- How to find Array Length in Java
- Java Array Length: How do you find the length of an array?
- Searching a value using Array Length in Java
- Searching for the lowest value in the array
- Searching for the highest value in the array
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Q. What is the difference between the Size of ArrayList and the length of an Array?
- Q. Are length and length() same in Java?
- Q. How to find the largest number in an array using the array length attribute in Java?
- Q. How to get the length in Java?
- Q. What do you mean by length function in Java?
- Conclusion
- String Array in Java
- String Array Declaration
- String Array Initialization
- Simple String Array Example in Java
- String array ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
- Iterating a String Array
- Adding elements to String array
- 1. Adding elements to an array by creating new array
- 2. Adding elements to an array using ArrayList
- Sorting string array
- Search an element in a String array
- Top Related Articles:
- About the Author
How to find Array Length in Java
Java Array Length: How do you find the length of an array?
The length attribute of Java holds the number of elements in the array. In Java, there is no predefined method by which you can find the length of an array. But you can use the length attribute to find the length of an array. When we declare an array, the total number of elements in it is called the array’s length, or we can also call it the size of the array. You can also take up a java programming free online course and learn more about the concepts before learning about arrays in java.
Let us see the below example for a better understanding:
Let us see a program using the Array Length attribute of Java:
import java.util.*; class Main < public static void main(String[] args) < Integer[] intArray = ; //integer array String[] strArray = < "one", "two", "three", “four” >; //string array //print each array and their corresponding length System.out.println("Contents of Integer Array : " + Arrays.toString(intArray)); System.out.println("The length of the array is : " + intArray.length); System.out.println("Contents of String array : " + Arrays.toString(strArray)); System.out.println("The length of the String array is : " + strArray.length); > > Contents of Integer Array: [1,2,5,7]
The length of the array is: 4
Contents of String array: [one, two, three, four]
The length of the String array is: 4
In the above program, the length function counts the total number of elements in the array, whether a string or a number. The length attribute takes the length of the array. There can be different scenarios where you can use the Array Length attribute, such as:
- To search for a minimum value in the array.
- To find the maximum number in an array.
- To get any specific value from the array.
- To check if any specific value is there in the array or not.
There can be more scenarios where you can use the Array Length attribute in Java.
In this article, we will see more scenarios of using the Array Length attribute of Java with some useful programs and examples.
Searching a value using Array Length in Java
The Array Length attribute can be used for several cases, so it is essential. It can also be used for searching for a value in an array. You need to use a loop that will iterate through all the elements in the array one after the other until it finds the searched element.
When the code runs, the loop will start searching the element in the array until it reaches the last element or traverses the complete length of the array. When it is traversing through each element in the array, it compares the value of each element to the value to be searched, and if the value of the element is matched, then it stops the loop.
The program below does the same we just discussed, and it will help you to understand better how the code will work:
import java.util.*; class Main< public static void main(String[] args) < String[] strArray = < “HTML”, “CSS”, "Java", "Python", "C++", "Scala", >; //array of strings //search for a string using searchValue function System.out.println(searchValue(strArray, "C++")?" value C++ found":"value C++ not found"); System.out.println(searchValue(strArray, "Python")?"value Python found":"value Python not found"); > private static boolean findValue(String[] searchArray, String lookup) < if (searchArray != null) < int arrayLength = searchArray.length; //computes the array length for (int i = 0; i > > return false; > In the above program, as you can see, we have an array that contains the names of some programming languages. There’s a function with the name ‘findValue’ that searches for the specific value we are trying to find in the array. We used the for loop that traverses through each element in the array and finds it the value exists in our array or not. We gave two statements for both the cases, such as if the value is in the array or not. What it does is it returns true if the value is found in the array and false otherwise.
In our case, the values C++ and Python were there in our array and that’s the reason it returned true or the statements that we provided as true.
Searching for the lowest value in the array
As we have seen, how the Array length attribute works and how it makes our code easier to find the value we are searching for. In this section, we will see how we can find the minimum value in an array.
The below program is used to find the lowest value in an array:
import java.util.*; class Main < public static void main(String[] args) < int[] intArray = < 2,40,11,10,3,44 >; //int array System.out.println("The given array:" + Arrays.toString(intArray)); int min_Val = intArray[0]; // we are assigning first element to min value int length = intArray.length; for (int i = 1; i > System.out.println("The lowest value in the array: "+min_Val); > > The given array: [2, 40, 11, 10, 3, 44]
The lowest value in the array: 2
We gave the first element as the lowest element in the array in the above program. But still, it assigned the first element 2 as the minimum value and compared it with other elements in the array. When it is found that the value 2 is the only minimum, it comes out from the loop and returns the min value from the array.
Suppose we have provided the minimum value at some other place in the array. In that case, it will assign each value in the array as a minimum value and compare it with other elements until it finds the correct one. This way, we can find the minimum value in the array.
Searching for the highest value in the array
In the above section, we saw how to find the minimum value in an array. The same logic will be applied in this example, where we search for the maximum value in an array. The only thing that will change is only the smaller than (<) sign.
Let us see the example below:
import java.util.*; class Main < public static void main(String[] args) < int[] intArray = < 2,40,1,10,95,24 >; //int array System.out.println("The given array:" + Arrays.toString(intArray)); int max_Val = intArray[0]; //reference element as maximum value int length = intArray.length; for (int i = 1; i max_Val) < max_Val = value; >> System.out.println("The largest value in the array: "+max_Val); > > The given array: [2,40,1, 10,95,24]
The largest value in the array: 95
The above code did the same as it did to find the smallest value in the array. The thing that is changed is the condition for comparing with another element. We compared the smallest elements, and now we used to find the largest ones.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. What is the difference between the Size of ArrayList and the length of an Array?
A. In the ArrayList attribute, there is no length property, but it still gives the length by using the size() method, whereas the length property of the array gives the total number of elements in the array or the length of the array.
Q. Are length and length() same in Java?
A. Length() is a method used for the string objects to return the number of characters in a string where ‘length’ is the property to find the total number of elements in an array, and it returns the size of the array.
Q. How to find the largest number in an array using the array length attribute in Java?
A. To find the largest number or value in an array, we need to create a loop that will traverse through each element in the array and compares each element by assigning the first value of the array as the maximum. To understand better, go to the section ‘Searching for the highest value in the array’ of this article, where we discussed an example.
Q. How to get the length in Java?
A. There are different scenarios to find the length. For example, we have two options to use the length() method or the java length attribute. Both of them are used for different purposes and return different values. So, if you want to find the length of characters in a string, you need to use the length() method, whereas if you want to find the length or size of an array, you must use the length attribute of Java.
Q. What do you mean by length function in Java?
A. The length() function in Java is used to get the number of characters in a string.
Conclusion
Thus, we have come to the end of this article where we discussed the Java Array Length attribute, which is very useful in different programming scenarios. We also discussed specific cases, such as finding the largest and smallest value in an array. However, there are more uses for this attribute. So, we encourage you to find more cases and try to use this length attribute.
Great Learning’s Blog covers the latest developments and innovations in technology that can be leveraged to build rewarding careers. You’ll find career guides, tech tutorials and industry news to keep yourself updated with the fast-changing world of tech and business.
String Array in Java
In this guide, you will learn about string array in java, how to use them and various operations that you can perform on string array in java.
String array is a collection of strings, stored in contiguous memory locations.
For example: The following string array contains four elements. These elements are stored in contiguous memory locations and can be accessed using array index such as: names[0] represents first element «Chaitanya» . Similarly names[1] represents second element «Ajeet» , names[2] represents third element «Hari ” and so on.
String Array Declaration
There are two ways to declare a String array in Java.
1. Without specifying the array size:
2. Array size is specified: The following array can hold upto 5 strings.
String[] strArray = new String[5];
String Array Initialization
1. Inline Initialization:
String[] names = new String[] ; OR String[] names = ;
2. Normal Initialization after declaration:
Here, we have declared an array names with the fixed size of 4 and initialized the array later.
String[] names= new String[4]; names[0]= "Chaitanya"; //first element names[1]= "Ajeet"; //second element names[2]= "Hari"; //third element names[3]= "Rahul"; //last element
Simple String Array Example in Java
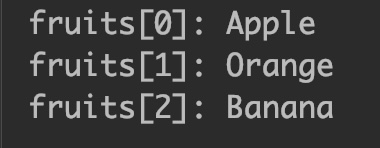
In this example, we have a string array fruits . This array contains three elements (strings). We are displaying the elements of string array using for loop. The length property of array ( fruits.length ) returns the number of elements in an array, in this case its 3.
public class JavaExample < public static void main(String a[])< //declared and initialized a string array String[] fruits = new String[]; for (int i=0; i > >
String array ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
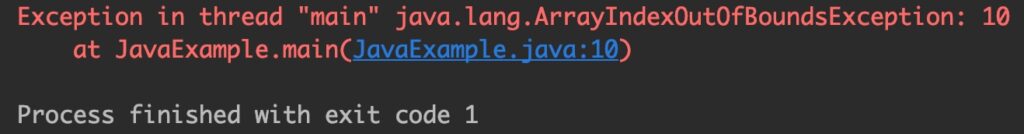
If the specified index is beyond the size of the array then the compiler throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException .
public class JavaExample < public static void main(String a[])< //declared and initialized a string array String[] fruits = new String[]; //We are trying to print 11th element of the array //but the array contains only 3 elements. This will //throw ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException System.out.println(fruits[10]); > >
Iterating a String Array
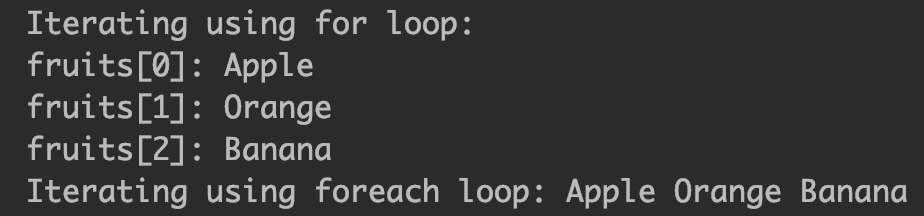
Let’s see how to iterate a string array. We can iterate using normal for loop or enhanced for loop (for each loop).
public class JavaExample < public static void main(String a[])< //declared and initialized a string array String[] fruits = new String[]; //iterating using normal for loop System.out.println("Iterating using for loop:"); for (int i=0; i //iterating using for-each loop System.out.print("Iterating using foreach loop: "); for (String str: fruits) < System.out.print(str+ " "); >> >
Adding elements to String array
You already learned that the size of the array is fixed, which means if it is full, you cannot add any more elements to it. However there are two ways, you can add elements to an array. Technically it’s not adding the elements to the existing array, rather a new array with all the elements of previous array along with the new elements.
1. Creating a new array
2. Using ArrayList
1. Adding elements to an array by creating new array
Steps followed in this program are:
1. Create a new array with the larger size to accommodate new elements.
2. Copy all elements from old array to new array.
3. Add new elements to new array.
4. Print new array
public class JavaExample < public static void main(String a[])< //declared and initialized a string array String[] fruits = new String[]; //we want to add two more elements to the fruits array so let's //create a new array with the size of 5 String[] newFruits = new String[fruits.length+2]; //copying elements from old array to new array for (int i=0; i //Adding new elements newFruits[newFruits.length-2]= "Mango"; //second last element newFruits[newFruits.length-1]= "Kiwi"; //last element //print new array for (String str: newFruits) < System.out.println(str); >> >
Apple Orange Banana Mango Kiwi
2. Adding elements to an array using ArrayList
Steps followed in this program are:
1. Convert array to ArrayList.
2. Add as many elements as you like in ArrayList as ArrayList is dynamic and can grow and shrink automatically.
3. Once addition is done, convert back the ArrayList to an Array.
4. Print the array.
import java.util.*; public class JavaExample < public static void main(String a[])< //declared and initialized a string array String[] fruits = new String[]; //Convert the array "fruits" to an ArrayList ArrayList fruitList = new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(fruits)); //Adding elements to ArrayList fruitList.add("Mango"); fruitList.add("Kiwi"); //Convert the ArrayList to array String[] newFruits = fruitList.toArray(new String[fruitList.size()]); //print new array for (String str: newFruits) < System.out.println(str); >> > Apple Orange Banana Mango Kiwi
Sorting string array
Here, we are demonstrating how to sort a string array. It is simple, just import java.util.Arrays package to use the sort() method of Arrays class. The array passed in the sort() method is sorted in ascending order.
import java.util.Arrays; public class JavaExample < public static void main(String a[])< String[] names = new String[]; //print array before sorting System.out.println("Array before sorting: "); for (String str: names) < System.out.print(str+ " "); >//sorting array Arrays.sort(names); //new line System.out.println(); //print array after sorting System.out.println("Array after sorting: "); for (String str: names) < System.out.print(str+ " "); >> >
Search an element in a String array
Here, we are searching an element in string array. We are iterating the whole array and matching every element with the searchItem , if a match is found, we are storing the index and setting the foundFlag to true . If the whole array is traversed and no match is found then the if-else statement after for loop, prints the message that “String is not found”.
public class JavaExample < public static void main(String a[])< String[] names = new String[]; //this will represent the index of search element when it is found int index=0; //This will set to true, if element is found in array, else it //will remain false. boolean foundFlag = false; //This is the search element, we are searching for this element in array String searchItem ="Rob"; for (int i = 0; i < names.length; i++) < if(searchItem.equals(names[i])) < //if element found, get index, set flag to true and break the loop index = i; foundFlag = true; break; >> if(foundFlag) System.out.println("String "+searchItem +" is found at index: "+index); else System.out.println("String "+searchItem +" is not found"); > > String Rob is found at index: 2
Top Related Articles:
About the Author
I have 15 years of experience in the IT industry, working with renowned multinational corporations. Additionally, I have dedicated over a decade to teaching, allowing me to refine my skills in delivering information in a simple and easily understandable manner.