- Get started with functions in JavaScript
- Function Definition
- Various ways of defining a function
- Calling the function
- Argument and Parameter
- Function In JavaScript
- What is a function?
- Javascript Function Declaration
- Syntax
- Example
- Javascript function call
- How to call a function in javascript?
- Call Javascript Function From HTML
- Javascript function parameter
- Javascript Function Return
- Javascript Function Local Variable
- Javascript Function Expression
- Javascript Function Declaration VS Expression
- Javascript Immediately Invoked Function Expression(IIFE)
- Syntax of IIFE
- Frequently Asked Questions
Get started with functions in JavaScript
Functions are one of the fundamental building blocks in JavaScript. A function in JavaScript is similar to a procedure — a set of statements that performs a task or calculates a value, but for a procedure to qualify as a function, it should take some input and return an output where there is some obvious relationship between the input and the output. To use a function, you must define it somewhere in the scope from which you wish to call it.
Function Definition
- The name of the function.
- A list of parameters to the function, enclosed in parentheses and separated by commas.
- The JavaScript statements that define the function, enclosed in curly brackets, .
For example, the following code defines a simple function named square:
function square(number) return number * number; > The function square takes one parameter, called number. The function consists of one statement that says to return the parameter of the function (that is, number) multiplied by itself. The statement return specifies the value returned by the function: return number * number;
Various ways of defining a function
function square(number) return number * number; > const square = function() return number * number; > const square = () => return number * number; > The above definition can further be shortened to:
const square = () => number * number; Since this function contains only 1 line of code, we may safely omit the < >as well as the return keyword.
You can use any of the above mentioned ways to define a function named «square«.
Calling the function
Defining a function does not execute it. That’s not fair, I have written so much code for nothing to be executed! Let’s get into the magical way by which a function is called and the function defined above gets executed.
Defining a function would name the function and specify what to do when the function is called. It prepares javascript understand what logic or code is to be run when this function is called.
Calling the function actually performs the specified actions with the indicated parameters. For example, if you define the function square, you could call it as follows:
The above statement would call the function with an argument of value 5. The function executes its statements and returns the value 25.
However, this would still not display the returned value of 25 anywhere. In order to display this value, we can use console.log().
let result = square(5); console.log(result); //25 or directly pass the function call within console.log()
By this, we understand that console.log() is also a function which can take different types of arguments. However, this is a special function since it has a ‘.’ dot parameter in between console and log.
Argument and Parameter
An argument is a value (primitive or object) passed as input to a function.
A parameter is a named variable passed into a function. Parameter variables are used to import arguments into functions.
Let’s simplify this using the above function’s example. Within the function definition, we observed the variable named number which was used within the square function. The value — number, is called as the parameter accepted by sqaure().
Similary, during the function call, we passed the value of 5 to the function as square(5); . Here, the value 5 is referred as the argument passed to square().
I hope this article was helpful in understanding the basics of functions in JavaScript.
Function In JavaScript
In this tutorial, you will learn about javascript functions, how to define them, how to use them, why to use them, etc with various examples.
What is a function?
A function is a named sequence of statements that performs a specific operation. Functions are used to break down a program into smaller, reusable pieces.
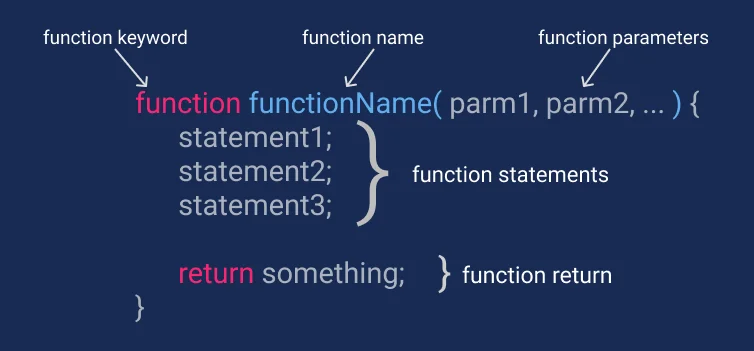
function name(param1, param2, . ) < // statements >In javascript, a function is defined using the keyword function and is immediately followed by the function name and a pair of parenthesis.
Inside the parenthesis, you can define any number of arguments that are passed to the function when it is called.
The function can return a value by using the return statement, or it can end the function by using the return keyword.
The basic idea of a function is to reduce the number of repeated code blocks and executing a code block whenever needed.
function add(a, b) < let sum = a + b; // statement return sum; // return >console.log(add(1, 2));Javascript Function Declaration
A function declaration is a way to declare a function in javascript. It is a way to tell javascript that you want to create a function and to give it a name.
To use a function you must first declare it. In javascript, the function is declared by using the function keyword.
Syntax
function name_of_function (param1, param2. ) < // javascript statements return something; >Here are the steps to declare a function in javascript.
- Start function with the function keyword
- Then write the name of the function with a space. The naming convention of function is the same as a variable naming convention.
- Then give arguments to the function enclosed in parentheses and separated by commas like (parameter1, parameter2, . )
- Then define the function body by curly braces
- At the end of the function use return keyword to return any object or value.
Example
// Function declaration function hello()
Javascript function call
Just defining a function does nothing until it is invoked or called.
How to call a function in javascript?
To call a function, you need to use the function name followed by a parenthesis and the arguments that you want to pass to the function.
If there is no parameter then write blank parenthesis.
// Function declaration function hello() < console.log("Hello World!"); >// Function call hello();// Function declaration function hello(name) < console.log(`Hello $!`); > // Function call hello("John");Call Javascript Function From HTML
You can call a javascript function from HTML using events.
When an event occurs like button click, mouse move, document load, etc then you can use some event handler to trigger the event which will call the function.
Use some event to call a function from HTML.
function message() Note : You can call a function from any event we want and as many times.
Javascript function parameter
Javascript function parameters are the values that are passed in the function to be used inside its statements.
The actual values that are passed in the function are known as arguments while the variable that is declared in the function is known as a parameter.
The data type of javascript function parameter could be any valid data type, for example, string, number, array, etc.
function message(user, message) < console.log("User: " + user + " , Message: " + message); >message("Herry", "How are you?"); message("John", "I'm fine.");What happens when you provide more or fewer parameters to the function than the defined arguments?
- When a number of arguments are less than parameters then the rest parameters will be undefined
- when the number of arguments are more than parameters then extra arguments will be ignored
Let’s see an example to understand.
function fullName(firstname, lastname) < console.log(firstname + " " + lastname); >fullName("Stephen", "Hawking"); // Stephen Hawking fullName("Stephen", "William", "Hawking"); // Stephen William fullName("Stephen"); // Stephen undefinedJavascript Function Return
Javascript function can return values to the caller. The return value is known as return value.
To return something from the function return keyword is used with the return value separated by space.
The function stops execution when reached to return statement even if there are more statements in the function after a return.
The return value can be stored in a variable.
function multiply(a, b) < return a * b; >// storing return value in a variable var value = multiply(4, 6); console.log(value);The return value can be placed anywhere in the function but as soon as the function finds a return statement it stops further execution of the code in a function.
Also, you can use a return statement without returning any value just to stop the execution of the function.
function pass(mark) < if (!mark) < console.log("Invalid Marks!"); return; >if (mark > 40) < console.log("Pass!"); return true; >else < console.log("Fail!"); return false; >> pass(60);Javascript Function Local Variable
The variables that are defined inside the function have local scope. This means these variables can’t be accessed outside the function.
But a function can access the variable that is defined outside the function.
function localVariable() < // local scope let a = 10; console.log("'a' inside function is " + a); >localVariable(); console.log("'a' outside function is " + typeof a);Javascript Function Expression
Function expression lets us define the function and assign it to some variable.
A function expression, in general, has no name hence it is also called an anonymous function.
A function expression is more convenient to pass as an argument in callback functions.
var sum = function (num1, num2) < return num1 + num2; >// function called using variable name console.log(sum(12, 32));Javascript Function Declaration VS Expression
These are 2 important differences between function declaration and function expression:
- A function declaration can be hoisted but a function expression can’t be hoisted. It means you can use a function before it is declared while you can’t use a function before function expression is declared.
hello(); // run successfully function hello() < // function declaration return "Hello World!"; >hello(); // error function not declared let hello = function() < // function expression return "Hello World!"; >Javascript Immediately Invoked Function Expression(IIFE)
immediately Invoked Function Expression (IIFE) is the function is executed right after the function is declared.
Syntax of IIFE
The variables defined inside IIFE is not accessible outside the function.
If you assign IIFE to some variable then it stored the function’s return value, not the function itself.
var example = (function()< return "Returned value is stored." >)(); console.log(example);Frequently Asked Questions
- What is function and method in JavaScript? A function is a block of code that is used to perform a specific task. A method is a function that is associated with a specific object. A method can also be an instance function, which means that it is associated with an object and can be called directly on that object.
- Function in javascript is declared using the function keyword.
- A function can have any number of arguments starting from 0.
- You can call the javascript function from HTML using some event.
- As soon as the function reaches the return statement it stops further execution of it.
- Variable defined in a function has local scope and can’t be accessed outside the function.