Python Script to Open a Web Browser
In this article we will be discussing some of the methods that can be used to open a web browser (of our choice) and visit the URL we specified, using python scripts.
In the Python package, we have a module named webbrowser, which includes a lot of methods that we can use to open the required URL in any specified browser we want. For that, we just have to import this module to our script file, and then we have to call some of its functions (declared and defined below) with our required inputs. Hence this module will then open up the browser we want and will get the page we want.
The methods present in this module are described below:
| S No. | Syntax of Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | webbrowser.open(url, new = 0, autoraise = true) | This is the main method where the web browser with the passed URL is opened and is displayed to the user. If the parameter “new” is 0 then URL is opened in the same browser and if it is 1 then URL is opened in another browser and if it’s 2, then the page is opened in another tab. |
| 2 | webbrowser.open_new(url) | URL passed is opened in the a new browser if it is possible to do that, else it is opened in default one. |
| 3 | webbrowser.open_new_tab(url) | Opens new tab of passpage URL passed in the browser which is currently active. |
| 4 | webbrowser.get(using=None) | This command is used to get the object code for the web browser we want to use. In simple words,, we could use this command to get the code of the web browser (stored in python) and then we could use that code to open that particular web browser. We passes the name of the web browser which we want to use as a string. |
| 5 | webbrowser.register(name, constructor, instance=None, preferred=False) | This method is used to register the name of the favorite browser in the Python environment if its code was not registered previously. Actually, at the beginning, none of the browsers is registered and only the default one is called each time. Hence we had to register them manually. |
Now we are going to use these methods to see how we could open browsers with our passed URLs.
Below is the implementation:
webbrowser — Convenient web-browser controller¶
The webbrowser module provides a high-level interface to allow displaying web-based documents to users. Under most circumstances, simply calling the open() function from this module will do the right thing.
Under Unix, graphical browsers are preferred under X11, but text-mode browsers will be used if graphical browsers are not available or an X11 display isn’t available. If text-mode browsers are used, the calling process will block until the user exits the browser.
If the environment variable BROWSER exists, it is interpreted as the os.pathsep -separated list of browsers to try ahead of the platform defaults. When the value of a list part contains the string %s , then it is interpreted as a literal browser command line to be used with the argument URL substituted for %s ; if the part does not contain %s , it is simply interpreted as the name of the browser to launch. 1
For non-Unix platforms, or when a remote browser is available on Unix, the controlling process will not wait for the user to finish with the browser, but allow the remote browser to maintain its own windows on the display. If remote browsers are not available on Unix, the controlling process will launch a new browser and wait.
The script webbrowser can be used as a command-line interface for the module. It accepts a URL as the argument. It accepts the following optional parameters: -n opens the URL in a new browser window, if possible; -t opens the URL in a new browser page (“tab”). The options are, naturally, mutually exclusive. Usage example:
python -m webbrowser -t "https://www.python.org"
This module does not work or is not available on WebAssembly platforms wasm32-emscripten and wasm32-wasi . See WebAssembly platforms for more information.
The following exception is defined:
exception webbrowser. Error ¶
Exception raised when a browser control error occurs.
The following functions are defined:
webbrowser. open ( url , new = 0 , autoraise = True ) ¶
Display url using the default browser. If new is 0, the url is opened in the same browser window if possible. If new is 1, a new browser window is opened if possible. If new is 2, a new browser page (“tab”) is opened if possible. If autoraise is True , the window is raised if possible (note that under many window managers this will occur regardless of the setting of this variable).
Note that on some platforms, trying to open a filename using this function, may work and start the operating system’s associated program. However, this is neither supported nor portable.
Raises an auditing event webbrowser.open with argument url .
Open url in a new window of the default browser, if possible, otherwise, open url in the only browser window.
webbrowser. open_new_tab ( url ) ¶
Open url in a new page (“tab”) of the default browser, if possible, otherwise equivalent to open_new() .
webbrowser. get ( using = None ) ¶
Return a controller object for the browser type using. If using is None , return a controller for a default browser appropriate to the caller’s environment.
webbrowser. register ( name , constructor , instance = None , * , preferred = False ) ¶
Register the browser type name. Once a browser type is registered, the get() function can return a controller for that browser type. If instance is not provided, or is None , constructor will be called without parameters to create an instance when needed. If instance is provided, constructor will never be called, and may be None .
Setting preferred to True makes this browser a preferred result for a get() call with no argument. Otherwise, this entry point is only useful if you plan to either set the BROWSER variable or call get() with a nonempty argument matching the name of a handler you declare.
Changed in version 3.7: preferred keyword-only parameter was added.
A number of browser types are predefined. This table gives the type names that may be passed to the get() function and the corresponding instantiations for the controller classes, all defined in this module.
python browser
Python browser with PyQt4
In this tutorial we will build a webbrowser with Python. We will use the PyQT library which has a web component. In this tutorial you will learn how to link all the components together. We will use the default rendering engine and not roll one in this tutorial.
If you have not done our pyqt4 beginner tutorial, you could try it. If python-kde4 cannot be found update your repository to find it. The Ubuntu or Debian install guide .
Related course:
PyQt installation
sudo pip install python-qt4
sudo apt-get install qt4-designer
sudo apt-get install pyqt4-dev-tools
sudo apt-get install python-kde4
Creating the GUI with PyQT
Select Main Window and press Create. We now have our designer window open. Drag a KWebView component on the window. If you have a QtWebView (qtwebkit) in the component list. use that instead. We also add an Line Edit on top. Press File > Save As > browser.ui. Run the command:
pyuic4 browser.ui > browser.py
This will generate a Python file. Remove the line “from kwebview import KWebView” from the bottom of the browser.py file. Change KWebView to QtWebView. We want to use QtWebView instead. If you are lazy to change that, take the browser.py file from below.
QWebView exploration
import sys
from browser import BrowserDialog
from PyQt4 import QtCore, QtGui
from PyQt4.QtCore import QUrl
from PyQt4.QtWebKit import QWebView
class MyBrowser(QtGui.QDialog):
def __init__(self, parent=None):
QtGui.QWidget.__init__(self, parent)
QWebView.__init__(self)
self.ui = BrowserDialog()
self.ui.setupUi(self)
self.ui.lineEdit.returnPressed.connect(self.loadURL)
def loadURL(self):
url = self.ui.lineEdit.text()
self.ui.qwebview.load(QUrl(url))
self.show()
#self.ui.lineEdit.setText(«»)
if __name__ == «__main__»:
app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv)
myapp = MyBrowser()
myapp.ui.qwebview.load(QUrl(‘http://www.pythonspot.com’))
myapp.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
This code will use the UI as defined in browser.py and add logic to it. The lines
self.ui.lineEdit.returnPressed.connect(self.loadURL)
def loadURL(self):
url = self.ui.lineEdit.text()
self.ui.qwebview.load(QUrl(url))
self.show()
#self.ui.lineEdit.setText(«»)
The first line defines the callback or event. If a person presses enter (returnPressed), it will call the function loadURL. It makes sure that once you press enter, the page is loaded with that function. If you did everything correctly, you should be able to run the browser with the command:
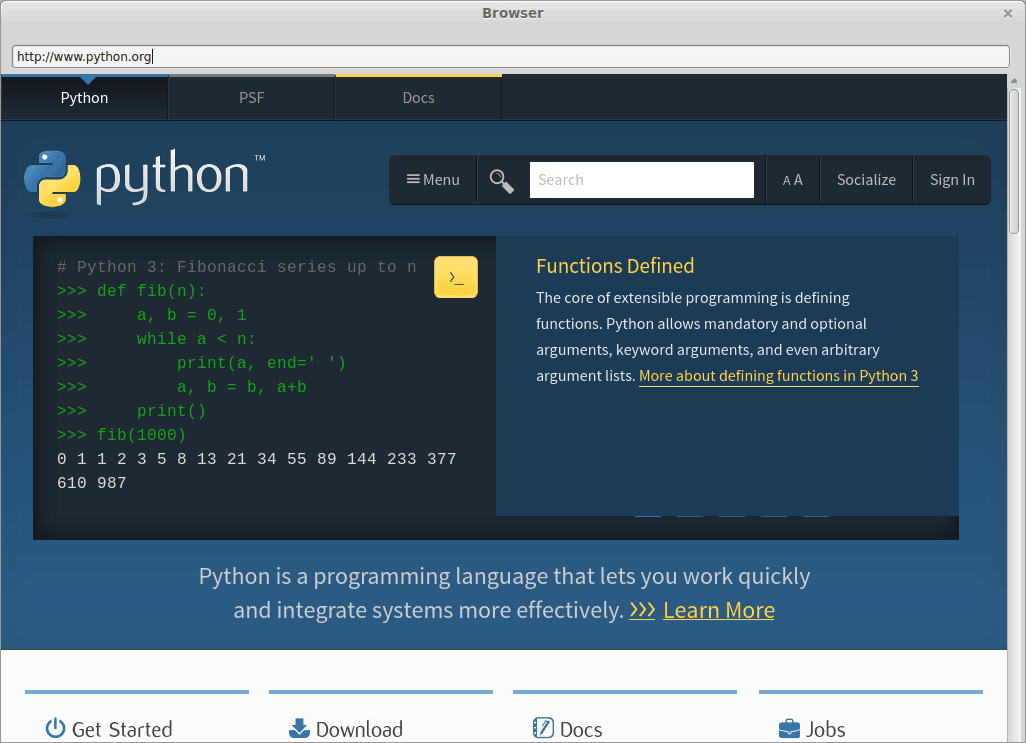
Please make sure you type the full url, e.g. : https://pythonspot.com including the http:// part. Your browser should now start:
If your code does not run, please use the codes below (or look at the differences and change whats wrong):
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Form implementation generated from reading ui file ‘browser.ui’
#
# Created: Fri Jan 30 20:49:32 2015
# by: PyQt4 UI code generator 4.10.4
#
# WARNING! All changes made in this file will be lost!
import sys
from PyQt4 import QtCore, QtGui
from PyQt4.QtGui import QApplication
from PyQt4.QtCore import QUrl
from PyQt4.QtWebKit import QWebView
try:
_fromUtf8 = QtCore.QString.fromUtf8
except AttributeError:
def _fromUtf8(s):
return s
try:
_encoding = QtGui.QApplication.UnicodeUTF8
def _translate(context, text, disambig):
return QtGui.QApplication.translate(context, text, disambig, _encoding)
except AttributeError:
def _translate(context, text, disambig):
return QtGui.QApplication.translate(context, text, disambig)
class BrowserDialog(object):
def setupUi(self, Dialog):
Dialog.setObjectName(_fromUtf8(«Dialog»))
Dialog.resize(1024, 768)
self.qwebview = QWebView(Dialog)
self.qwebview.setGeometry(QtCore.QRect(0, 50, 1020, 711))
self.qwebview.setObjectName(_fromUtf8(«kwebview»))
self.lineEdit = QtGui.QLineEdit(Dialog)
self.lineEdit.setGeometry(QtCore.QRect(10, 20, 1000, 25))
self.lineEdit.setObjectName(_fromUtf8(«lineEdit»))
self.retranslateUi(Dialog)
QtCore.QMetaObject.connectSlotsByName(Dialog)
def retranslateUi(self, Dialog):
Dialog.setWindowTitle(_translate(«Browser», «Browser», None))
import sys
from browser import BrowserDialog
from PyQt4 import QtCore, QtGui
from PyQt4.QtCore import QUrl
from PyQt4.QtWebKit import QWebView
class MyBrowser(QtGui.QDialog):
def __init__(self, parent=None):
QtGui.QWidget.__init__(self, parent)
QWebView.__init__(self)
self.ui = BrowserDialog()
self.ui.setupUi(self)
self.ui.lineEdit.returnPressed.connect(self.loadURL)
def loadURL(self):
url = self.ui.lineEdit.text()
self.ui.qwebview.load(QUrl(url))
self.show()
#self.ui.lineEdit.setText(«»)
if __name__ == «__main__»:
app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv)
myapp = MyBrowser()
myapp.ui.qwebview.load(QUrl(‘http://www.pythonspot.com’))
myapp.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())