- trouble getting the current url on selenium
- 3 Answers 3
- Get Current URL in Selenium using Python: Tutorial
- Current URL in Selenium using Python: Example
- Pre-requisites
- Using the Current URL method in Selenium to perform a URL check on google.com
- Performing URL checks with Current URL in Selenium using Python
trouble getting the current url on selenium
I want to get the current url when I am running Selenium. I looked at this stackoverflow page: How do I get current URL in Selenium Webdriver 2 Python? and tried the things posted but it’s not working. I am attaching my code below:
from selenium import webdriver #launch firefox driver = webdriver.Firefox() url1='https://poshmark.com/search?' # search in a window a window driver.get(url1) xpath='//input[@id="user-search-box"]' searchBox=driver.find_element_by_xpath(xpath) brand="freepeople" style="top" searchBox.send_keys(' '.join([brand,"sequin",style])) from selenium.webdriver.common.keys import Keys #EQUIValent of hitting enter key searchBox.send_keys(Keys.ENTER) print(driver.current_url) The issue is that there is no lag between your searchBox.send_keys(Keys.ENTER) and print(driver.current_url) . There should be some time lag, so that the statement can pick the url change. If your code fires before url has actually changed, it gives you old url only. The workaround would be to add time.sleep(1) to wait for 1 second.
3 Answers 3
The issue is that there is no lag between your searchBox.send_keys(Keys.ENTER) and print(driver.current_url) .
There should be some time lag, so that the statement can pick the url change. If your code fires before url has actually changed, it gives you old url only.
The workaround would be to add time.sleep(1) to wait for 1 second. A hard coded sleep is not a good option though. You should do one of the following
- Keep polling url and wait for the change to happen or the url
- Wait for a object that you know would appear when the new page comes
- Instead of using Keys.Enter simulate the operation using a .click() on search button if it is available
Usually when you use click method in selenium it takes cared of the page changes, so you don’t see such issues. Here you press a key using selenium, which doesn’t do any kind of waiting for page load. That is why you see the issue in the first place
I had the same issue and I came up with solution that uses default explicit wait (see how explicit wait works in documentation).
class UrlHasChanged: def __init__(self, old_url): self.old_url = old_url def __call__(self, driver): return driver.current_url != self.old_url: @contextmanager def url_change(driver): current_url = driver.current_url yield WebDriverWait(driver, 10).until(UrlHasChanged(current_url)) - At first, I created my own wait condition (see here) that takes old_url as a parameter (url from before action was made) and checks whether old url is the same like current_url after some action. It returns false when both urls are the same and true otherwise.
- Then, I created context manager to wrap action that I wanted to make, and I saved url before action was made, and after that I used WebDriverWait with created before wait condition.
Thanks to that solution I can now reuse this function with any action that changes url to wait for the change like that:
with url_change(driver): login_panel.login_user(normal_user['username'], new_password) assert driver.current_url == dashboard.url It is safe because WebDriverWait(driver, 10).until(UrlHasChanged(current_url)) waits until current url will change and after 10 seconds it will stop waiting by throwing an exception.
What do you think about this?
Get Current URL in Selenium using Python: Tutorial
Selenium is a well-established automation testing framework that provides tools tailor-made for browser automation. When it comes to deftly navigating various websites and web scraping material, or carrying out repetitive tasks Selenium is quintessential.
This tutorial illustrates a core method to get the current URL in selenium using python. The current_url method is generally employed in cases where you require an intermediate URL from a redirect chain or need to do a series of navigations among different URLs.
This method is ubiquitous in most situations involving browser automation.
To give an instance, let’s assume you need to web scrape tables containing data on a certain species’ population information from different biological databases. This task requires taking user input for the URL of each database to be used, and the species to search for. As we navigate to these web databases it’s imperative that the correct URL is accessed, and the best method to ensure navigation to the correct URL is to administer wait commands and check for it using the current_url method in Selenium.
Current URL in Selenium using Python: Example
To instantiate the usefulness of the current_url method, a basic example involving navigation to a website using google chrome was performed. To further illustrate its import, navigation between multiple websites while screen scraping information was also implemented. This example showcased how the current_url method is indispensable to verify correct navigation with browser automation.
Before executing the code to navigate to the URL https://www.google.com, the following prerequisites are needed.
Pre-requisites
- Set up a python environment.
- Install Selenium. If you have conda or anaconda set up then using the pip package installer would be the most efficient method for Selenium installation. Simply run this command (on anaconda prompt, or directly on the Linux terminal):
pip install webdriver_manager
Using the Current URL method in Selenium to perform a URL check on google.com
Step 1: Import the required packages using the following command.
from selenium import webdriver from selenium.webdriver.chrome.service import Service from webdriver_manager.chrome import ChromeDriverManager
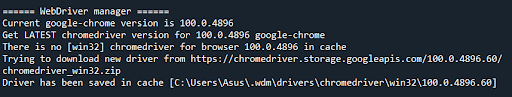
Step 2: Use WebDriver manager to download the required WebDriver for your browser (currently ChromeDriver, GeckoDriver, IEDriver, OperaDriver, and EdgeChromiumDriver can be downloaded via this package).
First, the WebDriver manager package will search for the version of the browser being used. Following this, it will check your cache to see if the WebDriver is already present in your cache. If there is no WebDriver present, or an old version is present, the package will download and save the latest version of the WebDriver.
In this example google chrome is being used, therefore the WebDriver manager installed the latest version of the ChromeDriver.
driver = webdriver.Chrome(service=Service(ChromeDriverManager().install()))
In the above command, the Service object inherits and sets the executable path as the location where the WebDriver has been saved following installation.
Step 3: You can also manually download the WebDriver for your respective browser here. If you manually downloaded the WebDriver you will either need to place the driver on your system path (put the chromedriver.exe file in the same location as your python code file) or alternatively set your executable path as the location of the WebDriver.
If your driver is on your system path:
from selenium import webdriver driver = webdriver.Chrome()
Alternatively set executable path as the location of webdriver:
from selenium import webdriver from selenium.webdriver.chrome.service import Service ser = Service(r"C:/Users/Asus/Downloads/chromedriver_win32/chromedriver.exe") driver = webdriver.Chrome(service=ser)
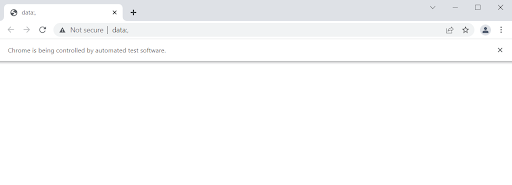
Following this, the chrome browser should open with data; in the URL bar. When we attempt to get the current URL without fetching another URL, this is the URL, which will be obtained.
Step 4: Load your required URL using get(), in this example, we fetched google.com from the WebDriver as seen below.
driver.get("https://www.google.com") Step 5: Use the current_url method to obtain the current URL from the driver and print it.
get_url = driver.current_url print("The current url is:"+str(get_url)) driver.quit() Performing URL checks with Current URL in Selenium using Python
One can ensure precise navigation across multiple websites following the methodology of the code below.
from selenium import webdriver from selenium.webdriver.chrome.service import Service from selenium.webdriver.support.ui import WebDriverWait from selenium.webdriver.support import expected_conditions as EC from bs4 import BeautifulSoup import codecs ser = Service(r"C:/Users/Asus/Downloads/chromedriver_win32/chromedriver.exe") driver = webdriver.Chrome(service=ser) driver.get("https://www.google.com") get_url = driver.current_url print("The current url is:"+str(get_url)) #Redirect val = input("Enter a url: ") wait = WebDriverWait(driver, 10) driver.get(val) wait.until(EC.url_to_be(val)) page_source = driver.page_source soup = BeautifulSoup(page_source,features="html.parser") title = soup.title.text file=codecs.open('article_titles.txt', 'a+') file.write(title+"\n") file.close() get_url = driver.current_url print("The current url is:"+str(get_url)) val = input("Enter a url: ") wait = WebDriverWait(driver, 10) driver.get(val) wait.until(EC.url_to_be(val)) page_source = driver.page_source soup2 = BeautifulSoup(page_source,features="html.parser") title = soup2.title.text file=codecs.open('article_titles.txt', 'a+') file.write(str(title)+"\n") file.close() get_url = driver.current_url print("The current url is:"+str(get_url)) driver.quit() The current url is:https://www.google.com/
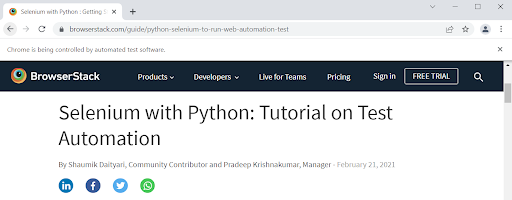
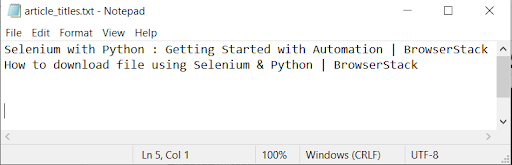
The program first opens https://www.google.com/. Then it asks for a URL input; The URL of the article Selenium with Python : Getting Started with Automation is entered as input by the user. The title of the article on this page is then scraped and stored in article_titles.txt as shown below.
Fetching the input URL and scraping the title of the article.
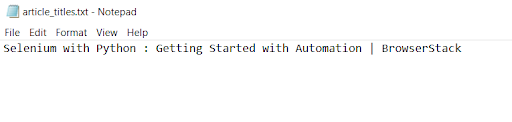
Writing the article title into article_titles.txt.
Saving the article_titles.txt file.
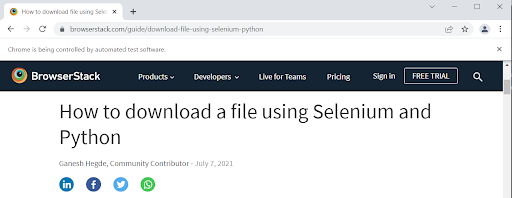
Next another url for an article titled How to download a file using Selenium and Python is entered as input. The program scrapes the title of this article as well, appending it the article_titles.txt document as shown in the screenshots below.
Fetching the input URL and scraping the title of the article
Writing the article title into article_titles.txt
In the example above a series of navigations are demonstrated and the current URL is obtained after each navigation. In order to be certain that the correct navigations are taking place, and the correct URL is being obtained, the wait command is utilized to ascertain that the URL is equivalent to the desired URL before scraping the title.
An explicit wait command is often required when working with the current_url method since a slow internet connection or intermediate URLs can interfere and lead to you retaining an incorrect URL. If you are carrying out web scraping using Selenium Python or testing this could thus lead you to obtain incorrect information. The wait command makes it so that the code waits for a certain condition to occur before carrying on; Depending on the use case there are various conditions, other than the one used above, such as staleness_of or text_to_be_present_in_element which can be utilized.
Following the wait command, the title of the article on the web page was scraped using beautiful soup and then stored in a text file called article_titles. Without the wait command or the check using the current_url method we could end up obtaining the same title twice or no title at all.