- Python Read Text file
- Steps to Read Text File in Python
- Python open() function
- Methods for Reading file contents
- Python close() function
- Examples for Reading a Text file in Python
- Example 1 – Read the entire text file using the read() function
- Example 2 – Read the specific length of characters in a text file using the read() function
- Example 3 – Read a single line in a file using the readline() function
- Example 4- Read text file line by line using the readline() function
- Example 5 – Read all the lines as a list in a file using the readlines() function
- Read characters in file python
- # Table of Contents
- # Read a file character by character in Python
- # Using the open() function without the with statement
- # Adding the individual characters to a List
- # Read a file character by character using a for loop
- # Using the open() function directly
- # Additional Resources
- How to read a number of characters from a text file using Python?
- Syntax
- Example
- Output
- Reading a file in Python
- Example 1
- Output
- Using seek() and read()
- Example 2
- Output
Python Read Text file
Python provides built-in functions to perform file operations, such as creating, reading, and writing files. There are mainly two types of files that Python can handle, normal text files and binary files. In this tutorial, we will take a look at how to read text files in Python.
Steps to Read Text File in Python
In Python, to read a text file, you need to follow the below steps.
Step 1: The file needs to be opened for reading using the open() method and pass a file path to the function.
Step 2: The next step is to read the file, and this can be achieved using several built-in methods such as read() , readline() , readlines() .
Step 3: Once the read operation is performed, the text file must be closed using the close() function.
Now that we have seen the steps to read the file content let’s understand each of these methods before getting into examples.
Python open() function
The open() function opens the file if possible and returns the corresponding file object.
Syntax – open(file, mode=’r’, buffering=-1, encoding=None, errors=None, newline=None, closefd=True, opener=None)
The open() function has a lot of parameters. Let’s take a look at the necessary params for reading the text file. It opens the file in a specified mode and returns a file object.
- file – path like object which represents the file path
- mode (Optional) – The mode is an optional parameter. It’s a string that specifies the mode in which you want to open the file.
Methods for Reading file contents
- read() : The read() function returns the read bytes in the form of string. This method is useful when you have a small file, and you want to read the specified bytes or entire file and store it into a string variable.
- readline() : The readline() function returns one line from a text file and retuns in the form of string.
- readlines() : The readlines() function reads all the lines from the text file and returns each line as a string element in a list.
Python close() function
The file will remain open until you close the file using the close() function. It is a must and best practice to perform this operation after reading the data from the file as it frees up the memory space acquired by that file. Otherwise, it may cause an unhandled exception.
Examples for Reading a Text file in Python
Example 1 – Read the entire text file using the read() function
In the below example, we are reading the entire text file using the read() method. The file can be opened in the read mode or in a text mode to read the data, and it can be stored in the string variable.
# Program to read the entire file using read() function file = open("python.txt", "r") content = file.read() print(content) file.close() # Program to read the entire file (absolute path) using read() function file = open("C:/Projects/Tryouts/python.txt", "r") content = file.read() print(content) file.close()Dear User, Welcome to Python Tutorial Have a great learning . CheersExample 2 – Read the specific length of characters in a text file using the read() function
There are times where you need to read the specific bytes in a file. In that case, you can use the read() function by specifying the bytes. The method will output only the specified bytes of characters in a file, as shown below.
# Program to read the specific length # of characters in a file using read() function file = open("python.txt", "r") content = file.read(20) print(content) file.close() Example 3 – Read a single line in a file using the readline() function
If you want to read a single line in a file, then you could achieve this using readline() function. You also use this method to retrieve specific bytes of characters in a line, similar to the read() method.
# Program to read single line in a file using readline() function file = open("python.txt", "r") content = file.readline() print(content) file.close()Example 4- Read text file line by line using the readline() function
If you want to traverse the file line by line and output in any format, then you could use the while loop with the readline() method as shown below. This is the most effective way to read the text file line by line in Python.
# Program to read all the lines in a file using readline() function file = open("python.txt", "r") while True: content=file.readline() if not content: break print(content) file.close() Dear User, Welcome to Python Tutorial Have a great learning . CheersExample 5 – Read all the lines as a list in a file using the readlines() function
The readlines() method will read all the lines in the file and outputs in a list of strings, as shown below. Later you can use the list to traverse and extract the specified content from the list.
# Program to read all the lines as a list in a file # using readlines() function file = open("python.txt", "r") content=file.readlines() print(content) file.close() ['Dear User,\n', 'Welcome to Python Tutorial\n', 'Have a great learning . \n', 'Cheers']Read characters in file python
Last updated: Feb 22, 2023
Reading time · 4 min
# Table of Contents
# Read a file character by character in Python
To read a file character by character:
- Open the file in reading mode.
- Use the file.read(1) method to read the file character by character in a while loop.
- Use a break statement to exit the loop at the end of the file.
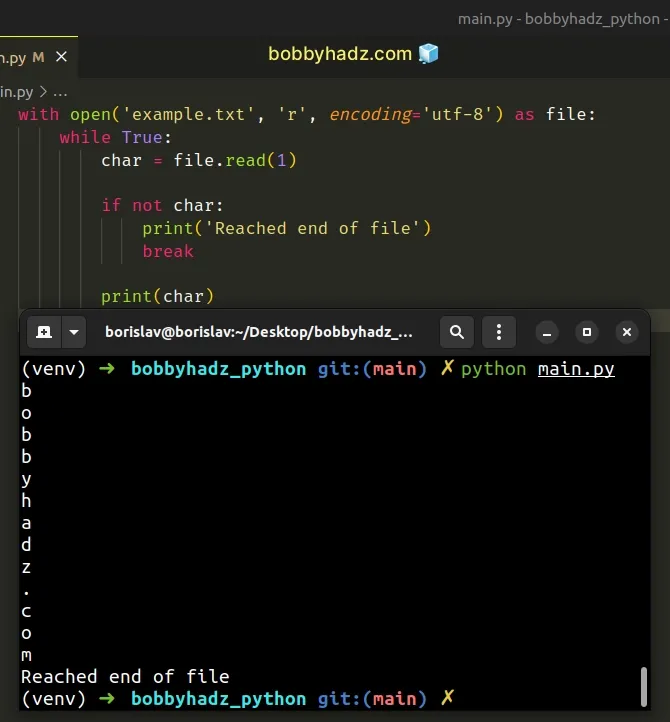
Copied!with open('example.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file: while True: char = file.read(1) if not char: print('Reached end of file') break print(char)
The code sample assumes that you have an example.txt file located in the same directory.
We used the with statement to open the file in reading mode.
The statement automatically takes care of closing the file for us.
We used a while True loop to iterate until we reach the end of the file.
The file.read() method takes a size argument that represents the number of characters to read from the file.
If you are reading a file in binary mode, then size represents the size of bytes to be read from the file.
We set the size argument to 1 to read the file character by character.
If the end of the file has been reached, the file.read() method returns an empty string.
On each iteration, we use an if statement to check if the end of the file has been reached.
If the condition is met, we use the break statement to exit the while loop.
The break statement breaks out of the innermost enclosing for or while loop.
# Using the open() function without the with statement
An alternative approach is to use the open() function without the with statement.
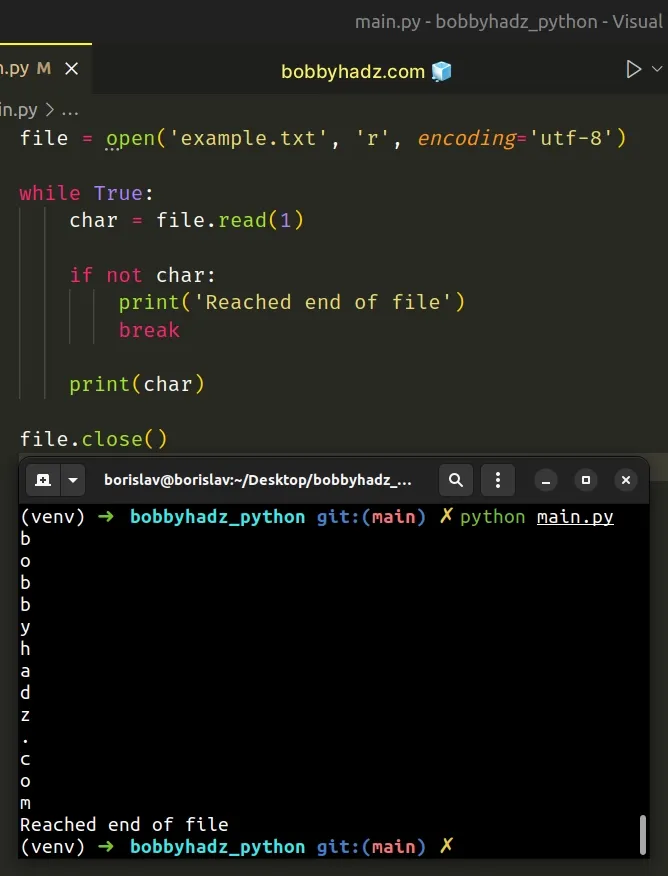
Copied!file = open('example.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') while True: char = file.read(1) if not char: print('Reached end of file') break print(char) file.close()
The code sample achieves the same result but uses the open() function without with .
When we use the open() function directly, we have to take care of closing the file.
The with open() statement should be your preferred approach because it takes care of closing the file even if an error occurs.
# Adding the individual characters to a List
You can use the append() method if you need to add the individual characters to a list.
Copied!with open('example.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file: characters = [] while True: char = file.read(1) if not char: print('Reached end of file') break characters.append(char) print(char) print(characters) # 👉️ ['a', 'p', 'p', 'l', 'e']
On each iteration of the while loop, we add the current character to a list.
The list.append() method adds an item to the end of the list.
Alternatively, you can use a for loop.
# Read a file character by character using a for loop
This is a four-step process:
- Open the file in reading mode.
- Use a for loop to iterate over the file.
- Use a nested for loop to iterate over each line.
- The nested for loop will read the file character by character.
Copied!with open('example.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file: for line in file: for char in line: print(char)
The code sample assumes that you have an example.txt file located in the same directory.
We used a for loop to iterate over the collection of lines in the file.
The nested for loop is used to iterate over each line.
The char variable gets assigned each character.
When using this approach, we store an entire line in memory, which might not be suitable if your file has very long lines.
The while loop from the first example doesn’t have this issue.
On the other hand, when using a nested for loop, we don’t have to manually break out of the loop as it is done for us automatically.
# Using the open() function directly
Here is an equivalent example that uses the open() function directly.
Copied!file = open('example.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') for line in file: for char in line: print(char) file.close()
Notice that we had to call the file.close() method to avoid memory leaks.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Remove the Extension from a Filename in Python
- How to save user input to a File in Python
- Write a List of Tuples to a File in Python
- Write a String to a File on a New Line every time in Python
- How to check if a File is Empty in Python
- Count number of unique Words in a String or File in Python
- Create a file name using Variables in Python
- How to create a Zip archive of a Directory in Python
- How to recursively delete a Directory in Python
- OSError: [Errno 8] Exec format error in Python [Solved]
- OSError: [WinError 193] %1 is not a valid Win32 application
- How to open an HTML file in the Browser using Python
I wrote a book in which I share everything I know about how to become a better, more efficient programmer.
How to read a number of characters from a text file using Python?
Python has a built-in file creation, writing, and reading capabilities. In Python, there are two sorts of files that can be handled: text files and binary files (written in binary language, 0s, and 1s).
Let us understand how to open a file in python. Python is a good general purpose programming language that has a lot of helpful file IO functions and modules in its standard library. You can use the built in open() function to open a file object for either reading or writing. You can use it to open a file in the following way.
Syntax
The syntax of the open() method is as follows.
File = open(“txt_file_name” ,”access_mode”)
Example
The following is an example to open a file named example.txt in read mode.
Output
On executing the above program, the following output is generated.
The file example.txt is opened in read mode.
Reading a file in Python
To read the contents of a file, use file_name.read(size), which reads a specified amount of data and returns it as a string. The size is a number argument that can be used. The complete contents of the file will be read and returned if size is omitted or negative. Otherwise, the maximum number of bytes read and returned is size. The file_name.read() will return an empty string if the file has reached its end («»).
Example 1
In the following example, if you wish to read 10 ASCII characters, the value 15 has to be passed as a parameter. Then, close the file using the close() function.
file = open('example.txt', 'r') print(file.read(15)) file.close() Output
On executing the above program, the following output is generated.
Using seek() and read()
To read a specific number of characters from a particular position in the file we can use seek() function. The seek() function in Python is used to shift the file handler’s position to a certain location. A file handle functions similarly to a cursor, indicating where data should be read or written in the file.
The read() function reads a specified number of bytes from a file and returns them. The default value is 1, which means the entire file.
Example 2
The following is an example to read characters from a file. Firstly, the file is opened in the read only mode. To start reading from a specific position in a file, seek() function is used. The read characters are printed using the print() function. The file is then closed using the close() function.
#python program to read characters from a file #Opening a file in read access mode file = open('example.txt', 'r') #To start reading from a specific position in a file, for say 10 #the read happens from the 10th position file.seek(10) #printing 15 characters using read() print(file.read(55)) #closing the opened file file.close() Output
On executing the above program, the following output is generated.
important because it develops our thoughts, gives us e