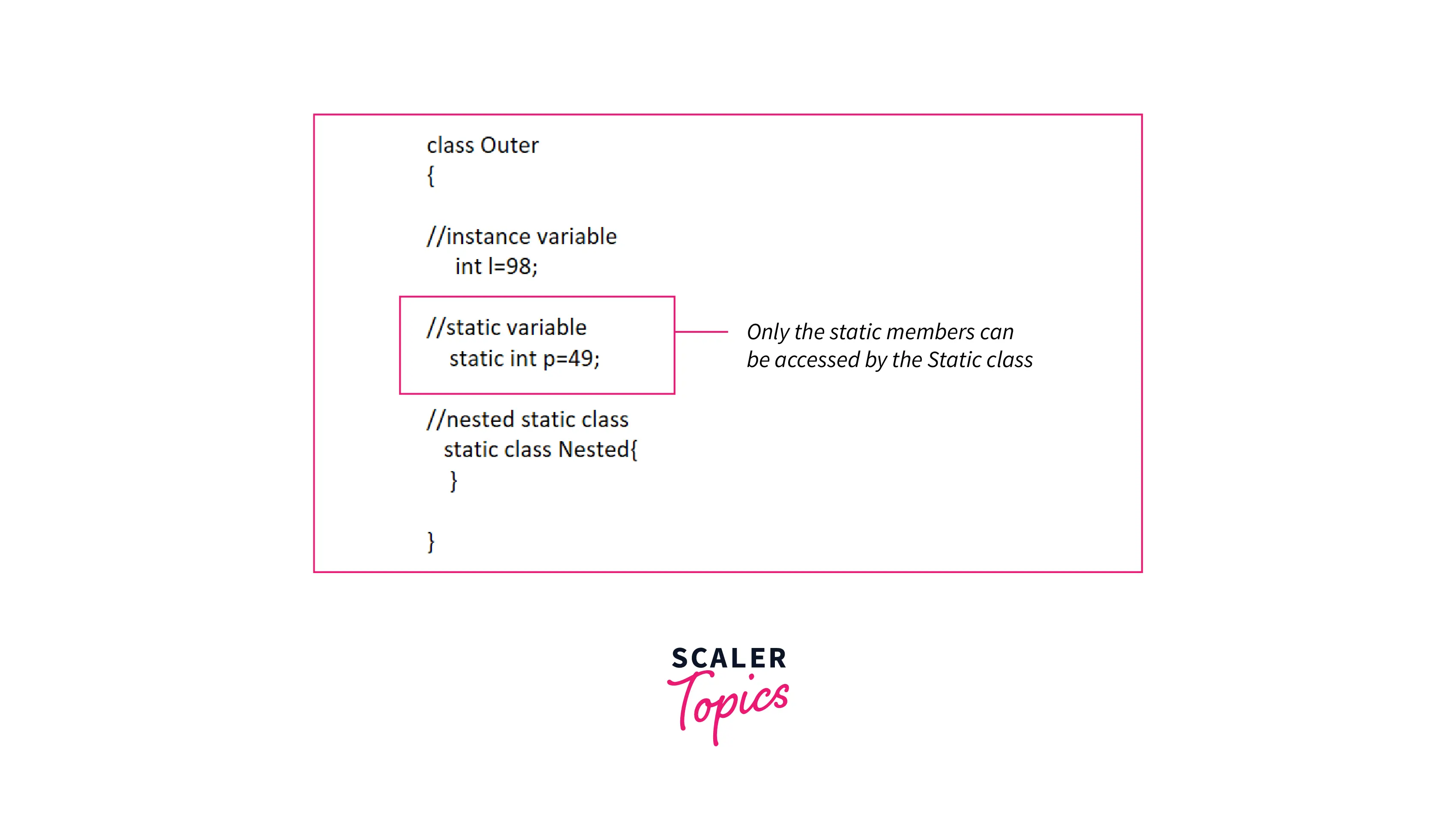
An instance of a static nested class can be created without the instance of the outer class. The static member of the outer class can be accessed only by the static nested class.
The following figure illustrates the inner, outer, and nested classes.
- The nested static class can access the static variables.
- Static nested classes do not have access to other members of the enclosing class which means it has no access to the instance variables (non-static variables) which are declared in the outer class.
Example
Explanation:
- We have declared Outer and Nested classes. In the outer class, we have created a static member which can be accessed by the static class.
- As we know, static members can be accessed by the static class only, so in the main() method, we have created an instance of the nested class without the instance of the outer class as our nested class is static.
Why We Use Static Class in Java?
In Java, the static keyword helps in efficient memory management. We can access the static members without creating an instance of a class. We can access them simply by using their class name. It is also a way of grouping classes together. Also, an instance of a static nested class can be created without the instance of the outer class.
Difference between Static and Non-static Nested Class
- Static nested class can access the static members of the outer class and not the non-static members, whereas non-static nested class, i.e., the inner class can access the static as well as the non-static members of the outer class.
- We can create an instance of the static nested class without creating an instance of the outer class.
Conclusion
- Static class in Java is a nested class and it doesn’t need the reference of the outer class.
- Static class can access only the static members of its outer class.
- Static class cannot access the non-static member of the outer classes.
- Inner classes can access the static and the non-static members of the outer class.
- We can create an instance of the static nested class without creating an instance of the outer class.
- The static keyword helps in memory management.