- Present SQL injection in Python (CWE-89)
- What is a SQL injection?
- How do SQL injections happen in Python?
- What Python modules are vulnerable to SQL injections?
- How to avoid SQL injections in Python?
- Eliminate SQL injections in your Python code
- Use an Object Relational Mapper (ORM)
- Automatically detect and fix SQL injections in Python?
- More resources
- Python SQL Injection
- What is Python SQL Injection?
- How to Build Python SQL Injection?
- Examples of Python SQL Injection
- Example #1
- Example #2
- Conclusion
- Recommended Articles
Present SQL injection in Python (CWE-89)
Julien is the CEO of Codiga. Before starting Codiga, Julien was a software engineer at Twitter and Amazon Web Services. Julien has a PhD in computer science from Universite Pierre et Marie Curie in Paris, France.
What is a SQL injection?
A SQL injection (listed as CWE-89 by MITRE) is a vulnerability where inputs are not sanitized, and a user passes data that injects random SQL commands into the query. Imagine that you have a SQL query built in Python like this
query = f"SELECT * FROM users WHERE >user_id>" If one user manages to set user_id to the value 1 ; DELETE FROM users ; , the query will be the following:
SELECT * FROM users WHERE id=1 ; DELETE FROM users; How do SQL injections happen in Python?
SQL injections in Python occur by building queries by hand, using raw strings. When users build their queries manually, there is a high chance of introducing SQL injections. This occurs when using the database modules directly. For example, if you are using the mysql module, use the following code, you may be vulnerable to a MySQL injection attack by not sanitizing or checking the customer_id value.
import mysql.connector def get_user(customer_id): mydb = mysql.connector.connect(...) mycursor = mydb.cursor() mycursor.execute(f"SELECT * FROM customers WHERE >customer_id>") ... What Python modules are vulnerable to SQL injections?
This vulnerability exists with all database modules, either mysql, postgresql or generally, any module that interacts with a relational database.
How to avoid SQL injections in Python?
- Check all code that queries the database directly and make sure all data is sanitized
- Use an Object Relational Mapper (ORM) that sanitizes the data for you.
We detail each one in the following sub-sections.
Eliminate SQL injections in your Python code
To prevent SQL injections in your Python code, you need to review each query and ensure the data is properly sanitized.
Instead of building a query manually, such as:
cursor.execute(f"SELECT * from users where id=user_id>) cursor.execute(f"SELECT * from users where >, (user_id, )) In the latter code, cursor.execute sanitizes the data and prevents any SQL injection.
Use an Object Relational Mapper (ORM)
An ORM maps your data from the database to your language directly. It saves you from writing SQL queries manually and automatically prevent SQL injections.
The most popular ORM for Python is SQLAlchemy. It works well for all Python versions and is compatible with most databases.
Automatically detect and fix SQL injections in Python?
Codiga provides IDE plugins and integrations with GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket to detect unsafe deserialization for SQL-related Python modules. The Codiga static code analysis detects SQL injections directly in your IDE or code reviews.
There are multiple rules in the Codiga engine that checks for SQL injection, there is an example of a rule that detects SQL injections for MySQL.
To use this rule consistently, all you need to do is to install the integration in your IDE (for VS Code or JetBrains) or code management system and add a codiga.yml file at the root of your profile with the following content:
rulesets: - python-security It will then check all your Python code against 100+ rules that detect unsafe and insecure code and suggests fixes for each of them.
More resources
Python SQL Injection
Python SQL injection is a vulnerability and security which was legendary for a webcomic. It is a typical task to create and execute SQL queries. However, when it comes to constructing SQL statements, businesses all around the world frequently make terrible blunders. Although the ORM layer normally generates SQL queries, we may need to write our own occasionally. When we run queries straight into a database, there’s a danger.
Web development, programming languages, Software testing & others
What is Python SQL Injection?
- SQL injection is nothing but the multiple commands which was embedded in a URL string or data structure to extract the desired response from databases connected to web applications. This kind of attack is most common on PHP or ASP.NET-based websites.
- A common example of an SQL injection attack is changing the content of the database to run multiple queries from the application end.
- This attack occurs when an application fails to validate inputs properly before delivering them to a SQL statement. Normally, injections are placed in search areas or data fields.
How to Build Python SQL Injection?
- Using the “‘” character in a string and seeing if we get an error is the quickest way to see if a web application is vulnerable to a SQL injection attack.
- SQLi is the most common and harmful code insertion technique in general. The most typical attack target is mass knowledge extraction. Attackers can dump database tables containing tens of thousands of client records. Depending on the environment, SQL injection can also swap or remove data.
- SQL injection is carried by user input; we will extract the forms using a method described below. Then we’ll see if a web page has any SQL issues, which will come in handy when testing for SQL injection attacks, and we’ll put it to the test on HTML forms.
Below steps shows how to build python SQL injection as follows:
1. In the first step, we import the module names as requests and sys. This module is used to build the python SQL injection.
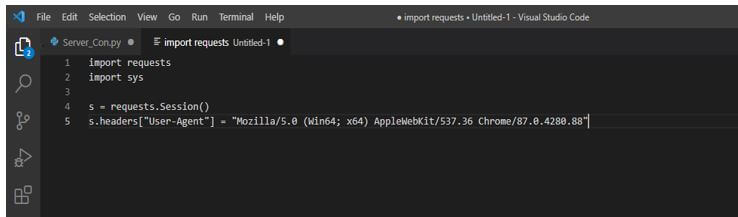
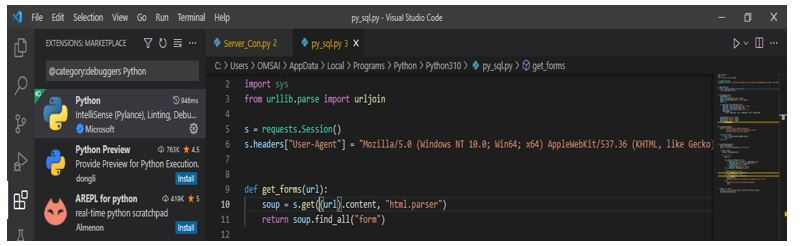
2. After importing the module, in this step, we are initializing the http session and setting up the latest agent for our browser.
We initialize the http module with Mozilla and Chrome browsers in the below step.
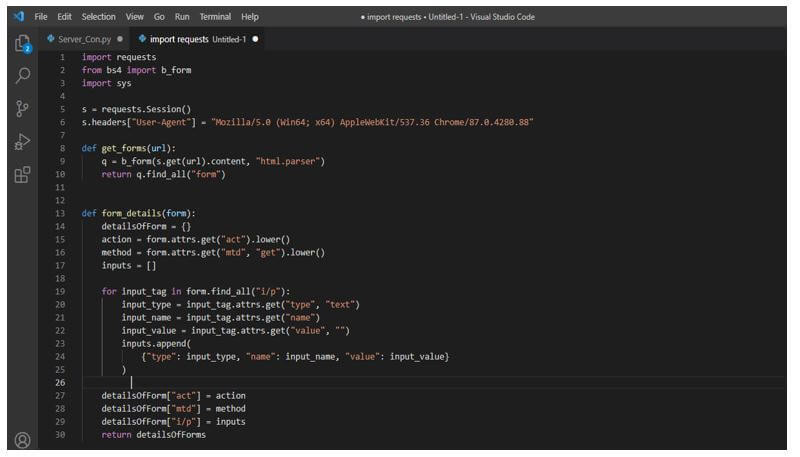
s = requests.Session () s.headers ["User-Agent"] = "Mozilla/5.0 (Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 Chrome/87.0.4280.88"3. After initializing the http session and setting up the agent in this step, we extract the web forms. For extracting the web forms first, we are writing the function giving the URL and making the request to the page which was extracting the html from the tags. After this, tags will be returned as a list. We can be using this tag as a list afterward.
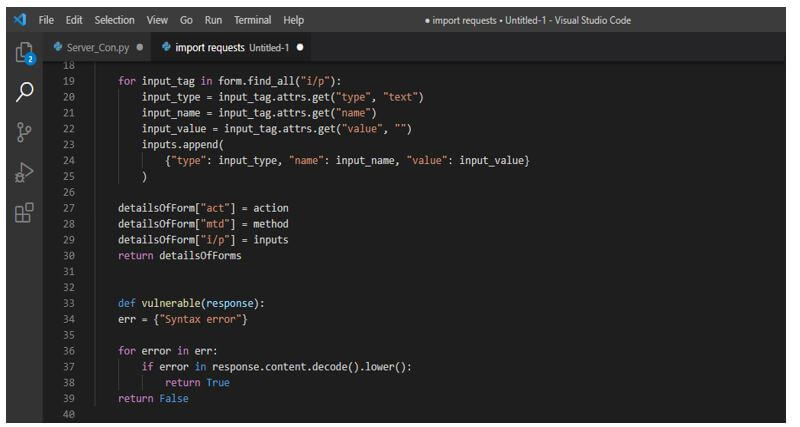
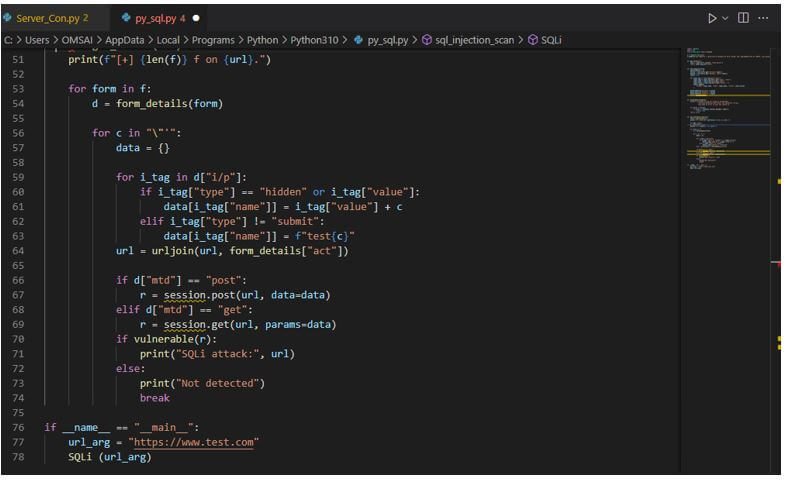
def get_forms(url): q = b_form(s.get(url).content, "html.parser") return q.find_all("form") def form_details(form): detailsOfForm = <> action = form.attrs.get ("act").lower() method = form.attrs.get ("mtd", "get").lower() inputs = [] for input_tag in form.find_all ("i/p"): input_type = input_tag.attrs.get ("type", "text") input_name = input_tag.attrs.get ("name") input_value = input_tag.attrs.get ("value", "") inputs.append ( ) detailsOfForm ["act"] = action detailsOfForm ["mtd"] = method detailsOfForm ["i/p"] = inputs return detailsOfForms4. After extracting the web forms in this step, we check whether the page contains the vulnerabilities in response output. We can say the page is vulnerable if we have received a syntax error. Although there are several database problems, we will focus on MySQL and PostgreSQL Errors because they are the most commonly encountered.
def vulnerable(response): err = for error in err: if error in response.content.decode ().lower(): return True return False5. After checking the vulnerabilities in this step, we are applying the search approach for all the forms on the web page of html.
def SQLi (url): f = get_forms (url) print(f"[+] f on .") for form in f: d = form_details(form) for c in "\"'": data = <> for i_tag in d["i/p"]: if i_tag["type"] == "hidden" or i_tag["value"]: data[i_tag["name"]] = i_tag["value"] + c elif i_tag["type"] != "submit": data[i_tag["name"]] = f"test" url = urljoin(url, form_details["act"]) if d["mtd"] == "post": r = session.post(url, data=data) elif d["mtd"] == "get": r = session.get(url, params=data) if vulnerable(r): print("SQLi attack:", url) else: print("Not detected") break if __name__ == "__main__": url_arg = "https://www.test.com" SQLi (url_arg)6. Run the code and provide the URL at runtime.
Examples of Python SQL Injection
The interpreter will run the code when we import the module. This implies we should be cautious when importing modules; PyPi is a fantastic resource, but the contributed code isn’t verified, and dangerous packages have been discovered in PyPi with common misspellings. If we are unsure about the validity or substance of an external package, conduct some investigation and ignore it if we are still unsure.
The first step in preventing most code bugs is to list potential errors and double-check for their absence. This can be done as part of the testing process or as a pre-testing phase.
Below is the example of SQL injection in python as follows. The below example shows select with SQL injection as follows.
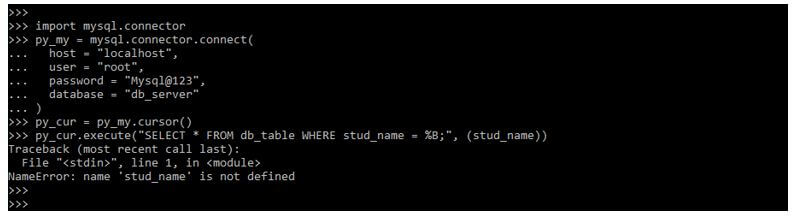
Example #1
import mysql.connector py_my = mysql.connector.connect( host = "localhost", user = "root", password /cdn-cgi/l/email-protection" data-cfemail="9dd0e4eeecf1ddacafae">[email protected]", database = "db_server" ) py_cur = py_my.cursor() py_cur.execute("SELECT * FROM db_table WHERE stud_name = %B;", (stud_name,))The above code will produce the error because we are making mistakes while creating a code. However, we are taking all the data from the table in the below code, so we have not made any syntax errors.
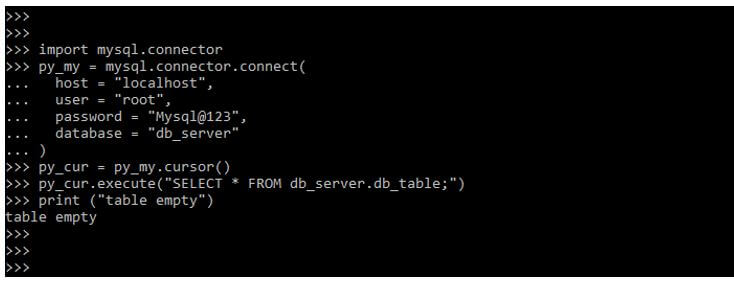
Example #2
import mysql.connector py_my = mysql.connector.connect( host = "localhost", user = "root", password /cdn-cgi/l/email-protection" data-cfemail="4d00343e3c210d7c7f7e">[email protected]", database = "db_server" ) py_cur = py_my.cursor() py_cur.execute ("SELECT * FROM db_server.db_table;") print ("table empty")Conclusion
SQL injection is nothing but the multiple commands which was embedded in a URL string or data structure to extract the desired response from databases. Python SQL injection is a vulnerability and security which was legendary for webcomics. It is a typical task to create and execute SQL queries.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Python SQL Injection. Here we discuss the introduction and how to build python SQL injection with examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –