Python sqlite3 – Create Table
You can create one or more tables in sqlite3 database.
In this tutorial, we will learn how to create a table in sqlite3 database programmatically in Python.
Steps to Create Table in sqlite3 Database
To create a table using Python sqlite3, follow these steps
- Create a connection object to the sqlite database.
- Create a cursor to the connection.
- Create table using the sqlite3.execute() method with the CREATE query passed to the method.
Examples
1. Create database table with sqlite3
In this example, we will create a sqlite3 database named mysqlite.db and create a table named students inside the database.
Python Program
import sqlite3 conn = sqlite3.connect('mysqlite.db') c = conn.cursor() #create table c.execute('''CREATE TABLE students (rollno real, name text, class real)''') #commit the changes to db conn.commit() #close the connection conn.close()When you run this program, a table students should be created successfully inside mysqlite.db.
If you run this program the second time, you would get the following error.
Traceback (most recent call last): File "example.py", line 8, in (rollno real, name text, class real)''') sqlite3.OperationalError: table students already existsIf you would like to not mind if the table already exists or not, you can refer the following example, where we will create the table only if it does not exist.
2. Create table only if it does not exist
In the Query, we can define to create the table only if it does not exist already. You may use IF NOT EXISTS before the table name in the query to create the table only if it does not exist.
In this example, we will try creating a sqlite3 database named mysqlite.db and create a table named students (which is already created in the previous example) inside the database.
Python Program
import sqlite3 conn = sqlite3.connect('mysqlite.db') c = conn.cursor() # Create table c.execute('''CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS students (rollno real, name text, class real)''') #commit the changes to db conn.commit() #close the connection conn.close()Summary
In this tutorial of Python Examples, we learned how to create a table in sqlite3 database. Also, we have seen the scenario of creating a table only when it does not exist in the database.
SQLite Python: Creating Tables
Summary: in this tutorial, we will show you how to create tables in the SQLite database from the Python program using the sqlite3 module.
To create a new table in an SQLite database from a Python program, you use the following steps:
- First, create a Connection object using the connect() function of the sqlite3 module.
- Second, create a Cursor object by calling the cursor() method of the Connection object.
- Third, pass the CREATE TABLE statement to the execute() method of the Cursor object and execute this method.
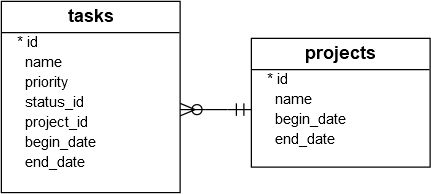
For the demonstration, we will create two tables: projects and tasks as shown in the following database diagram:
The following CREATE TABLE statements create these two tables:
-- projects table CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS projects ( id integer PRIMARY KEY, name text NOT NULL, begin_date text, end_date text ); -- tasks table CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS tasks ( id integer PRIMARY KEY, name text NOT NULL, priority integer, project_id integer NOT NULL, status_id integer NOT NULL, begin_date text NOT NULL, end_date text NOT NULL, FOREIGN KEY (project_id) REFERENCES projects (id) );Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Let’s see how to create new tables in Python.
First, develop a function called create_connection() that returns a Connection object which represents an SQLite database specified by the database file parameter db_file.
def create_connection(db_file): """ create a database connection to the SQLite database specified by db_file :param db_file: database file :return: Connection object or None """ conn = None try: conn = sqlite3.connect(db_file) return conn except Error as e: print(e) return connCode language: Python (python)Second, develop a function named create_table() that accepts a Connection object and an SQL statement. Inside the function, we call the execute() method of the Cursor object to execute the CREATE TABLE statement.
def create_table(conn, create_table_sql): """ create a table from the create_table_sql statement :param conn: Connection object :param create_table_sql: a CREATE TABLE statement :return: """ try: c = conn.cursor() c.execute(create_table_sql) except Error as e: print(e)Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Third, create a main() function to create the projects and tasks tables.
def main(): database = r"C:\sqlite\db\pythonsqlite.db" sql_create_projects_table = """ CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS projects ( id integer PRIMARY KEY, name text NOT NULL, begin_date text, end_date text ); """ sql_create_tasks_table = """CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS tasks ( id integer PRIMARY KEY, name text NOT NULL, priority integer, status_id integer NOT NULL, project_id integer NOT NULL, begin_date text NOT NULL, end_date text NOT NULL, FOREIGN KEY (project_id) REFERENCES projects (id) );""" # create a database connection conn = create_connection(database) # create tables if conn is not None: # create projects table create_table(conn, sql_create_projects_table) # create tasks table create_table(conn, sql_create_tasks_table) else: print("Error! cannot create the database connection.") Code language: Python (python)Fourth, execute the main() function.
if __name__ == '__main__': main()Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)import sqlite3 from sqlite3 import Error def create_connection(db_file): """ create a database connection to the SQLite database specified by db_file :param db_file: database file :return: Connection object or None """ conn = None try: conn = sqlite3.connect(db_file) return conn except Error as e: print(e) return conn def create_table(conn, create_table_sql): """ create a table from the create_table_sql statement :param conn: Connection object :param create_table_sql: a CREATE TABLE statement :return: """ try: c = conn.cursor() c.execute(create_table_sql) except Error as e: print(e) def main(): database = r"C:\sqlite\db\pythonsqlite.db" sql_create_projects_table = """ CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS projects ( id integer PRIMARY KEY, name text NOT NULL, begin_date text, end_date text ); """ sql_create_tasks_table = """CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS tasks ( id integer PRIMARY KEY, name text NOT NULL, priority integer, status_id integer NOT NULL, project_id integer NOT NULL, begin_date text NOT NULL, end_date text NOT NULL, FOREIGN KEY (project_id) REFERENCES projects (id) );""" # create a database connection conn = create_connection(database) # create tables if conn is not None: # create projects table create_table(conn, sql_create_projects_table) # create tasks table create_table(conn, sql_create_tasks_table) else: print("Error! cannot create the database connection.") if __name__ == '__main__': main()Code language: Python (python)Let’s verify if the program has created those tables successfully in the pythonsqlite.db database.
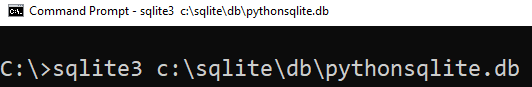
First, launch the command line and connect to the pythonsqlite.db database:
>sqlite3 c:\sqlite\db\pythonsqlite.db
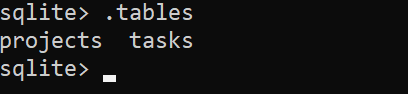
Then, use the .tables command to display the tables in the database.
sqlite> .tables projects tasksCode language: CSS (css)As you can see clearly from the output, we are having the projects and tasks tables in the pythonsqlite.db database. And the program works as expected.
In this tutorial, you have learned how to create new tables in the SQLite database using the execute() method of the Cursor object.