- Python TypeError: unhashable type: ‘slice’ Solution
- TypeError: unhashable type: ‘slice’
- TypeError: unhashable type: ‘slice’
- The Solution
- Conclusion
- [Solved] TypeError: Unhashable Type: ‘slice’
- What is a TypeError?
- What is an Unhashable Type?
- What Causes this Error?
- Solution
- TypeError: Unhashable Type: ‘slice’ for Pandas Data Frames
- Solution
- TypeError: Unhashable Type: ‘slice’ for JSON
- Solution
- TypeError: Unhashable Type: ‘slice’ for Beautiful Soup Module
- Solution
- TypeError: Unhashable Type res = cache.get(item)
- Solution
- FAQs on TypeError: Unhashable Type: ‘slice’
- Conclusion
Python TypeError: unhashable type: ‘slice’ Solution
Values in a Python dictionary cannot be sliced like a list. This is because dictionaries can have custom key values. They are not indexed from zero. If you try to slice a dictionary as if it were a list, you’ll encounter the “TypeError: unhashable type: ‘slice’” error.
This guide discusses what this error means and why you see it in your code. It discusses an example of this error to help you solve it.
By continuing you agree to our Terms of Service and Privacy Policy, and you consent to receive offers and opportunities from Career Karma by telephone, text message, and email.
By continuing you agree to our Terms of Service and Privacy Policy, and you consent to receive offers and opportunities from Career Karma by telephone, text message, and email.
TypeError: unhashable type: ‘slice’
A slice is a subset of a sequence such as a string, a list, or a tuple. The name gives away the purpose of a slice: it is “a slice” of a sequence.
Consider the following program:
news_sites = ["New York Times", "Washington Post", "CNN"] print(news_sites[:2])
This code retrieves the first two values in our “news_sites” list and prints them to the console. Our code returns: [‘New York Times’, ‘Washington Post’].
This is an example of slicing. You’re retrieving two objects from the list. By specifying a colon and an index value, you are telling Python which objects to retrieve.
Dictionaries cannot be sliced like a list. Dictionaries do not have any index numbers and so this syntax does not apply.
TypeError: unhashable type: ‘slice’
Build a program that displays information about a keyboard for sale at a computer hardware store. To start, define a dictionary with data about a keyboard:
The program stores information about the name of a keyboard, its price, the brand of the keyboard, and the switch type used by the keyboard. You only want to show: the name of a keyboard, the brand of the keyboard, and its price.
To do this, use slicing to retrieve the first three items in our dictionary. These items are the name of the keyboard, the brand, and the price:
show_to_customer = keyboard[:3]
This code retrieves the first three items in the dictionary. Next, use a for loop to iterate over this list and print each item to the console:
for s in show_to_customer: print(s[1])
You use indexing to retrieve the value from each record in the “show_to_customer” variable. You then print that value to the console using a print() statement.
Let’s run the code and see what happens:
Traceback (most recent call last): File "main.py", line 8, in show_to_customer = keyboard[:3] TypeError: unhashable type: 'slice'
Our code returns an error.
The Solution
Unlike lists, dictionaries cannot be sliced. You cannot retrieve any items in the dictionary using slicing because dictionaries do not have index numbers. Data is stored in key-value pairs. Because dictionaries cannot be sliced, the for loop from earlier is not appropriate.
You must directly specify what values you want to access from our dictionary. To do this, refer to the appropriate key names in the dictionary.
To solve the code, let’s individually access each value you want to display on the console:
keyboard = < "name": "Huntsman Mini", "brand": "Razer", "price": 119.99, "switch_type": "Razer Switches", >print("Name: " + keyboard["name"]) print("Brand: " + keyboard["brand"]) print("Price: $" + str(keyboard["price"])) Each print() statement refers to a different value from the dictionary. The first print statement prints the label “Name: ”, followed by the value of “name” in the dictionary, to the console. The second and third statements print the value of “brand” and “price” to the console, respectively.
You convert the “price” value to a string using the str() method to concatenate it with the “Price: $” label using the concatenation operator (+).
Name: Huntsman Mini Brand: Razer Price: $119.99
The code successfully prints out the three pieces of information you wanted to display to the console. The user can see the name, brand, and price of a keyboard.
Conclusion
The “TypeError: unhashable type: ‘slice’” error is raised when you try to access items from a dictionary using slicing syntax. To solve this error, make sure you refer to the items you want to access from a dictionary directly.
Now you have the knowledge you need to solve this error like an expert!
About us: Career Karma is a platform designed to help job seekers find, research, and connect with job training programs to advance their careers. Learn about the CK publication.
[Solved] TypeError: Unhashable Type: ‘slice’
In this article we will we looking the Python exception TypeError: Unhashable Type: ‘slice’. Python dictionaries store their data in key-value format. Since Python 3.7 dictionaries are considered ordered data.
Index values are not assigned to dictionaries. Therefore, any operation that involves index values like slicing will throw the said exception.
Let’s look at the exception in detail
What is a TypeError?
Any invalid operations performed on a data type object will cause TypeErrors. For example, using the addition operator (+) between a string type and an integer. The common causes for TypeErrors are:
– Unsupported operation between two types
– Incorrect type of list index
– Calling a non-callable identifier
– Iterating through a non-iterative identifier
What is an Unhashable Type?
Hash values are used in place of index values for dictionary elements. Python compares dictionary keys with hash values while working with dictionary elements. We can hash strings or integers but cannot slice them. A slice is nothing but a small subset of a sequential type. It usually consists of a small portion from a bigger data sequence. As slice values are unhashable, any attempts to slice hashed types raise said exception.
What Causes this Error?
Any slice operations on a dictionary object will give rise to this error . A Python Dictionary is a hashable type and does not support slicing like other sequential data types.
Let’s look at the following example:
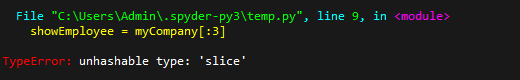
myCompany = < 'employee1':, 'employee2':, 'employee3':, 'employee4':, 'employee5': > showEmployee = myCompany[:3] print(showEmployee)
Solution
Using the print() statement and the dictionary keys, we can display the contents of the dictionary.
myCompany = < 'employee1':, 'employee2':, 'employee3':, 'employee4':, 'employee5': > print("Employee 1 " + myCompany["employee1"]) print("Employee 2 " + myCompany["employee2"]) print("Employee 3" + myCompany["employee3"]) TypeError: Unhashable Type: ‘slice’ for Pandas Data Frames
The below code demonstrates how we can print a subset of rows in a pandas data frame.
print(sample_data[25:150, :]) print(sample_data[100:300, :].shape)
Error Output
TypeError: unhashable type: 'slice'Solution
.iloc() function allows indexing in pandas data frames. .iloc() function is similar to normal indexing, except that its indices are based on position.
print(sample_data.iloc[25:1150, :]) print(sample_data.iloc[100:300, :].shape)
TypeError: Unhashable Type: ‘slice’ for JSON
Let’s refer to the following implementation. An API request is sent data is fetched in JSON format.
import requests import json req = requests.get('http://sampleAPI.net/sample) date = json.loads(req.text) data = req.json() for i in data['myItem'][:3]: res = i['attribute'] print(res) TypeError: unhashable type: 'slice' error
Solution
myItem seems to be of type Dictionary. Therefore, any attempt at indexing will throw the exception. It’s better to use the .items() function.
import requests import json req = requests.get('http://sampleAPI.net/sample) date = json.loads(req.text) data = req.json() for i in data(['myItem'].items())[:3]: res = i['attribute'] print(res) TypeError: Unhashable Type: ‘slice’ for Beautiful Soup Module
The BeautifulSoup module is used for web scraping data from HTML and XML sources. Let’s look at the following implementation that scrapes text data from a website.
import requests from bs4 import BeautifulSoup r = requests.get('https://samplewebsite.com/samplePage01') soup = BeautifulSoup(r.text, 'html.parser') results = soup.find_all('td', attrs=) records = [] for result in results: name = result.contents[0][0:-1] TypeError: unhashable type: 'slice' error
Solution
.contents consist of tag objects. Therefore an exception is thrown when accessing a tag attributes dictionary.
Furthermore, using .strings allows you to fetch only NavigableString data.
for result in results: name = list(result.strings)[0][0:-1]
TypeError: Unhashable Type res = cache.get(item)
Let’s look at the following implementation for a “Random Forest” model.
import pandas as pd from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix import sklearn import sklearn.datasets import sklearn.ensemble import numpy as np import lime import lime.lime_tabular class Randomforest: def __init__(self): self.trained_model = None self.clf = None pass . . . . rf = Randomforest() . . . . dataset = pd.read_csv("filename.csv") train_x, test_x, train_y, test_y = rf.split_dataset(dataset, 0.7, Headers[1:-1], Headers[-1]) trained_model = rf.random_forest_classifier(train_x, train_y) predictions = trained_model.predict(test_x) feature_names = Headers[1:-1] class_names = ['1', '0'] explainer = lime.lime_tabular.LimeTabularExplainer(train_x, feature_names= feature_names, class_names=class_names, categorical_features= None, categorical_names=None, discretize_continuous=True, kernel_width=3) TypeError: Unhashable TypeSolution
We are passing the training data ( train_x ) into the model as a pandas data frame. Pandas do not allow slice operations on data frames. Hence, pass train_x as train_x.values .
FAQs on TypeError: Unhashable Type: ‘slice’
TypeErrors are one of Python’s many exceptions types. Operations performed on unsupported object types cause the error. The common causes for TypeErrors are:
– Unsupported operation between two types
– Incorrect type of list index
– Calling a non-callable identifier
– Iterating through a non-iterative identifier
Sliceable objects in Python include:
– Strings
– Bytes
– Tuples
– Lists
A sliceable object must support indexing. Hashable data types are not sliceable.
Conclusion
Indexing on dictionary types and other hashable data types gives rise to the error.
The main reasons for TypeErrors are:
- Unsupported operation between two types
- The incorrect type of list index
- Calling a non-callable identifier
- Iterating through a non-iterative identifier
A more convenient way to access dictionary elements is to provide the key value. An iteration may be provided to access multiple dictionary elements at a time.
Therefore, we have demonstrated various instances where the error may take place.