- Style left Property
- Browser Support
- Syntax
- Property Values
- Technical Details
- More Examples
- Example
- Example
- Example
- Style left Property
- Browser Support
- Syntax
- Property Values
- Technical Details
- More Examples
- Example
- Example
- Example
- Set element left javascript
- # Table of Contents
- # Set the Position of an Element using JavaScript
- # Position an Element under the Mouse on Click
- # Additional Resources
- Style left Property
- Browser Support
- Syntax
- Property Values
- Technical Details
- More Examples
- Example
- Example
- Example
Style left Property
The left property sets or returns the left position of a positioned element.
This property specifies the left position of the element including padding, scrollbar, border and margin.
Tip: A positioned element is an element with the position property set to: relative, absolute, or fixed.
Tip: To set or return the right position of a positioned element, use the right property.
Browser Support
Syntax
Property Values
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| auto | Lets the browser set the left position. This is default |
| length | Defines the left position in length units. Negative values are allowed |
| % | Sets the left position in % of the width of the parent element |
| initial | Sets this property to its default value. Read about initial |
| inherit | Inherits this property from its parent element. Read about inherit |
Technical Details
| Default Value: | auto |
|---|---|
| Return Value: | A String, representing the left position of a positioned element |
| CSS Version | CSS2 |
More Examples
Example
Set the left position of a element:
Example
Using negative values — Set the left position of a element:
Example
Return the left position of a element:
Style left Property
The left property sets or returns the left position of a positioned element.
This property specifies the left position of the element including padding, scrollbar, border and margin.
Tip: A positioned element is an element with the position property set to: relative, absolute, or fixed.
Tip: To set or return the right position of a positioned element, use the right property.
Browser Support
Syntax
Property Values
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| auto | Lets the browser set the left position. This is default |
| length | Defines the left position in length units. Negative values are allowed |
| % | Sets the left position in % of the width of the parent element |
| initial | Sets this property to its default value. Read about initial |
| inherit | Inherits this property from its parent element. Read about inherit |
Technical Details
| Default Value: | auto |
|---|---|
| Return Value: | A String, representing the left position of a positioned element |
| CSS Version | CSS2 |
More Examples
Example
Set the left position of a element:
Example
Using negative values — Set the left position of a element:
Example
Return the left position of a element:
Set element left javascript
Last updated: Jan 11, 2023
Reading time · 3 min
# Table of Contents
# Set the Position of an Element using JavaScript
To set the position of an element:
- Select the element and set its position property to absolute .
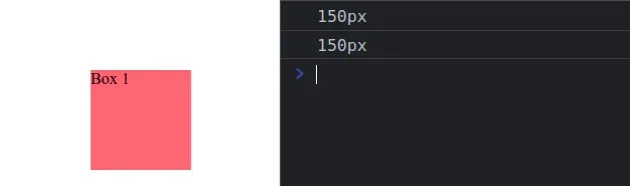
- Use the top property to set the element’s vertical position, e.g. box.style.top = ‘150px’ .
- Use the left property to set the element’s horizontal position, e.g. box.style.left = ‘150px’ .
Here is the HTML for the examples.
Copied!DOCTYPE html> html lang="en"> head> meta charset="UTF-8" /> title>bobbyhadz.comtitle> head> body> div id="box" style="background-color: salmon; width: 100px; height: 100px"> Box 1 div> script src="index.js"> script> body> html>
And here is the related JavaScript code.
Copied!const box = document.getElementById('box'); box.style.position = 'absolute'; box.style.top = '150px'; box.style.left = '150px'; console.log(box.style.top); // 👉️ "150px" console.log(box.style.left); // 👉️ "150px"
We first set the element’s position to absolute .
The element’s final position is determined by the values of top , right , bottom and left properties.
The top , right , bottom and left properties do not affect non-positioned elements.
We set the element’s top CSS property to 150px .
The top property specifies the distance to the top edge of the element’s containing block.
Copied!const box = document.getElementById('box'); box.style.position = 'absolute'; box.style.top = '150px'; box.style.left = '150px'; console.log(box.style.top); // 👉️ "150px" console.log(box.style.left); // 👉️ "150px"
We then used the left property to set the distance to the left edge of the element’s containing block.
If you have to set the element’s position at multiple different places in your code, create a reusable function.
Copied!function positionElement(el, x, y) el.style.position = 'absolute'; el.style.left = x + 'px'; el.style.top = y + 'px'; > const box = document.getElementById('box'); console.log(positionElement(box, 50, 150)); console.log(box.style.left); // 👉️ "50px" console.log(box.style.top); // 👉️ "150px"
The function takes the element, the x and y position as parameters, sets the element’s position property to absolute and positions it.
# Position an Element under the Mouse on Click
To position an element under the mouse on click:
- Set the element’s position property to absolute .
- Add a click event listener to the document object.
- Each time the mouse is clicked, set the element’s top and left properties to the coordinates of the mouse.
Here is the HTML for the next example.
Copied!DOCTYPE html> html lang="en"> head> meta charset="UTF-8" /> title>bobbyhadz.comtitle> head> body> div id="box" style="background-color: salmon; width: 100px; height: 100px"> Box 1 div> script src="index.js"> script> body> html>
And here is the related JavaScript code.
Copied!const box = document.getElementById('box'); box.style.position = 'absolute'; document.addEventListener('click', function handleClick(event) box.style.top = event.clientY - 50 + 'px'; box.style.left = event.clientX - 50 + 'px'; >);
If you open your browser and click at different places on the screen, you will see that the element gets positioned under your mouse cursor.
We added a click event listener on the document object, which invokes a function anytime the document is clicked.
Your requirements may vary but to position the element in the center of the cursor, we subtracted 50 from the clientY and clientX coordinates.
The clientY property provides the vertical coordinate at which the event occurred.
And the clientX property provides the horizontal coordinate at which the MouseEvent event occurred.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
I wrote a book in which I share everything I know about how to become a better, more efficient programmer.
Style left Property
The left property sets or returns the left position of a positioned element.
This property specifies the left position of the element including padding, scrollbar, border and margin.
Tip: A positioned element is an element with the position property set to: relative, absolute, or fixed.
Tip: To set or return the right position of a positioned element, use the right property.
Browser Support
Syntax
Property Values
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| auto | Lets the browser set the left position. This is default |
| length | Defines the left position in length units. Negative values are allowed |
| % | Sets the left position in % of the width of the parent element |
| initial | Sets this property to its default value. Read about initial |
| inherit | Inherits this property from its parent element. Read about inherit |
Technical Details
| Default Value: | auto |
|---|---|
| Return Value: | A String, representing the left position of a positioned element |
| CSS Version | CSS2 |
More Examples
Example
Set the left position of a element:
Example
Using negative values — Set the left position of a element:
Example
Return the left position of a element: