- Difference between static and non static nested class in Java? Example
- Difference between static and non-static nested class in Java
- What is static and non-static in Java
- What is static in Java?
- How to Create static Variables in Java?
- How to Create static Method in Java?
- What is non-static in Java?
- How to Create non-static Variables in Java?
- How to Create non-static Method in Java?
- Difference Between static and non-static Methods in Java
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Farah Batool
Difference between static and non static nested class in Java? Example
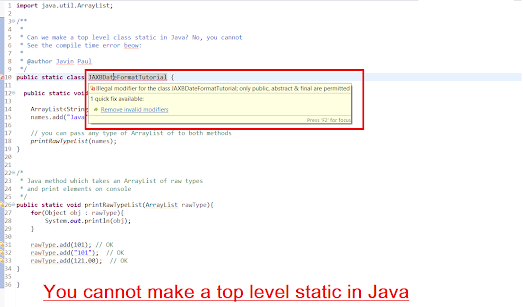
In Java, you can make a class either static or non-static. Now, what is the difference between making a class static vs. non-static? Well, there is a lot of difference between them. First of all, there are two kinds of classes in Java, one is called a top-level class, and the other is called a nested class. As the name suggested, a top-level class is a class that is declared in the .java file and not enclosed under any other class. On the other hand, a nested class is declared inside another class. The class which enclosed nested class is known as Outer class.
Now let’s come back to static vs. non-static class. In the Java programming language, you can not make a top-level class static. You can only make nested classes, either static or non-static.
If you make a nested class non-static, then it is also referred to as Inner class. Now let’s come to the point regarding the Difference between static and non-static nested classes in Java
Difference between static and non-static nested class in Java
1. Nested static class doesn’t need reference of Outer class but a non-static nested class or Inner class requires Outer class reference. You can not create an instance of the Inner class without creating an instance of the Outer class. This is by far the most important thing to consider while making a nested class static or non-static. You can also see these free Java courses to learn more about essential Java concepts like static and non-static members, variables, and classes
2. static class is actually a static member of the class and can be used in the static context, like a static method or a static block of Outer class.
3. Another difference between static and non-static nested classes is that you can not access non-static members, like method and field, into the nested static class directly. If you do, you will get errors like «non-static member can not be used in the static context.» While the Inner class can access both static and nonstatic members of the Outer class.
/**
* Java program to demonstrate What is nested static and non-static class.
* How to create instances of the static and non-static classes and How to call
* methods of nested static and Inner class in Java. Overall comparison of
* static vs. non-static class.
*/
class Outer <
private static String message = «HelloWorld» ;
// Static nested class
private static class MessagePrinter <
//Only static member of Outer class is directly accessible in a nested static class
// Compile time error if message field is not static
System. out . println ( «Message from nested static class : » + message ) ;
>
>
//non-static nested class — also called Inner class
private class Inner
// Both static and non-static member of Outer class is accessible in this Inner class
public void display () <
System. out . println ( » Message from non static nested or Inner class : » + message ) ;
>
>
// How to create instances of static and non-static nested class
public static void main ( String. args )
// creating instance of nested Static class
Outer. MessagePrinter printer = new Outer. MessagePrinter () ;
//calling non static method of nested static class
printer. printMessage () ;
// creating instance of a non static nested class or Inner class
// In order to create an instance of Inner class, you need an Outer class instance
Outer outer = new Outer () ; //outer class instance for creating non static nested class
Outer. Inner inner = outer. new Inner () ;
//calling non static method of Inner class
inner. display () ;
// we can also combine the above steps in one step to create an instance of Inner class
Outer. Inner nonStaticIner = new Outer () . new Inner () ;
// similarly you can now call Inner class method
nonStaticIner. display () ;
>
Output:
Message from nested static class : HelloWorld
Message from non-static nested or Inner class : HelloWorld
Message from non-static nested or Inner class : HelloWorld
That’s all on the difference between the Static and non Static nested class in Java. So far, we have only touched members Inner class and not discussed the other two types of Inner class, like Local and Anonymous Inner classes. In this Java tutorial, we have seen What is nested static class is in Java and How to create instances of both nested static and non-static classes in Java.
In summary, it’s easy to create instances of the nested static class as it doesn’t require instances of Outer class while non-static nested class, e.g., Inner class, will always need an Outer class instance and can not exist without Outer class. If you have to choose between static vs. non-static class, then prefer static nested class if you can use that.
What is static and non-static in Java
Java primarily uses the “static” keyword for memory management. Variables, blocks, and methods all can be used with the static keyword. Instead of a particular class instance, the static keyword refers to the class as a whole. Without the static keyword, in Java, the methods and variables are by default considered “non-static”.
This article will explain the static and non-static in Java.
What is static in Java?
The “static” is a keyword in Java utilized for memory management of the variables and methods that belong to a class. In Java, there are static variables and static methods in the classes, which will be discussed in the below sections.
How to Create static Variables in Java?
The static variables are class variables and can be created at the class level. When a variable is declared as “static”, the compiler creates a copy of the variable and shares it with all objects of the class. On the other hand, static variables effectively function as global variables. It can be retrieved by the class name alone and does not need to be used with an object. It saves memory and enhances the software’s memory efficiency.
For creating the static variable in a class, use the below syntax:
Here, “x” is the static variable that stores the integer type value “10”.
Let’s discuss what a static method in Java is and how to create it.
How to Create static Method in Java?
A static class method can be accessed without the creation of an object or instance of a defined class. It can retrieve only static data members and methods of the same class or another class; they cannot access non-static methods or variables.
Additionally, any static data member’s values can be changed by a static method.
Follow the given syntax for creating a static method in Java:
The syntax below indicates how to call the static method:
Note: For calling the static method, we will use the class name. We do not need the class object for calling the method because the static keyword fixes a specific memory location for that method in RAM, and the memory allocation only occurs once in the static method.
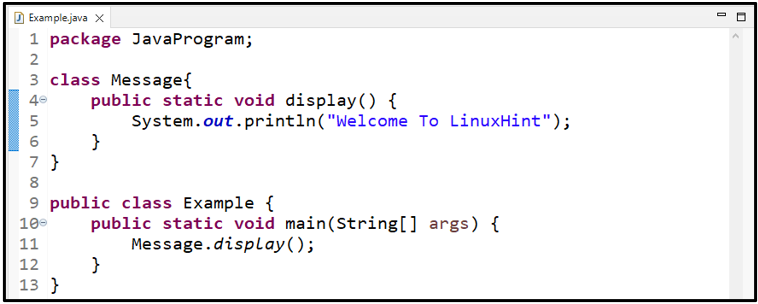
We will create a static method named “display()” in the “Message” class and invoke it in another class:
Here, in the main() method of another class named “Example”, we will call the static method display() without creating an instance or object of the “Message” class:
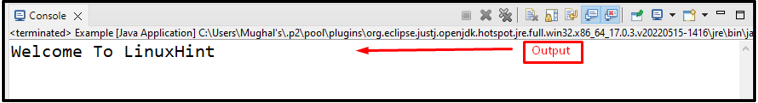
The output shows that we have successfully accessed the static method of the class in another class:
Let’s move to non-static in Java.
What is non-static in Java?
Every method and variable in Java without the “static” keyword is “non-static”, and it can access all static methods and variables. The non-static keyword use runtime binding, also known as dynamic binding.
How to Create non-static Variables in Java?
A “non-static” variable is a class variable that is not static. The non-static variables are also called local variables. It is defined inside a method, constructor, or block. The scope of these variables is restricted. That’s why we can only access these variables within the defined block.
Use the given syntax for creating a non-static variable in Java:
Here, “x” is the local variable called a non-static variable that stores the integer type value “10”.
Let’s see what a non-static method is in Java and what is the process of creation.
How to Create non-static Method in Java?
Java permits you to override the non-static method. This type of method is created using the keyword “non-static”. In non-static methods, dynamic and runtime binding is utilized. As a result, we cannot call it without the class’s instance. In this case, memory is allocated whenever the method is called in the non-static method, and it happens each time.
Follow the given syntax for the non-static method:
To invoke the non-static method in Java, we will first need to create an object of the class and then call it.
Let’s move to the example to see how to access a non-static method in Java.
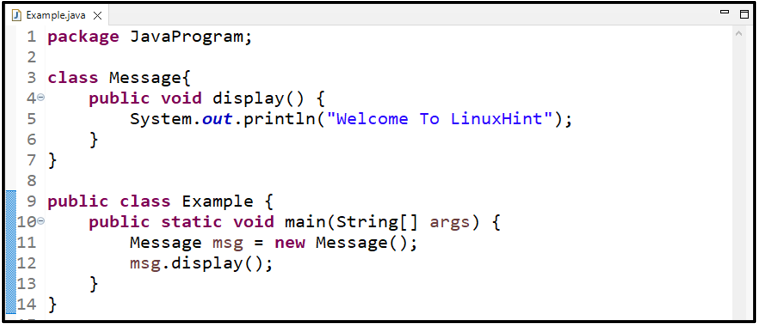
Here, we will access the non-static method of a class in another class by creating an object of the class. To do so, first, we will create a non-static method named “display()” that will print the statement using the “System.out.println()” method in a “Message” class:
Now, we will create an object “msg” of the Message class in the main() method of the other class named “Example”, then, we will call the non-static display() method with it, because the non-static methods are not accessed without the object of the class:
public class Example {
public static void main ( String [ ] args ) {
Message msg = new Message ( ) ;
msg.display ( ) ;
}
}
Output
Let’s move towards the key difference points between a static method and non-static method in Java.
Difference Between static and non-static Methods in Java
static Method
non-static Method
We have included all of the guidance for Java’s static and non-static variables and methods.
Conclusion
In Java, the variables and methods are non-static by default, but the main() method is static. For managing memory, you can utilize the static keyword. The static methods can be made accessible without creating a class object, in contrast to the non-static methods, which cannot be accessed without creating an object. In this article, we explained the static and non-static variables and methods with detailed explanations and examples.
About the author
Farah Batool
I completed my master’s degree in computer science. I am an academic researcher and love to learn and write about new technologies. I am passionate about writing and sharing my experience with the world.