«Hello World!» for Microsoft Windows
It’s time to write your first application! The following instructions are for users of Windows Vista, Windows 7, and Windows 8. Instructions for other platforms are in «Hello World!» for Solaris OS, Linux, and Mac OS X and «Hello World!» for the NetBeans IDE.
A Checklist
To write your first program, you’ll need:
- The Java SE Development Kit 8 (JDK 8) You can download the Windows version now. (Make sure you download the JDK, not the JRE.) Consult the installation instructions.
- A text editor In this example, we’ll use Notepad, a simple editor included with the Windows platforms. You can easily adapt these instructions if you use a different text editor.
These two items are all you’ll need to write your first application.
Creating Your First Application
Your first application, HelloWorldApp , will simply display the greeting «Hello world!». To create this program, you will:
- Create a source file A source file contains code, written in the Java programming language, that you and other programmers can understand. You can use any text editor to create and edit source files.
- Compile the source file into a .class file The Java programming language compiler ( javac ) takes your source file and translates its text into instructions that the Java virtual machine can understand. The instructions contained within this file are known as bytecodes.
- Run the program The Java application launcher tool ( java ) uses the Java virtual machine to run your application.
Create a Source File
To create a source file, you have two options:
- You can save the file HelloWorldApp.java on your computer and avoid a lot of typing. Then, you can go straight to Compile the Source File into a .class File.
- Or, you can use the following (longer) instructions.
First, start your editor. You can launch the Notepad editor from the Start menu by selecting Programs > Accessories > Notepad. In a new document, type in the following code:
/** * The HelloWorldApp class implements an application that * simply prints "Hello World!" to standard output. */ class HelloWorldApp < public static void main(String[] args) < System.out.println("Hello World!"); // Display the string. >> Be Careful When You Type
Note: Type all code, commands, and file names exactly as shown. Both the compiler ( javac ) and launcher ( java ) are case-sensitive, so you must capitalize consistently.
HelloWorldApp is not the same as helloworldapp .
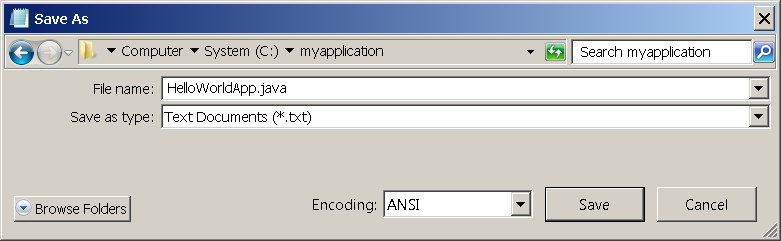
Save the code in a file with the name HelloWorldApp.java . To do this in Notepad, first choose the File > Save As . menu item. Then, in the Save As dialog box:
- Using the Save in combo box, specify the folder (directory) where you’ll save your file. In this example, the directory is myapplication on the C drive.
- In the File name text field, type «HelloWorldApp.java» , without the quotation marks.
- From the Save as type combo box, choose Text Documents (*.txt).
- In the Encoding combo box, leave the encoding as ANSI.
When you’re finished, the dialog box should look like this .
The Save As dialog just before you click Save.
Now click Save, and exit Notepad.
Compile the Source File into a .class File
Bring up a shell, or «command,» window. You can do this from the Start menu by choosing Run. and then entering cmd . The shell window should look similar to the following figure .
The prompt shows your current directory. When you bring up the prompt, your current directory is usually your home directory for Windows XP (as shown in the preceding figure.
To compile your source file, change your current directory to the directory where your file is located. For example, if your source directory is myapplication on the C drive, type the following command at the prompt and press Enter:
Now the prompt should change to C:\myapplication> .
To change to a directory on a different drive, you must type an extra command: the name of the drive. For example, to change to the myapplication directory on the D drive, you must enter D: , as follows:
C:\>D: D:\>cd myapplication D:\myapplication>
If you enter dir at the prompt, you should see your source file, as follows:
C:\>cd myapplication C:\myapplication>dir Volume in drive C is System Volume Serial Number is F2E8-C8CC Directory of C:\myapplication 2014-04-24 01:34 PM . 2014-04-24 01:34 PM .. 2014-04-24 01:34 PM 267 HelloWorldApp.java 1 File(s) 267 bytes 2 Dir(s) 93,297,991,680 bytes free C:\myapplication>
Now you are ready to compile. At the prompt, type the following command and press Enter.
The compiler has generated a bytecode file, HelloWorldApp.class . At the prompt, type dir to see the new file that was generated as follows:
C:\myapplication>javac HelloWorldApp.java C:\myapplication>dir Volume in drive C is System Volume Serial Number is F2E8-C8CC Directory of C:\myapplication 2014-04-24 02:07 PM . 2014-04-24 02:07 PM .. 2014-04-24 02:07 PM 432 HelloWorldApp.class 2014-04-24 01:34 PM 267 HelloWorldApp.java 2 File(s) 699 bytes 2 Dir(s) 93,298,032,640 bytes free C:\myapplication>
Now that you have a .class file, you can run your program.
If you encounter problems with the instructions in this step, consult the Common Problems (and Their Solutions).
Run the Program
In the same directory, enter the following command at the prompt:
You should see the following on your screen:
C:\myapplication>java -cp . HelloWorldApp Hello World! C:\myapplication>
Congratulations! Your program works!
If you encounter problems with the instructions in this step, consult the Common Problems (and Their Solutions).
Previous page: «Hello World!» for the NetBeans IDE
Next page: «Hello World!» for Solaris OS, Linux, and Mac OS X
How to Run Java Program?
At first, check that Java is installed in your system and the path is properly set then we will see how to run the java program. If Java is not installed on the system or path is not defined properly, then we can’t run any Java programs on our system. After the JDK installation, compiling and running the java program is very easy.
A java file is compiled using the javac command which generates a platform-independent bytecode that can be executed in any machine by a Java Virtual Machine (JVM). The bytecode is executed using the java command which executes the bytecode and produces the result.
How to Run a Java Program Using Command Prompt and Notepad?
Here we will be using Notepad and Command Prompt to run the Java programs. Let’s see the process step-by-step:
- Create a new folder.
- Go to the folder, and make the new Java file in that folder.
- Press Alt+D, and just type Notepad there.
- Notepad will open, now paste the java code given below in the Notepad and save it with extension java.
Let’s see the above steps with images:
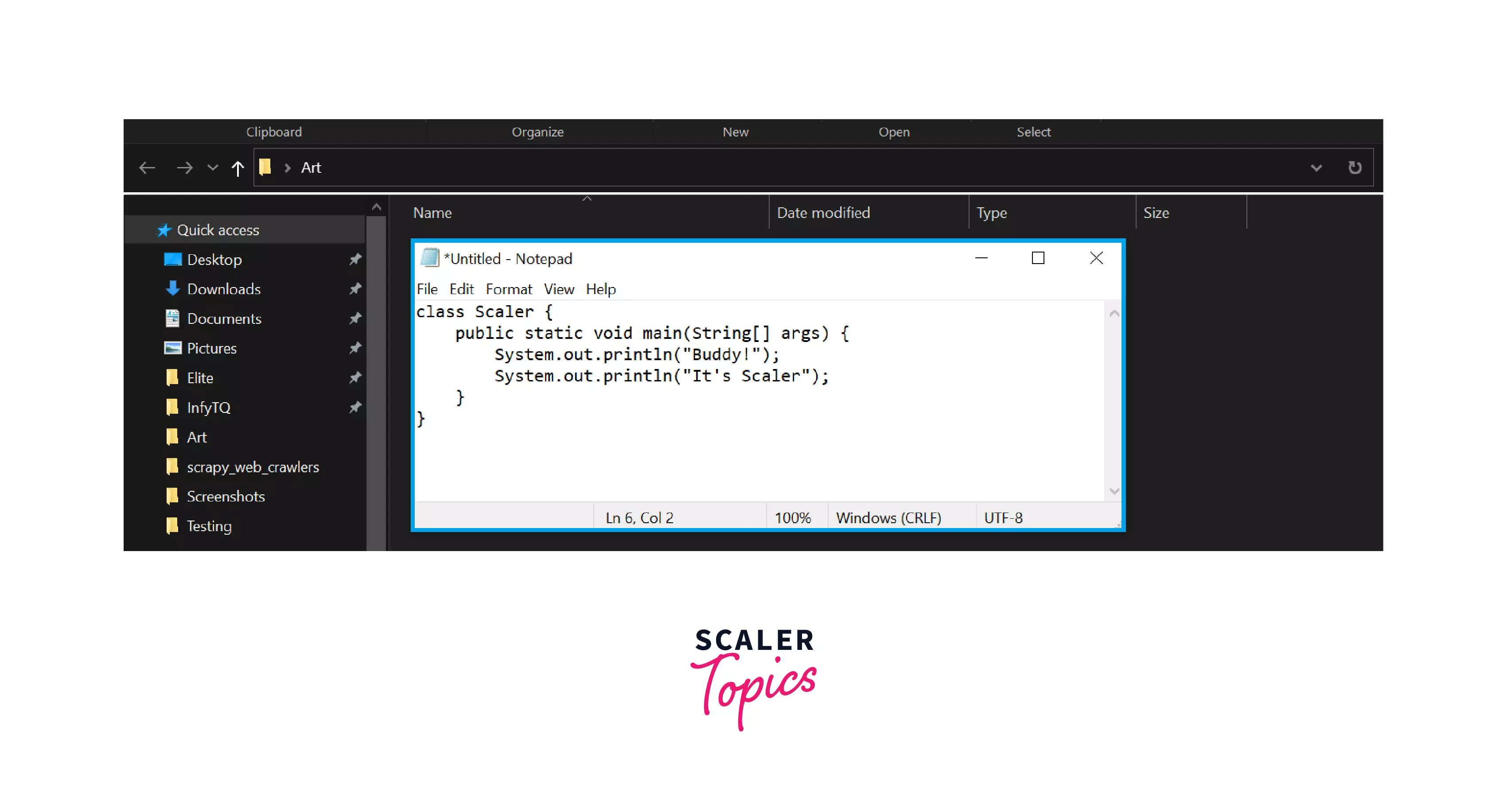
Step 1: I have used the code given below for performing all the below operations. Open the Notepad and copy this code in the notepad and save that file with the extension .java.
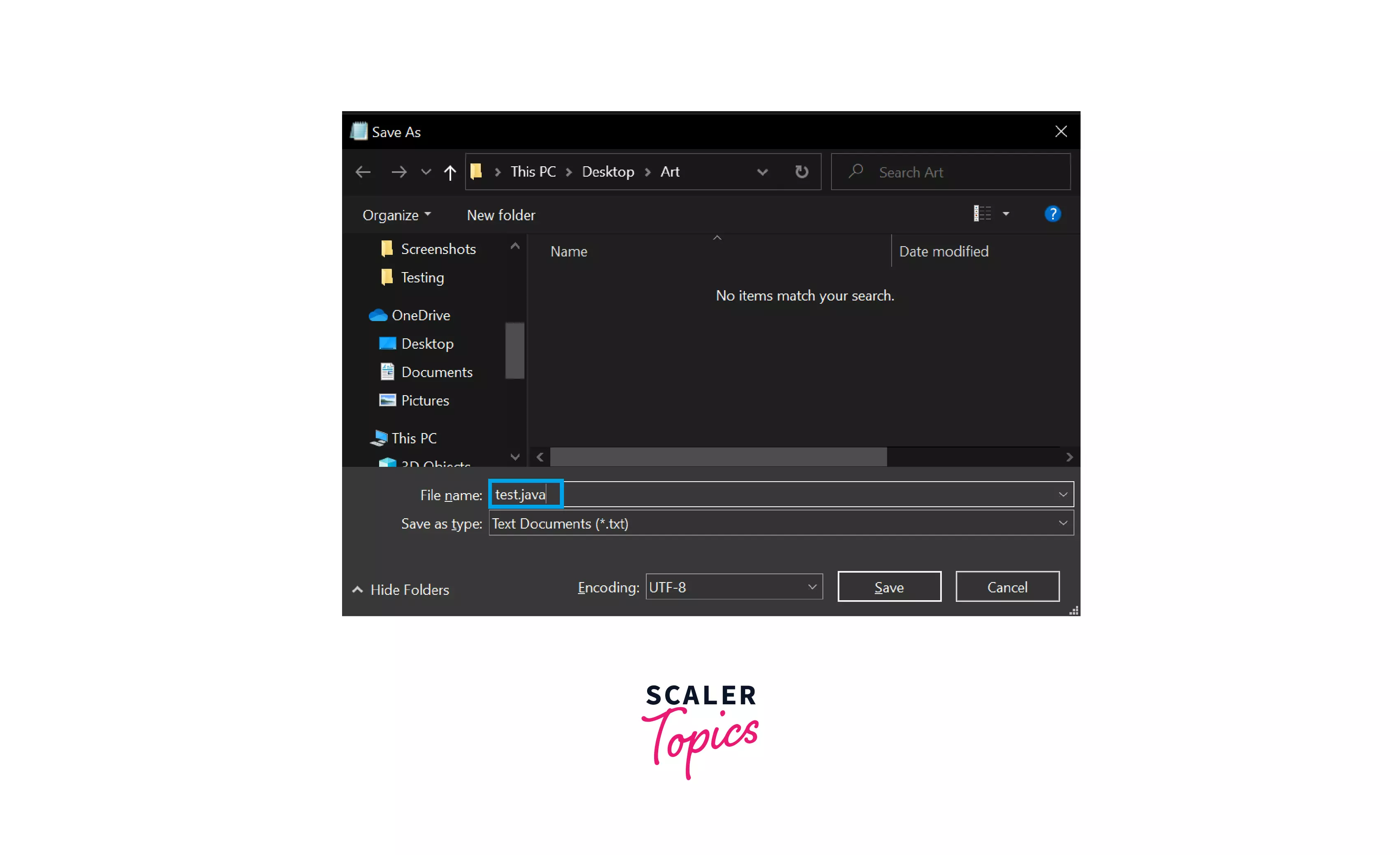
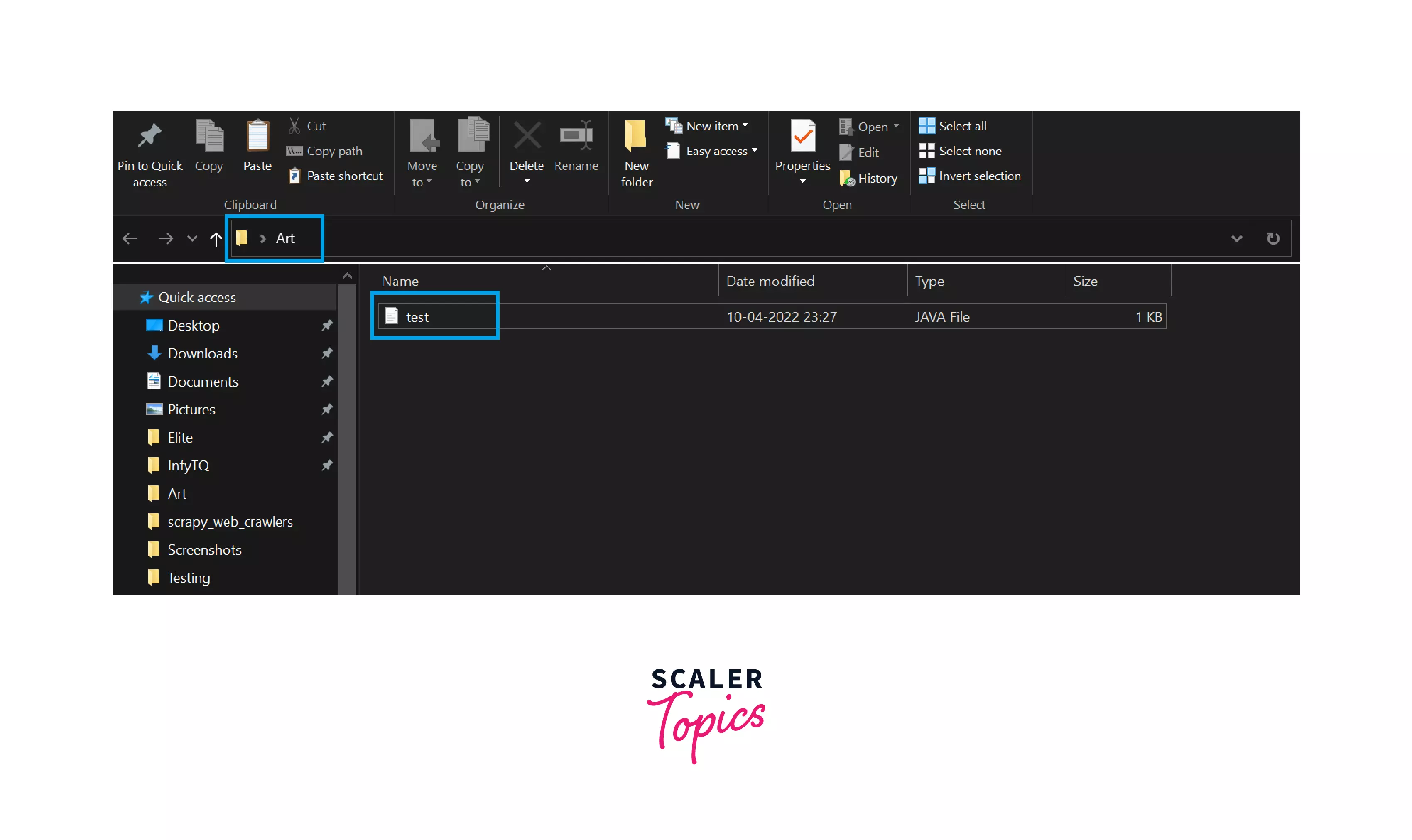
You can see in the below images that, I have written the java code and saved it as test.java. Now the new file will be created with the name test.java.
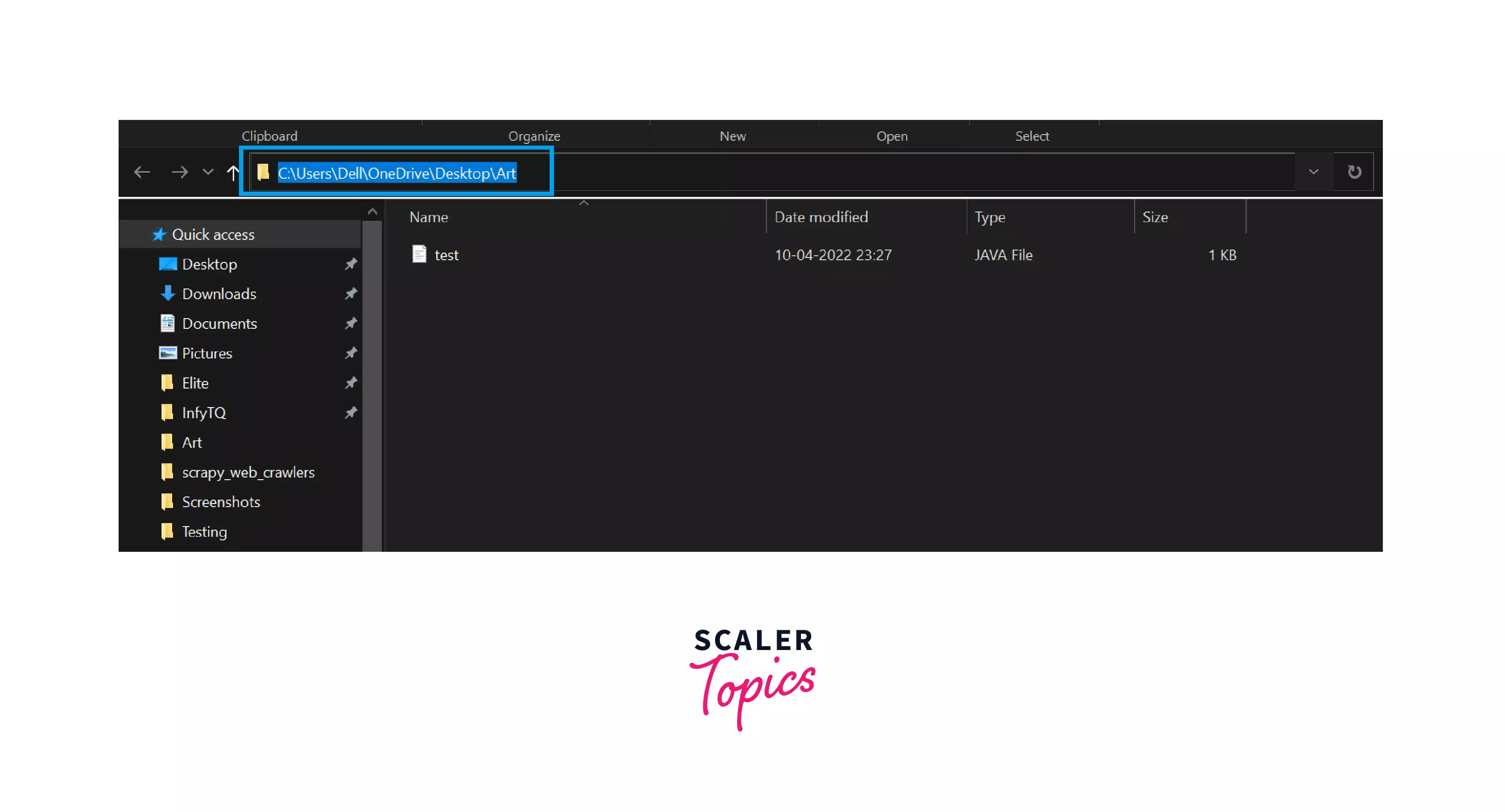
Step 2: You can see that inside the Art folder, there is a java file with the name test.java.
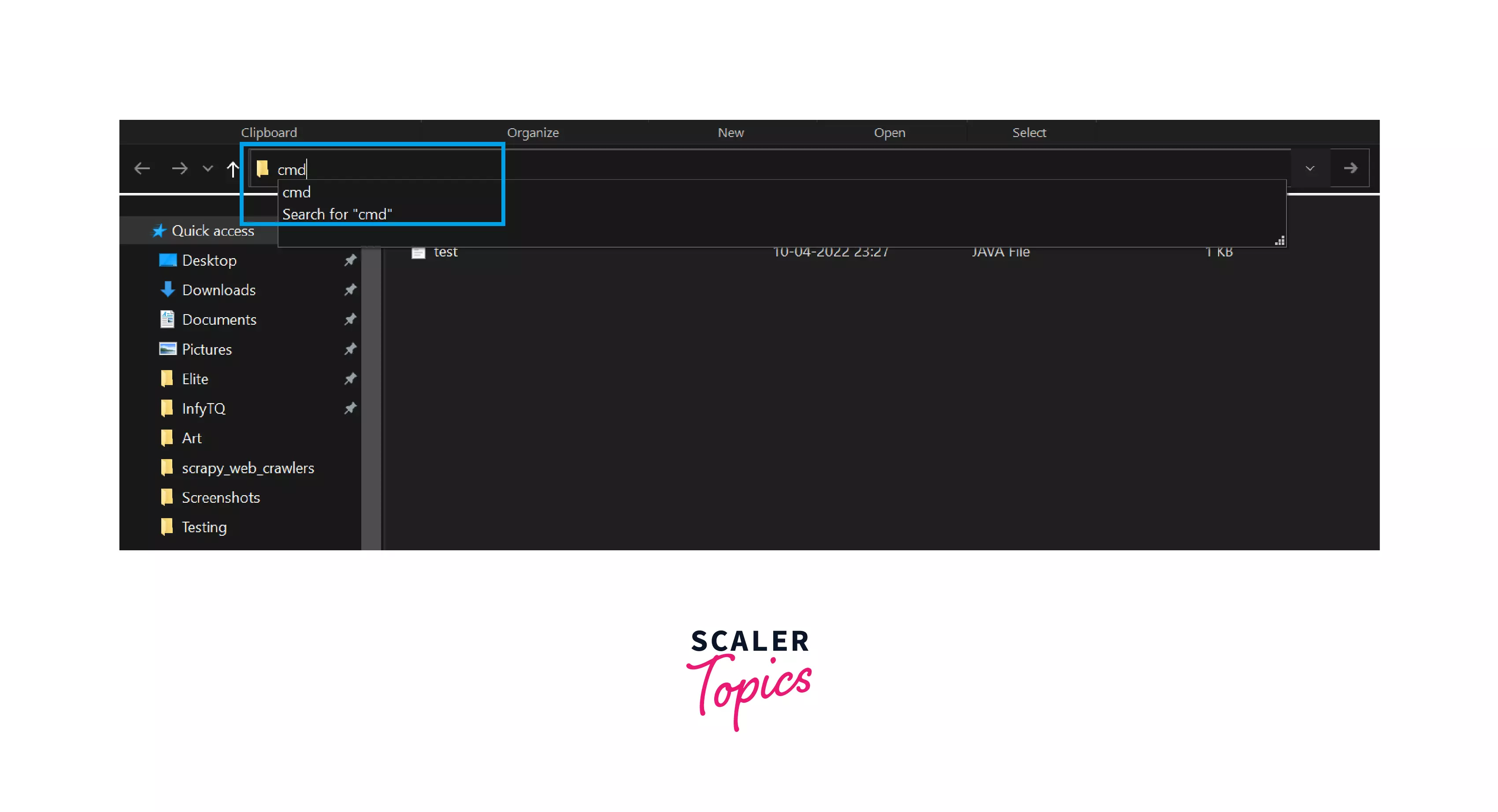
Step 3: Now press Alt+D , and you will get into the above search bar.
Step 4: Type CMD and press enter key.
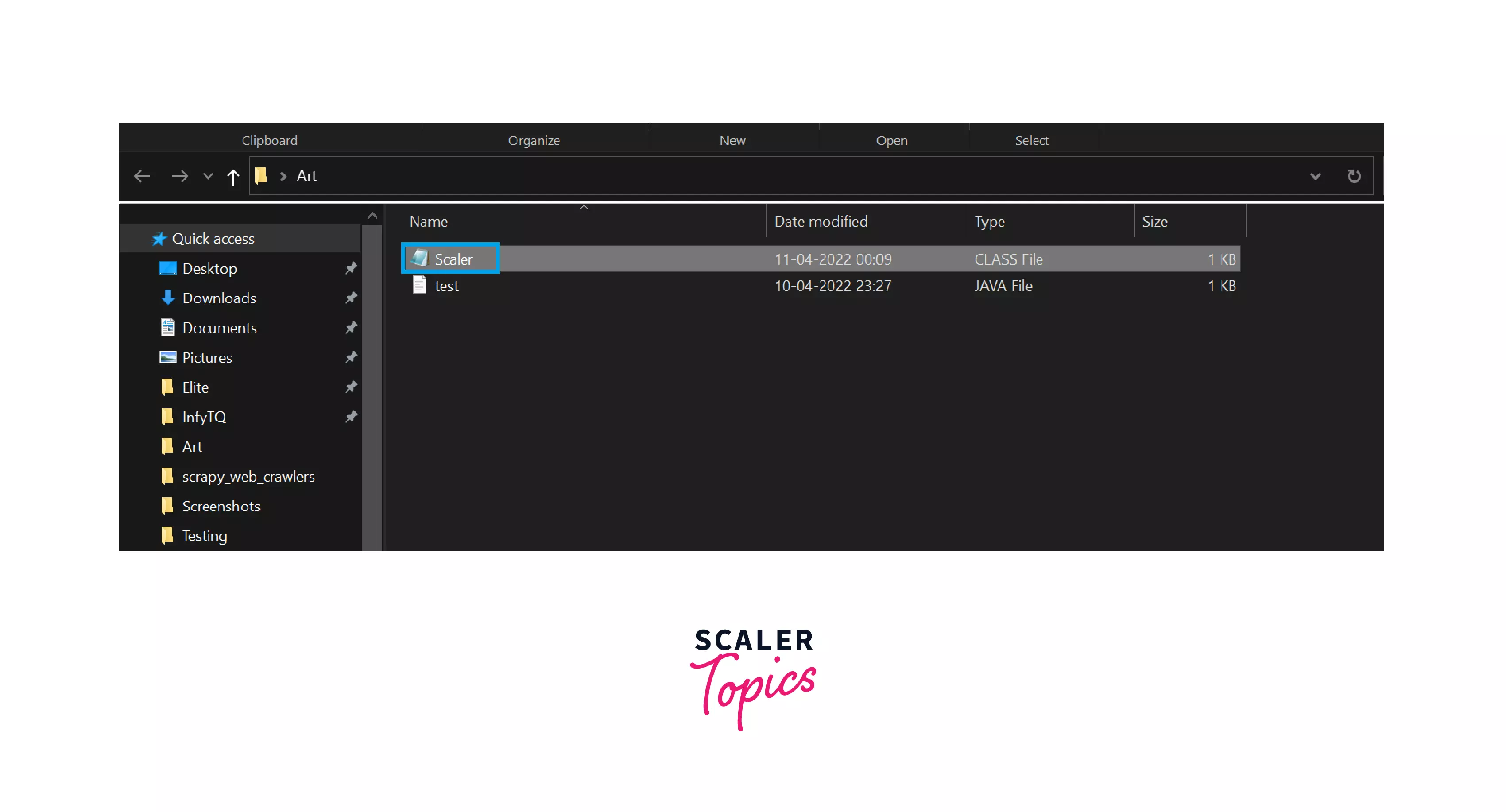
Step 5: You can see that the CMD is open. Now type javac test.java , as you can see in the below image.
Step 6: You can see that a new file has been created with the .class extension . The name of the file would be the name of the class you have used inside your program. In my case, I have used the Scaler as a class name.
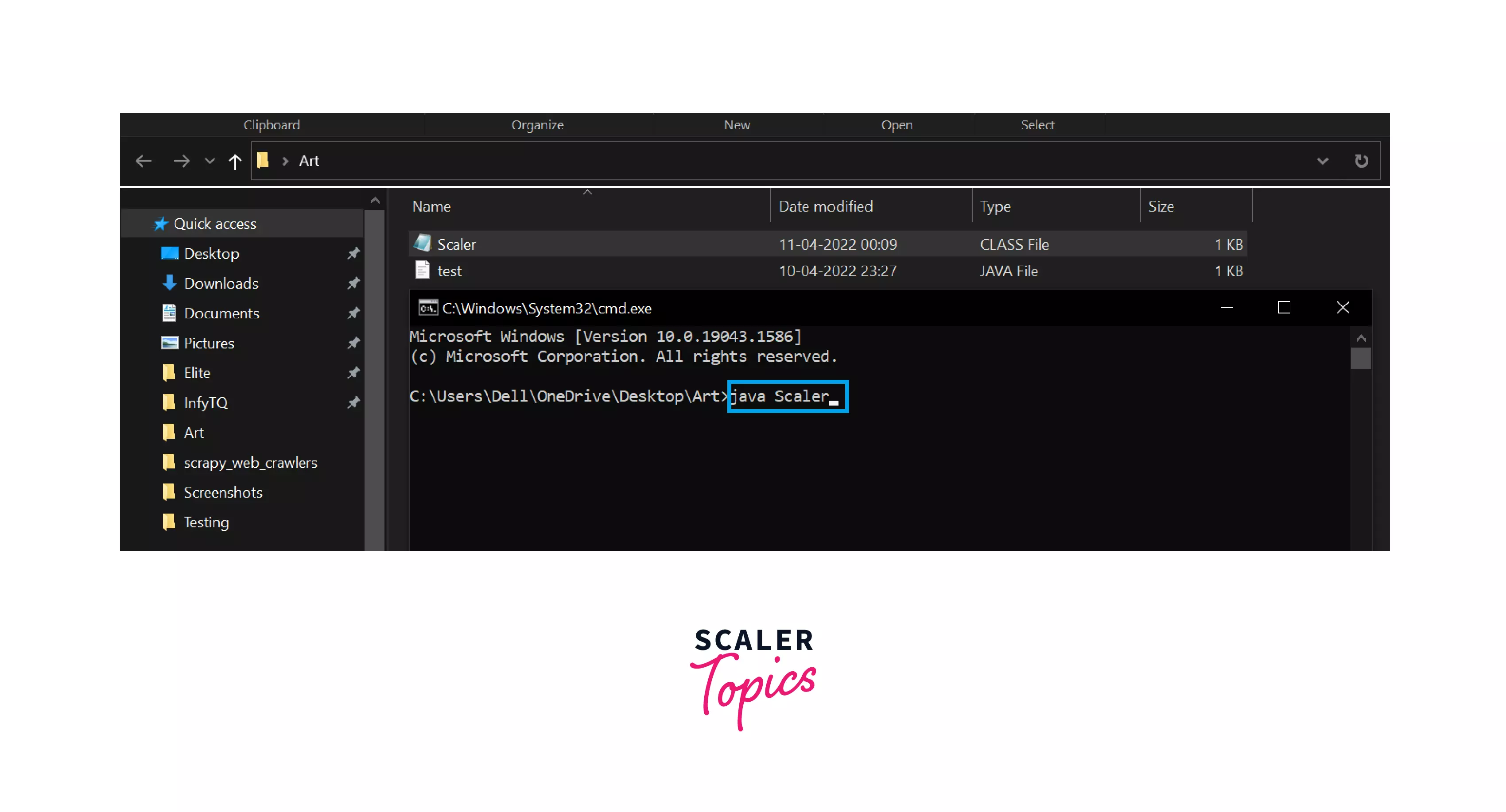
Step 7: Now again, open the cmd and type the command java Scaler as you can see in the below image.
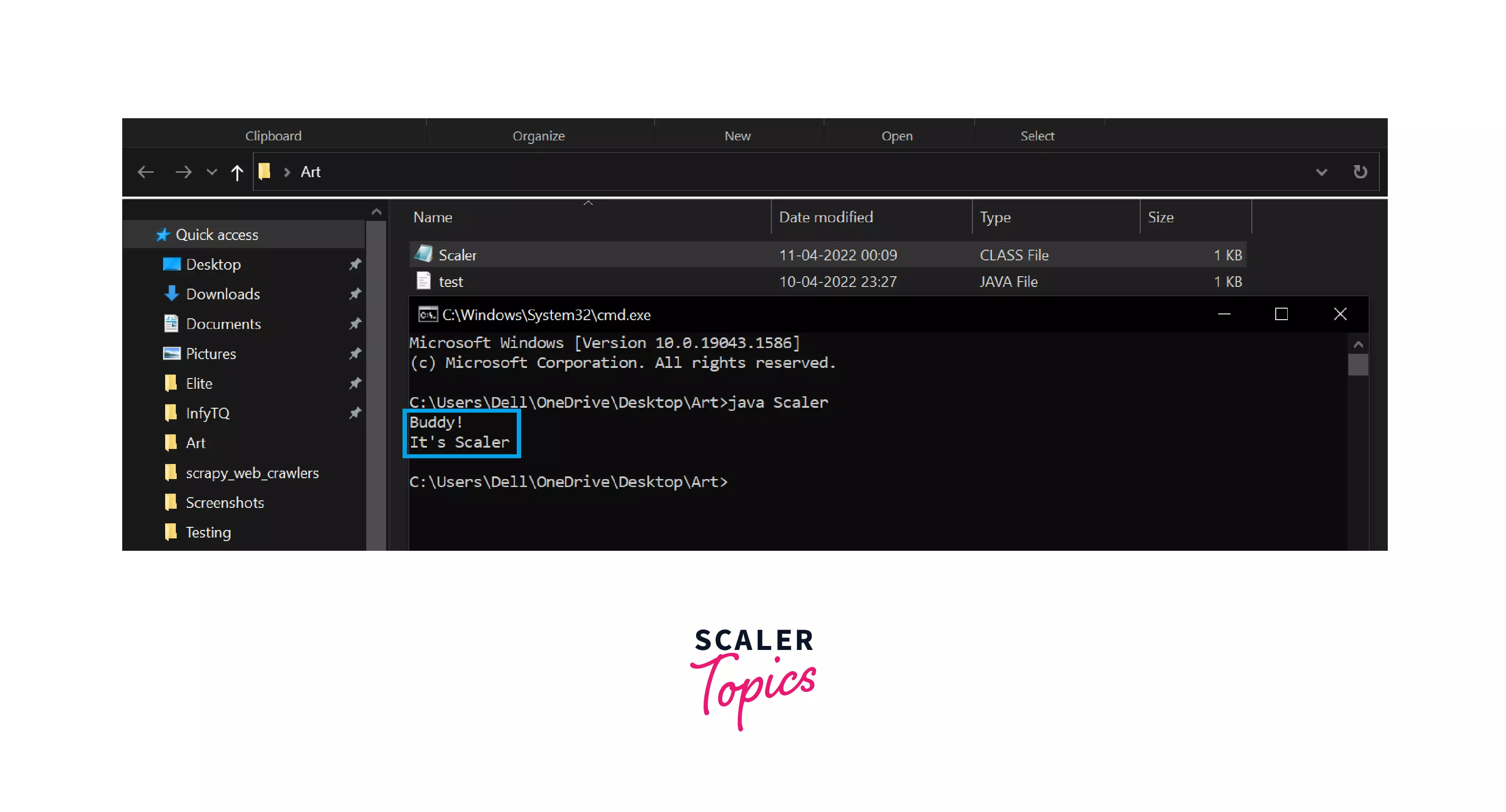
Step 8: At last, you will see that the content of the file has been displayed .
The javac Command
Java programs are compiled using the javac command. It takes .java files as input and generates bytecode.
The java Command
The java command is used to execute Java bytecodes. It takes bytecode as input, executes it, and outputs the result.
Conclusion
- We have seen how to run a Java program using notepad .
- Create the Java file using Notepad and run it using java and javac commands.
- Java programs are compiled using the javac command.
- The java command is used to execute the Java bytecode generated as a result of compilation.