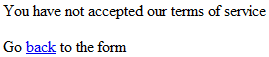- Using the POST method in a PHP form
- Introduction to the form
- Using “isset”
- Can I use both GET and POST in the same page?
- Register globals off?
- More on POST
- PHP Registration Form using GET, POST Methods with Example
- When and why we are using forms?
- Create a form
- Registration Form
- Submitting the form data to the server
- PHP POST method
- PHP GET method
- GET vs POST Methods
- Processing the registration form data
- Thank You You have been registered as Go back to the form Registration Form First name: Last name:
- Registration Form
- More examples
- Simple search engine
- Search Results For The GET method displays its values in the URL Sorry, no matches found for your search term Go back to the form Simple Search Engine - Type in GET Search Term:
- Simple Search Engine - Type in GET
- Working with check boxes, radio buttons
- Thank You You have been registered as Go back to the form Registration Form First name: Last name: Agree to Terms of Service:
- Registration Form
- Summary
Using the POST method in a PHP form
This tutorial will cover how PHP handles form data posted via the POST method.
Introduction to the form
POST data is submitted by a form and “posted” to the web server as form data. POST data is encoded the same way as GET data, but isn’t typically visible to the user in standard browsers.
Most forms use the post method because it “hides” the form data away from the user and doesn’t clutter up the URL in the address bar. Note that GET and POST methods are equally (in)secure.
As easily as a user can monkey with GET data in a URL, the same thing can be done with POST data. You should always assume that the user can submit whatever form and form data that they want to, and process the data accordingly. Don’t trust user input, whether it’s from GET or from POST!
Post data is accessed with the $_POST array in PHP.
php echo("First name: " . $_POST['firstname'] . "
\\n"); echo("Last name: " . $_POST['lastname'] . "
\\n"); ?> form action="myform5.php" method="post"> p>First name: input type="text" name="firstname" />p> p>Last name: input type="text" name="firstname" />p> input type="submit" name="submit" value="Submit" /> form> Using “isset”
You can use the “isset” function on any variable to determine if it has been set or not. You can use this function on the $_POST array to determine if the variable was posted or not. This is often applied to the submit button value, but can be applied to any variable.
php if(isset($_POST['submit']) echo("First name: " . $_POST['firstname'] . "
\\n"); echo("Last name: " . $_POST['lastname'] . "
\\n"); > ?> form action="myform5.php" method="post"> p>First name: input type="text" name="firstname" />p> p>Last name: input type="text" name="firstname" />p> input type="submit" name="submit" value="Submit" /> form> The above code will only display the submitted values if the submit button was clicked.
Can I use both GET and POST in the same page?
GET and POST occupy different spaces in the server’s memory, so both can be accessed on the same page if you want. One use might be to display different messages on a form depending on what’s in the query string.
php if(isset($_POST['submit']) if($_GET['lang'] == "english") echo("First name: " . $_POST['firstname'] . "
\\n"); echo("Last name: " . $_POST['lastname'] . "
\\n"); > else if($_GET['lang'] == "spanish") echo("Nombre: " . $_POST['firstname'] . "
\\n"); echo("Apellido: " . $_POST['lastname'] . "
\\n"); > ?> form method="post"> p>First name: input type="text" name="firstname" />p> p>Last name: input type="text" name="firstname" />p> input type="submit" name="submit" value="Submit" /> form> Instead of using GET and POST arrays, you can also use the $_REQUEST array, which will contain the combined contents of the data. If GET and POST variables have the same name, POST will take priority. It’s recommended not to do this unless you really have to, because it can be confusing, and it’s best to be clear about where an input is coming from.
One more thing to notice: the “action” on the form is now missing. Technically, this is not valid HTML. However, by not putting in an action, browsers will assume that the form is submitting to itself. This is important because it will also preserve the querystring when the form is submitted (the ?lang=english part). You can use server variables like $_SERVER[‘PHP_SELF’] and $_SERVER[‘QUERY_STRING’] to build an action value.
Register globals off?
If you are using a version of PHP earlier than 4.2.0, you should strongly consider setting register_globals to “off” in your .htaccess file (if you are using Apache server) for the exact same reasons as were mentioned in the previous tutorial on GET. If you have PHP 4.2.0 or later, don’t worry about it.
More on POST
POST values are unlimited in length, and thus are very well suited for forms, especially forms with a lot of fields.
PHP Registration Form using GET, POST Methods with Example
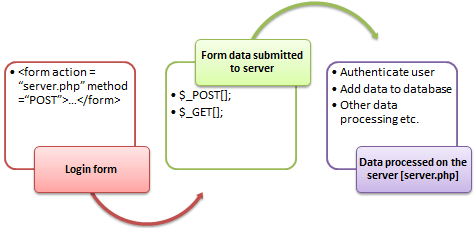
When you login into a website or into your mail box, you are interacting with a form.
Forms are used to get input from the user and submit it to the web server for processing.
The diagram below illustrates the form handling process.
A form is an HTML tag that contains graphical user interface items such as input box, check boxes radio buttons etc.
The form is defined using the
tags and GUI items are defined using form elements such as input.
In this tutorial, you will learn-
When and why we are using forms?
- Forms come in handy when developing flexible and dynamic applications that accept user input.
- Forms can be used to edit already existing data from the database
Create a form
We will use HTML tags to create a form. Below is the minimal list of things you need to create a form.
- Opening and closing form tags
- Form submission type POST or GET
- Submission URL that will process the submitted data
- Input fields such as input boxes, text areas, buttons,checkboxes etc.
The code below creates a simple registration form
Registration Form
First name:
Last name:
Viewing the above code in a web browser displays the following form.
- …
are the opening and closing form tags
- action=”registration_form.php” method=”POST”> specifies the destination URL and the submission type.
- First/Last name: are labels for the input boxes
- are input box tags
- is the new line tag
- is a hidden value that is used to check whether the form has been submitted or not
- is the button that when clicked submits the form to the server for processing
Submitting the form data to the server
The action attribute of the form specifies the submission URL that processes the data. The method attribute specifies the submission type.
PHP POST method
- This is the built in PHP super global array variable that is used to get values submitted via HTTP POST method.
- The array variable can be accessed from any script in the program; it has a global scope.
- This method is ideal when you do not want to display the form post values in the URL.
- A good example of using post method is when submitting login details to the server.
It has the following syntax.
PHP GET method
- This is the built in PHP super global array variable that is used to get values submitted via HTTP GET method.
- The array variable can be accessed from any script in the program; it has a global scope.
- This method displays the form values in the URL.
- It’s ideal for search engine forms as it allows the users to book mark the results.
It has the following syntax.
GET vs POST Methods
| POST | GET |
|---|---|
| Values not visible in the URL | Values visible in the URL |
| Has not limitation of the length of the values since they are submitted via the body of HTTP | Has limitation on the length of the values usually 255 characters. This is because the values are displayed in the URL. Note the upper limit of the characters is dependent on the browser. |
| Has lower performance compared to Php_GET method due to time spent encapsulation the Php_POST values in the HTTP body | Has high performance compared to POST method dues to the simple nature of appending the values in the URL. |
| Supports many different data types such as string, numeric, binary etc. | Supports only string data types because the values are displayed in the URL |
| Results cannot be book marked | Results can be book marked due to the visibility of the values in the URL |
The below diagram shows the difference between get and post
Processing the registration form data
The registration form submits data to itself as specified in the action attribute of the form.
When a form has been submitted, the values are populated in the $_POST super global array.
We will use the PHP isset function to check if the form values have been filled in the $_POST array and process the data.
We will modify the registration form to include the PHP code that processes the data. Below is the modified code
//this code is executed when the form is submittedThank You
You have been registered as
Go back to the form
Registration Form
First name:
Last name:
- checks if the form_submitted hidden field has been filled in the $_POST[] array and display a thank you and first name message. If the form_fobmitted field hasn’t been filled in the $_POST[] array, the form is displayed.
More examples
Simple search engine
We will design a simple search engine that uses the PHP_GET method as the form submission type.
For simplicity’s sake, we will use a PHP If statement to determine the output.
We will use the same HTML code for the registration form above and make minimal modifications to it.
Search Results For
The GET method displays its values in the URL
Sorry, no matches found for your search term
Go back to the form
Simple Search Engine - Type in GET
Search Term:
View the above page in a web browser
The following form will be shown
Type GET in upper case letter then click on submit button.
The following will be shown
The diagram below shows the URL for the above results
Note the URL has displayed the value of search_term and form_submitted. Try to enter anything different from GET then click on submit button and see what results you will get.
Working with check boxes, radio buttons
If the user does not select a check box or radio button, no value is submitted, if the user selects a check box or radio button, the value one (1) or true is submitted.
We will modify the registration form code and include a check button that allows the user to agree to the terms of service.
You have not accepted our terms of service
Thank You
You have been registered as
Go back to the form
Registration Form
First name:
Last name:
Agree to Terms of Service:
View the above form in a browser
Fill in the first and last names
Note the Agree to Terms of Service checkbox has not been selected.
You will get the following results
Click on back to the form link and then select the checkbox
You will get the following results
Summary
- Forms are used to get data from the users
- Forms are created using HTML tags
- Forms can be submitted to the server for processing using either POST or GET method
- Form values submitted via the POST method are encapsulated in the HTTP body.
- Form values submitted via the GET method are appended and displayed in the URL.