- Python Tkinter Combobox Event Binding
- Import the Module
- Tkinter combobox bind()
- Example of Tkinter Combobox Event Binding
- Tkinter Combobox
- Introduction to the Tkinter Combobox widget
- Create a combobox
- Define value list
- Bind events
- Set the current value
- Python Tkinter combobox example
- Summary
- Python tkinter combobox change
- Отслеживание выбора значения
Python Tkinter Combobox Event Binding
Combobox is an important widget, and it is found in many applications. It allows a user to select from a list of options. It holds multiple values but shows only one option at a time. You have generally seen this on a Macintosh or Windows interface. In this article, you will learn how to call a function on selecting an option from a combobox using Python Tkinter.
Import the Module
The combobox widget is a class of the ttk module of the Tkinter library. To start using Ttk, first import the Ttk module and follow the Tk module. By this way, we override the widgets of the Tk module with the Ttk module. The ttk module provides a better look and feel across many platforms. It is more modern and configured with styles.
Tkinter combobox bind()
In the previous article, we introduced a simple example of Tkinter combobox. Here you will learn the Tkinter combobox event binding process. The bind() method is used to bind the callback function with the combobox event when the user selects an option from the dropdown lists. The syntax of bind() method is-
widget.bind("event", function)If any event matching the given event occurs in the widget, the given function is called with an object describing the event. The combobox widgets generate a > virtual event when the user selects an element from the list of values.
Example of Tkinter Combobox Event Binding
The following Python program demonstrates how to bind the callbackFunc() function to the ComboboxSelected key pressed event of the ‘Select the Country‘ button. The callbackFunc() function changes the combobox list of choices.
import tkinter as tk from tkinter import ttk # Creating tkinter window and set dimensions window = tk.Tk() window.title('Combobox') window.geometry('500x250') def callbackFunc(event): country = event.widget.get() print(country) # label text for title ttk.Label(window, text = "Choose the country and vote for them", background = 'cyan', foreground ="black", font = ("Times New Roman", 15)).grid(row = 0, column = 1) # Set label ttk.Label(window, text = "Select the Country :", font = ("Times New Roman", 12)).grid(column = 0, row = 5, padx = 5, pady = 25) # Create Combobox n = tk.StringVar() country = ttk.Combobox(window, width = 27, textvariable = n) # Adding combobox drop down list country['values'] = (' India', ' China', ' Australia', ' Nigeria', ' Malaysia', ' Italy', ' Turkey', ' Canada') country.grid(column = 1, row = 5) country.current() country.bind("ComboboxSelected>>", callbackFunc) window.mainloop() Tkinter Combobox
Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn to create a Tkinter combobox widget that allows users to select one value from a set of values.
Introduction to the Tkinter Combobox widget
A combobox is a combination of an Entry widget and a Listbox widget. A combobox widget allows you to select one value in a set of values. In addition, it allows you to enter a custom value.
Create a combobox
To create a combobox widget, you’ll use the ttk.Combobox() constructor. The following example creates a combobox widget and links it to a string variable:
current_var = tk.StringVar() combobox = ttk.Combobox(container, textvariable=current_var)Code language: Python (python)The container is the window or frame on which you want to place the combobox widget.
The textvariable argument links a variable current_var to the current value of the combobox.
To get the currently selected value, you can use the current_var variable:
current_value = current_var.get()Code language: Python (python)Alternatively, you can use the get() method of the combobox object:
current_value = combobox.get()Code language: Python (python)To set the current value, you use the current_var variable or the set() method of the combobox object:
current_value.set(new_value) combobox.set(new_value)Code language: Python (python)Define value list
The combobox has the values property that you can assign a list of values to it like this:
combobox['values'] = ('value1', 'value2', 'value3')Code language: Python (python)By default, you can enter a custom value in the combobox. If you don’t want this, you can set the state option to ‘readonly’ :
combobox['state'] = 'readonly'Code language: Python (python)To re-enable editing the combobox, you use the ‘normal’ state like this:
combobox['state'] = 'normal'Code language: Python (python)Bind events
When a select value changes, the combobox widget generates a ‘>’ virtual event. To handle the event, you can use the bind() method like this:
combobox.bind('>', callback)Code language: Python (python)In this example, the callback function will execute when the selected value of the combobox changes.
Set the current value
To set the current value, you use the set() method:
combobox.set(self, value)Code language: Python (python)Also, you can use the current() method:
current(self, newindex=None)Code language: Python (python)The newindex specifies the index of values from the list that you want to select as the current value.
If you don’t specify the newindex , the current() method will return the index of the current value in the list of values or -1 if the current value doesn’t appear in the list.
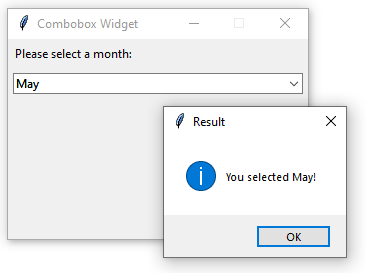
Python Tkinter combobox example
The following program illustrates how to create a combobox widget:
import tkinter as tk from tkinter import ttk from tkinter.messagebox import showinfo from calendar import month_name root = tk.Tk() # config the root window root.geometry('300x200') root.resizable(False, False) root.title('Combobox Widget') # label label = ttk.Label(text="Please select a month:") label.pack(fill=tk.X, padx=5, pady=5) # create a combobox selected_month = tk.StringVar() month_cb = ttk.Combobox(root, textvariable=selected_month) # get first 3 letters of every month name month_cb['values'] = [month_name[m][0:3] for m in range(1, 13)] # prevent typing a value month_cb['state'] = 'readonly' # place the widget month_cb.pack(fill=tk.X, padx=5, pady=5) # bind the selected value changes def month_changed(event): """ handle the month changed event """ showinfo( title='Result', message=f'You selected !' ) month_cb.bind('>', month_changed) root.mainloop()Code language: Python (python)The following program shows the same month combobox widget and uses the set() method to set the current value to the current month:
import tkinter as tk from tkinter import ttk from tkinter.messagebox import showinfo from calendar import month_name from datetime import datetime root = tk.Tk() # config the root window root.geometry('300x200') root.resizable(False, False) root.title('Combobox Widget') # label label = ttk.Label(text="Please select a month:") label.pack(fill=tk.X, padx=5, pady=5) # create a combobox selected_month = tk.StringVar() month_cb = ttk.Combobox(root, textvariable=selected_month) # get first 3 letters of every month name month_cb['values'] = [month_name[m][0:3] for m in range(1, 13)] # prevent typing a value month_cb['state'] = 'readonly' # place the widget month_cb.pack(fill=tk.X, padx=5, pady=5) # bind the selected value changes def month_changed(event): """ handle the month changed event """ showinfo( title='Result', message=f'You selected !' ) month_cb.bind('>', month_changed) # set the current month current_month = datetime.now().strftime('%b') month_cb.set(current_month) root.mainloop()Code language: Python (python)Summary
- Use ttk.Combobox(root, textvariable) to create a combobox.
- Set the state property to readonly to prevent users from entering custom values.
- A combobox widget emits the ‘>’ event when the selected value changes.
Python tkinter combobox change
Виджет Combobox представляет выпадающий список, из которого пользователь может выбрать один элемент. Фактически он представляет комбинацию виджетов Entry и Listbox.
Основные параметры конструктора Combobox:
- values : список строк для отображения в Combobox
- background : фоновый цвет
- cursor : курсор указателя мыши при наведении на текстовое поле
- foreground : цвет текста
- font : шрифт текста
- justify : устанавливает выравнивание текста. Значение LEFT выравнивает текст по левому краю, CENTER — по центру, RIGHT — по правому краю
- show : задает маску для вводимых символов
- state : состояние элемента, может принимать значения NORMAL (по умолчанию) и DISABLED
- textvariable : устанавливает привязку к элементу StringVar
- height : высота элемента
- width : ширина элемента
Определим простейший выпадающий список:
from tkinter import * from tkinter import ttk root = Tk() root.title("METANIT.COM") root.geometry("250x200") languages = ["Python", "C#", "Java", "JavaScript"] combobox = ttk.Combobox(values=languages) combobox.pack(anchor=NW, padx=6, pady=6) root.mainloop() Здесь для элемента combobox в качестве источника значений устанавливается список languages:
С помощью параметра textvariable мы можем установить привязку к выбранному в Combobox значению:
from cProfile import label from cgitb import text from tkinter import * from tkinter import ttk root = Tk() root.title("METANIT.COM") root.geometry("250x200") languages = ["Python", "C#", "Java", "JavaScript"] # по умолчанию будет выбран первый элемент из languages languages_var = StringVar(value=languages[0]) label = ttk.Label(textvariable=languages_var) label.pack(anchor=NW, padx=6, pady=6) combobox = ttk.Combobox(textvariable=languages_var, values=languages) combobox.pack(anchor=NW, padx=6, pady=6) print(combobox.get()) root.mainloop() Здесь выбранный в Combobox элемент привязан к переменной languages_var. По умолчанию выбран первый элемент списка languages. Для отслеживания изменения выбора определена метка Label, которая отображает выбранный элемент:
По умолчанию мы можем ввести в текстовое поле в Combobox любое значение, даже то, которого нет в списке. Такое поведение не всегда может быть удобно. В этом случае мы можем установить для виджета состояние только для чтения, передав параметру «state» значение «readonly»:
combobox = ttk.Combobox(textvariable=languages_var, values=languages, state="readonly")
Выбранный элемент можно получить с помощью метода get() класса Combobox
либо с помощью метода get() привязанной переменной
selection = languages_var.get()
Для установки нового значения можно использовать метод set() :
languages_var.set(new_value) combobox.set(new_value)
Для установки по индексу из привязанного набора значений также можно использовать метод current(newindex) , где с помощью параметра newindex задается индекс выбранного значения. Например, выберем второй элемент:
Отслеживание выбора значения
Для обработки выбора элементов в Combobox необходимо прикрепить функцию обработки к событию > с помощью метода bind :
combobox.bind(">", функция_обработки) Например, динамически обработаем выбор в Combobox:
from tkinter import * from tkinter import ttk root = Tk() root.title("METANIT.COM") root.geometry("250x200") def selected(event): # получаем выделенный элемент selection = combobox.get() print(selection) label["text"] = f"вы выбрали: " languages = ["Python", "C#", "Java", "JavaScript"] label = ttk.Label() label.pack(anchor=NW, fill=X, padx=5, pady=5) combobox = ttk.Combobox(values=languages, state="readonly") combobox.pack(anchor=NW, fill=X, padx=5, pady=5) combobox.bind(">", selected) root.mainloop() В данном случае при изменении выбора в списке срабатывает функция selected . Функция должна принимать один параметр, который несет информацию о событии — здесь это параметр event. Хотя в данном случае он никак не используется.
В самой функции получаем выбранный элемент и выводит соответствующую информацию на метку Label.