- Python SQLite BLOB to Insert and Retrieve file and images
- Table of contents
- Prerequisites
- What is BLOB
- Insert Image and File as a BLOB data into SQLite Table
- Retrieve Image and File stored as a BLOB from SQLite Table
- Next Steps:
- About Vishal
- Related Tutorial Topics:
- Python Exercises and Quizzes
- SQLite Blob Data
- Creating ( or displaying ) Blob data from table
- Displaying output image in Python console
- Updating Blob Data
- Deleting Blob Data
- Managing SQLite Blob data using Tkinter
Python SQLite BLOB to Insert and Retrieve file and images
In this article, you will learn to insert and retrieve a file stored as a BLOB in the SQLite table using Python’s sqlite3 module.
- Use SQLite BLOB data type to store any binary data into the SQLite table using Python. Binary can be a file, image, video, or a media
- Read BLOB data from the SQLite table in Python.
Table of contents
Prerequisites
Before executing the following SQLite BLOB operations, please make sure you know the SQLite table name and in which you want to store BLOB data.
To Store BLOB data in the SQLite table, we need to create a table that can hold binary data, or you can also modify any existing table and add one extra column with BLOB as its data type.
Please refer to creating an SQLite table from Python. For this lesson, I am using the ‘new_employee’ table present in my SQLite database.
You can use the following query to create a table with a BLOB column.
CREATE TABLE new_employee ( id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY, name TEXT NOT NULL, photo BLOB NOT NULL, resume BLOB NOT NULL);The table contains two BLOB columns.
- A photo column contains an employee picture.
- A resume column includes a file which is a developer resume.
Before proceeding to the examples first understand what is BLOB.
What is BLOB
A BLOB (large binary object) is an SQLite data type that stores large objects, typically large files such as images, music, videos, documents, pdf, etc.
We need to convert our files and images into binary data (byte array in Python) to store it into SQLite database.
Insert Image and File as a BLOB data into SQLite Table
As of now, a table is empty. Let’s insert employee’s photos and resume files in it.
To insert BLOB data into SQLite table from Python, you need to follow the below steps: –
- First, establish the SQLite connection from Python.
- Second, create a cursor object using the connection object.
- Then, define the SQLite INSERT Query. You need to know the table and the column name in which you want to insert data.
- Next, create a function to convert digital data, i.e., images or any file, to binary data
- Execute the INSERT query in Python using the cursor.execute() .
- After the successful execution of the SQLite insert operation, commit your changes to the database.
- Close the Cursor and SQLite database connection.
- Most important, Catch SQL exceptions, if any.
import sqlite3 def convertToBinaryData(filename): # Convert digital data to binary format with open(filename, 'rb') as file: blobData = file.read() return blobData def insertBLOB(empId, name, photo, resumeFile): try: sqliteConnection = sqlite3.connect('SQLite_Python.db') cursor = sqliteConnection.cursor() print("Connected to SQLite") sqlite_insert_blob_query = """ INSERT INTO new_employee (id, name, photo, resume) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?)""" empPhoto = convertToBinaryData(photo) resume = convertToBinaryData(resumeFile) # Convert data into tuple format data_tuple = (empId, name, empPhoto, resume) cursor.execute(sqlite_insert_blob_query, data_tuple) sqliteConnection.commit() print("Image and file inserted successfully as a BLOB into a table") cursor.close() except sqlite3.Error as error: print("Failed to insert blob data into sqlite table", error) finally: if sqliteConnection: sqliteConnection.close() print("the sqlite connection is closed") insertBLOB(1, "Smith", "E:\pynative\Python\photos\smith.jpg", "E:\pynative\Python\photos\smith_resume.txt") insertBLOB(2, "David", "E:\pynative\Python\photos\david.jpg", "E:\pynative\Python\photos\david_resume.txt") Connected to SQLite Image and file inserted successfully as a BLOB into a table the sqlite connection is closed Connected to SQLite Image and file inserted successfully as a BLOB into a table the sqlite connection is closed
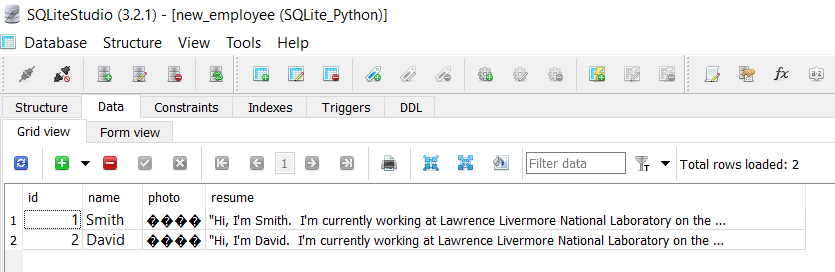
Let’s have a look at the new_developer table after inserting the image and file into it.
We inserted the employee id, name, photo, and resume file into the table. For the image and resume, we passed the location where it is present so our program can read and convert those files into binary data.
As you can see, we converted our image and file into a binary format by reading the image and data in rb mode before inserting it into a BLOB column.
Also, we used a parameterized query to insert dynamic data into an SQLite table.
Retrieve Image and File stored as a BLOB from SQLite Table
Assume you want to read the file or images stored in the SQLite table in BLOB format and write that file back to some location on the disk so you can view and read it in a proper format.
In this example, we are reading the employee photo and resume file that we stored in the SQLite table stored as a BLOB in the previous example.
To read BLOB data from SQLite Table using Python, you need to follow the below steps: –
- Establish the SQLite database connection in Python.
- Second, Define the SELECT query to fetch BLOB columns from the table.
- Execute the SELECT query in Python using a cursor.execute()
- Use the cursor.fetchall() to retrieve all the rows from the result set and iterate over it.
- Create a function to convert BLOB data in proper format and save it in a readable format.
- Close the Cursor and MySQL database connection.
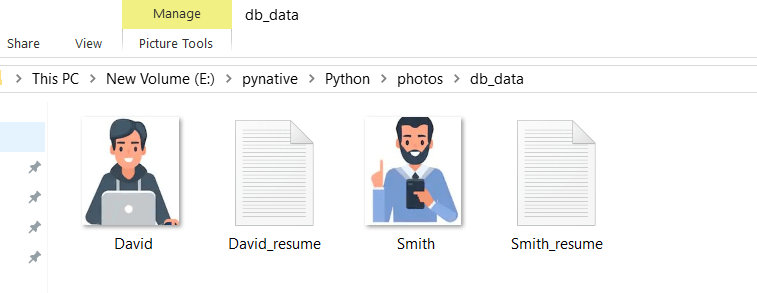
import sqlite3 def writeTofile(data, filename): # Convert binary data to proper format and write it on Hard Disk with open(filename, 'wb') as file: file.write(data) print("Stored blob data into: ", filename, "\n") def readBlobData(empId): try: sqliteConnection = sqlite3.connect('SQLite_Python.db') cursor = sqliteConnection.cursor() print("Connected to SQLite") sql_fetch_blob_query = """SELECT * from new_employee where cursor.execute(sql_fetch_blob_query, (empId,)) record = cursor.fetchall() for row in record: print("Id = ", row[0], "Name = ", row[1]) name = row[1] photo = row[2] resumeFile = row[3] print("Storing employee image and resume on disk \n") photoPath = "E:\pynative\Python\photos\db_data\\" + name + ".jpg" resumePath = "E:\pynative\Python\photos\db_data\\" + name + "_resume.txt" writeTofile(photo, photoPath) writeTofile(resumeFile, resumePath) cursor.close() except sqlite3.Error as error: print("Failed to read blob data from sqlite table", error) finally: if sqliteConnection: sqliteConnection.close() print("sqlite connection is closed") readBlobData(1) readBlobData(2) As you can see images and files are stored on disk after reading BLOB data from SQLite.
Note: To copy binary data on the hard drive, we converted binary data(BLOB) to the proper format and wrote it on Hard Disk. In our example, we converted the photo blob column into png and resume blob column data into txt file.
Next Steps:
To practice what you learned in this article, Please solve a Python Database Exercise project to Practice and master the Python Database operations.
Did you find this page helpful? Let others know about it. Sharing helps me continue to create free Python resources.
About Vishal
I’m Vishal Hule, Founder of PYnative.com. I am a Python developer, and I love to write articles to help students, developers, and learners. Follow me on Twitter
Related Tutorial Topics:
Python Exercises and Quizzes
Free coding exercises and quizzes cover Python basics, data structure, data analytics, and more.
- 15+ Topic-specific Exercises and Quizzes
- Each Exercise contains 10 questions
- Each Quiz contains 12-15 MCQ
SQLite Blob Data
Along with other data we are storing binary data in our student table. We used try except error handling to display error messages.
from sqlalchemy import create_engine from sqlalchemy.exc import SQLAlchemyError my_conn = create_engine("sqlite:///D:\\testing\\my_db\\my_db.db") fob=open('G:\\My Drive\\testing\\my_db\\sqlite-blob1.jpg','rb') #file object blob_data=fob.read() # Binary data is ready my_data=[(None, 'Tes Qry', 'Six', 78, 'male',blob_data)] # Data to store q="INSERT INTO student values(. )" # query with place holders try: r_set=my_conn.execute(q,my_data) except SQLAlchemyError as e: error=str(e.__dict__['orig']) print(error) else: print("Number of records added : ",r_set.rowcount)Creating ( or displaying ) Blob data from table
By using fetchone() we collected one row of data from the table.
In last two lines we created the file object and stored the binary data from the student table inside the given path.
from sqlalchemy import create_engine from sqlalchemy.exc import SQLAlchemyError my_conn = create_engine("sqlite:///D:\\testing\\my_db\\my_db.db") q='''SELECT * FROM student WHERE Drive\\testing\\my_db\\sqlite-blob2.jpg','wb') fob.write(data_row[5]) # create the image using above pathWhile storing ( inserting to table ) the image in SQLite database we used file name sqlite-blob1.jpg. At the same location another file sqlite-blob2.jpg will be created to store the same. Change the file location if it is required to store the data in different location.
Displaying output image in Python console
After retrieving the binary data ( Blob column data ) we can display the same by using io ( Core tools for working with streams) and PIL ( Python Image Library ).
from PIL import Image import io image = Image.open(io.BytesIO(data_row[5])) image.show()Using matplotlib we can display the image in Google Colab console.
Our binary data is available in r_set[5]
image = Image.open(io.BytesIO(r_set[5])) import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.imshow(image) plt.show()Updating Blob Data
By using another image file sqltie-blob3.jpg we will create the file object and update the same in table using the update query.
from sqlalchemy import create_engine from sqlalchemy.exc import SQLAlchemyError my_conn = create_engine("sqlite:///D:\\testing\\my_db\\my_db.db") fob=open('G:\\My Drive\\testing\\my_db\\sqlite-blob3.jpg','rb') blob_data=fob.read() my_data=(blob_data,37) # tuple to pass values to execute method q="UPDATE student SET photo=? WHERE " try: r_set=my_conn.execute(q,my_data) except SQLAlchemyError as e: error=str(e.__dict__['orig']) print(error) else: print("Number of records Updated : ",r_set.rowcount)Deleting Blob Data
We can delete the row containing the Blob data.
We can only remove the Blob column data by updating to empty string without removing the row.
Full code from above ( Updating Blob data ) can be used with this.
my_data=(37) # tuple to pass values to execute method q my_data=(37) # tuple to pass values to execute method q="UPDATE student set photo=NULL WHERE "Managing SQLite Blob data using Tkinter
Tkinter window provides user interface to upload or display the images. We can use filedialog() to browse local file system and select the file to store inside SQLite database. Similarly the user selected row can be collected from the database and image can be displayed inside the Tkinter window.
Tkinter to Manage Blob data »