- HTML Images
- Example
- Example
- Example
- HTML Images Syntax
- Syntax
- The src Attribute
- Example
- The alt Attribute
- Example
- Example
- Image Size — Width and Height
- Example
- Example
- Width and Height, or Style?
- Example
- Images in Another Folder
- Example
- Images on Another Server/Website
- Example
- Animated Images
- Example
- Image as a Link
- Example
- Image Floating
- Example
- Common Image Formats
- Chapter Summary
- HTML Exercises
- HTML Image Tags
- Adding an Image From a URL – HTML
- How to Add an Image From a URL in HTML/CSS?
- Method 1: Add Image by Using Element
- Step 1: Make a div Container
- Step 2: Insert Heading
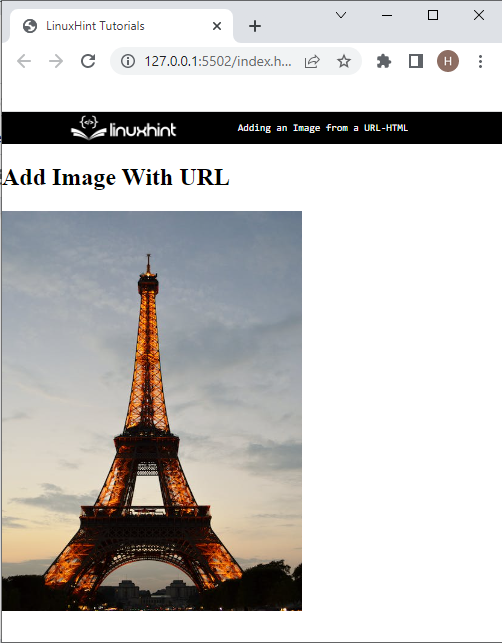
- Step 3: Add an Image Using URL
- Method 2: Add Image Using CSS Properties in HTML
- Step 1: Insert Heading
- Step 2: Create div Container
- Add Image With URL
- Step 3: Access Container
- Step 4: Add Image Using “background-image” CSS Property
- Conclusion
- HTML Images
HTML Images
Images can improve the design and the appearance of a web page.
Example

Example
Example

HTML Images Syntax
The HTML tag is used to embed an image in a web page.
Images are not technically inserted into a web page; images are linked to web pages. The tag creates a holding space for the referenced image.
The tag is empty, it contains attributes only, and does not have a closing tag.
The tag has two required attributes:
Syntax
The src Attribute
The required src attribute specifies the path (URL) to the image.
Note: When a web page loads, it is the browser, at that moment, that gets the image from a web server and inserts it into the page. Therefore, make sure that the image actually stays in the same spot in relation to the web page, otherwise your visitors will get a broken link icon. The broken link icon and the alt text are shown if the browser cannot find the image.
Example
The alt Attribute
The required alt attribute provides an alternate text for an image, if the user for some reason cannot view it (because of slow connection, an error in the src attribute, or if the user uses a screen reader).
The value of the alt attribute should describe the image:
Example
If a browser cannot find an image, it will display the value of the alt attribute:
Example
Tip: A screen reader is a software program that reads the HTML code, and allows the user to «listen» to the content. Screen readers are useful for people who are visually impaired or learning disabled.
Image Size — Width and Height
You can use the style attribute to specify the width and height of an image.
Example
Alternatively, you can use the width and height attributes:
Example
The width and height attributes always define the width and height of the image in pixels.
Note: Always specify the width and height of an image. If width and height are not specified, the web page might flicker while the image loads.
Width and Height, or Style?
The width , height , and style attributes are all valid in HTML.
However, we suggest using the style attribute. It prevents styles sheets from changing the size of images:
Example
Images in Another Folder
If you have your images in a sub-folder, you must include the folder name in the src attribute:
Example
Images on Another Server/Website
Some web sites point to an image on another server.
To point to an image on another server, you must specify an absolute (full) URL in the src attribute:
Example
Notes on external images: External images might be under copyright. If you do not get permission to use it, you may be in violation of copyright laws. In addition, you cannot control external images; they can suddenly be removed or changed.
Animated Images
HTML allows animated GIFs:
Example
Image as a Link
To use an image as a link, put the tag inside the tag:
Example
Image Floating
Use the CSS float property to let the image float to the right or to the left of a text:
Example
The image will float to the right of the text.
The image will float to the left of the text.
Tip: To learn more about CSS Float, read our CSS Float Tutorial.
Common Image Formats
Here are the most common image file types, which are supported in all browsers (Chrome, Edge, Firefox, Safari, Opera):
| Abbreviation | File Format | File Extension |
|---|---|---|
| APNG | Animated Portable Network Graphics | .apng |
| GIF | Graphics Interchange Format | .gif |
| ICO | Microsoft Icon | .ico, .cur |
| JPEG | Joint Photographic Expert Group image | .jpg, .jpeg, .jfif, .pjpeg, .pjp |
| PNG | Portable Network Graphics | .png |
| SVG | Scalable Vector Graphics | .svg |
Chapter Summary
- Use the HTML
element to define an image
- Use the HTML src attribute to define the URL of the image
- Use the HTML alt attribute to define an alternate text for an image, if it cannot be displayed
- Use the HTML width and height attributes or the CSS width and height properties to define the size of the image
- Use the CSS float property to let the image float to the left or to the right
Note: Loading large images takes time, and can slow down your web page. Use images carefully.
HTML Exercises
HTML Image Tags
| Tag | Description |
|---|---|
| Defines an image | |
| Defines an image map | |
| Defines a clickable area inside an image map | |
| Defines a container for multiple image resources |
For a complete list of all available HTML tags, visit our HTML Tag Reference.
Adding an Image From a URL – HTML
In HTML, images make websites more attractive and attain people’s intention. It allows developers to customize their web pages with different images. Additionally, they can add them directly from the internet by copying the URL of the desired image and then specifying it as the value of the “src” attribute inside the image tag. Moreover, developers can add the image with the help of the CSS property known as “background-image”.
This post will briefly explain the method for adding the image from a URL.
How to Add an Image From a URL in HTML/CSS?
In HTML/CSS, two methods are available to add an image using the URL, which is listed below:
Method 1: Add Image by Using ![]() Element
Element
The “ ” element is a single void element that has no child content and ending tag. The “src” and “alt” are two key attributes that are utilized inside the “” tag.
Let’s look at the below-given instructions to add an image using the element!
Step 1: Make a div Container
First, create a div container by utilizing the “ ” tag. Then, insert the “class” attribute and assign a name to the class according to desire.
Step 2: Insert Heading
Next, use the required heading tag from “ ” to “ ” tag. For instance, we will utilize the tag and add the particular text as a heading inside the opening and closing tags.
Step 3: Add an Image Using URL
After that, add an “ ” tag and insert the below-listed attributes inside the image tag:
- “src” attribute is used for adding the media file. For that purpose, launch your desired web browser and copy the desired image URL.
- Then, specify the URL as a value of the “src” attribute.
- Next, “alt” is utilized for adding a name for the image when it is not shown for some reason.
- “height” property specifies the element’s height according to the given value.
- “width” utilized for setting the width of the element:
According to the below-given output, the specified image has been added successfully:
Method 2: Add Image Using CSS Properties in HTML
Developers can also add the image from a URL using the CSS “background-image” CSS. for this purpose, follow the below-given steps.
Step 1: Insert Heading
First, insert a heading text with the help of the opening and closing tag.
Step 2: Create div Container
Next, create a div container by utilizing the tag and add a class attribute with its name:
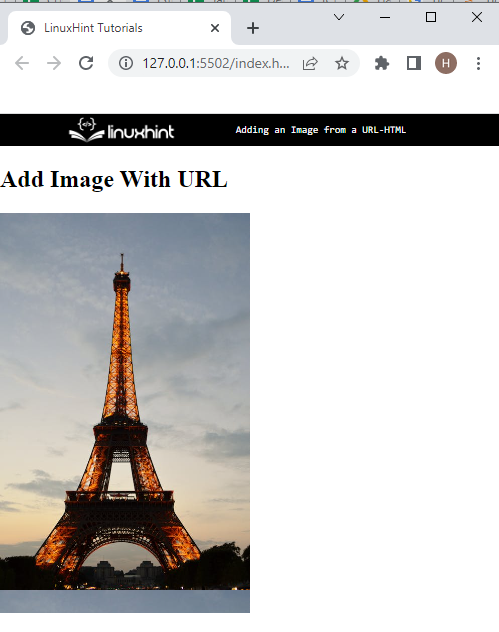
Add Image With URL
Step 3: Access Container
Now, access the class through the dot selector “.” and the class name which was created previously.
Step 4: Add Image Using “background-image” CSS Property
After that, apply the below-listed CSS properties to add the image from a URL inside the class:
Background-image : url ( https : //images .pexels .com/photos/ 2260800 /pexels-photo- 2260800 .jpeg? auto = compress&cs = tinysrgb&w = 1260 &h = 750 &dpr = 1 )
In the above-provided code:
- “height” property is used for setting the height of the element.
- “width” is used to specify the element’s width size.
- “background-size” is utilized for setting the background element size.
- “background-image” property adds an image at the element’s backside. For this corresponding purpose, the “url()” function is utilized for adding the image and pasting the URL of the image in the function “()”.
You have learned about the different methods for adding images from a URL.
Conclusion
To add an image from a URL, developers can utilize the “ ” tag. Then, insert the “src” attribute and assign the URL as the “src” value. Furthermore, the user can add an image from the URL by using the CSS “background-image” property. This write-up has stated the methods for adding the image from the URL in HTML/CSS.
HTML Images
In this article, we will know the HTML Image, how to add the image in HTML, along with knowing its implementation & usage through the examples. In earlier times, the web pages only contains textual contents, which made them appear quite boring and uninteresting. Fortunately, it wasn’t long enough that the ability to embed images on web pages was added for users. In this article, we will know how to add images to the web page that will make the website attractive & various methods to insert the images.
There are 2 ways to insert the images into a webpage:
- By providing a full path or address (URL) to access an internet file.
- By providing the file path relative to the location of the current web page file.
We will first discuss inserting the image to the webpage & simultaneously, we will understand both the above approaches.
Adding images on a webpage: The tag is used to add or embed the images to a webpage/website. The “img” tag is an empty tag, which means it can contain only a list of attributes and it has no closing tag. The addition of the images improves the quality along with enhancing the design structure, appearance of the webpage. Nowadays, a website does not directly add images to a web page, as the images are linked to web pages by using the
tag which holds space for the image.
Attribute: The tag has following attributes:
- src: It is used to specify the path to the image.
- alt: It is used to specify an alternate text for the image. It is useful as it informs the user about what the image means and also due to any network issue if the image cannot be displayed then this alternate text will be displayed.
- crossorigin: It is used to import images from third-party sites that allow cross-origin access to be used with canvas.
- height: It is used to specify the height of the image.
- width: It is used to specify the width of the image.
- ismap: It is used to specify an image as a server-side image map.
- loading: It is used to specify whether a browser should defer the loading of images until some conditions are met or load an image immediately.
- longdesc: It is used to specify a URL to a detailed description of an image.
- referrerpolicy: It is used to specify which referrer information to use when fetching an image i.e. no-referrer, no-referrer-when-downgrade, origin, origin-when-cross-origin, unsafe-url.
- sizes: It is used to specify image sizes for different page layouts.
- srcset: It is used to specify a list of image files to use in different situations.
- usemap: It is used to specify an image as a client-side image map.
src: The src stands for source. Every image has an src attribute which tells the browser where to find the image you want to display. The URL of the image provided points to the location where the image is stored. When the webpage loads for the first time, then the browser gets the image from a web server and inserts it into the page. If the image is not spotted by the browser then users will get a broken link icon. It might be possible if the file path is wrong or the image got deleted from that location.
Example 1: This simple example illustrates the use of the tag in HTML that is used to embed the image into the webpage.