- Check if String starts with a Letter in Python
- Check if String starts with a Letter using Regex
- Frequently Asked:
- Check if String starts with a Letter using isapha()
- Related posts:
- Share your love
- Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
- Terms of Use
- Disclaimer
- Python starts with letter
- # Table of Contents
- # Check if a string starts with a Number in Python
- # Handling a scenario where the string is empty
- # Check if each String in a List starts with a Number
- # Check if all Strings in a List start with a Number
- # Check if a string starts with a Number using re.match()
- # Check if a string starts with a Number using str.startswith()
- # Check if a string starts with a Letter in Python
- # Check if a string starts with an ASCII letter
- # Check if a string starts with a Letter using re.match()
Check if String starts with a Letter in Python
In this article, we will discuss different ways to check if a string starts with an alphabet or not in Python.
Table Of Contents
Check if String starts with a Letter using Regex
The regex module of Python provides a function regex.search(pattern, string). It accepts a regex pattern and a string as arguments. Then it scans through the string and look for a match to the given regex pattern. If a match is found, then it returns a Match object, otherwise, it returns None.
We will use this function and check if a string starts with an alphabet (either uppercase or lowercase). For this, we will use the regex pattern “^[a-zA-Z]”. This pattern checks that the string must only start with an uppercase or lowercase alphabet. For example,
Frequently Asked:
import re sample_str = "sample string" # Check if string starts with a letter if re.search("^[a-zA-Z]", sample_str) is not None: print("The String starts with a letter") else: print("The String do not starts with a letter") The String starts with a letter
The given string started with an alphabet.
import re sample_str = "55 Words" # Check if string starts with a letter if re.search("^[a-zA-Z]", sample_str) is not None: print("The String starts with a letter") else: print("The String do not starts with a letter") The String do not starts with a letter
It was a negative test because the given string started with a number instead of a letter.
Check if String starts with a Letter using isapha()
In Python, the string class provides a function isalpha(). It returns True if all the characters in the string are alphabetic and at least one character in the string. We can use this to check if a string starts with a letter.
Select the first character of string using the subscript operator like str[0] and then call the isalpha() on it to check if the first character is an alphabet or not. Let’s see some examples,
sample_str = "sample string" # Check if string starts with a letter if sample_str[0].isalpha(): print("The String starts with a letter") else: print("The String do not starts with a letter") The String starts with a letter
The given string started with an alphabet.
sample_str = "55 Words" # Check if string starts with a letter if sample_str[0].isalpha(): print("The String starts with a letter") else: print("The String do not starts with a letter") The String do not starts with a letter
It was a negative test because the given string started with a number instead of a letter.
We learned different ways to check if a string starts with an alphabet in Python.
Related posts:
Share your love
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed.
Terms of Use
Disclaimer
Copyright © 2023 thisPointer
To provide the best experiences, we and our partners use technologies like cookies to store and/or access device information. Consenting to these technologies will allow us and our partners to process personal data such as browsing behavior or unique IDs on this site and show (non-) personalized ads. Not consenting or withdrawing consent, may adversely affect certain features and functions.
Click below to consent to the above or make granular choices. Your choices will be applied to this site only. You can change your settings at any time, including withdrawing your consent, by using the toggles on the Cookie Policy, or by clicking on the manage consent button at the bottom of the screen.
The technical storage or access is strictly necessary for the legitimate purpose of enabling the use of a specific service explicitly requested by the subscriber or user, or for the sole purpose of carrying out the transmission of a communication over an electronic communications network.
The technical storage or access is necessary for the legitimate purpose of storing preferences that are not requested by the subscriber or user.
The technical storage or access that is used exclusively for statistical purposes. The technical storage or access that is used exclusively for anonymous statistical purposes. Without a subpoena, voluntary compliance on the part of your Internet Service Provider, or additional records from a third party, information stored or retrieved for this purpose alone cannot usually be used to identify you.
The technical storage or access is required to create user profiles to send advertising, or to track the user on a website or across several websites for similar marketing purposes.
Python starts with letter
Last updated: Feb 21, 2023
Reading time · 6 min
# Table of Contents
# Check if a string starts with a Number in Python
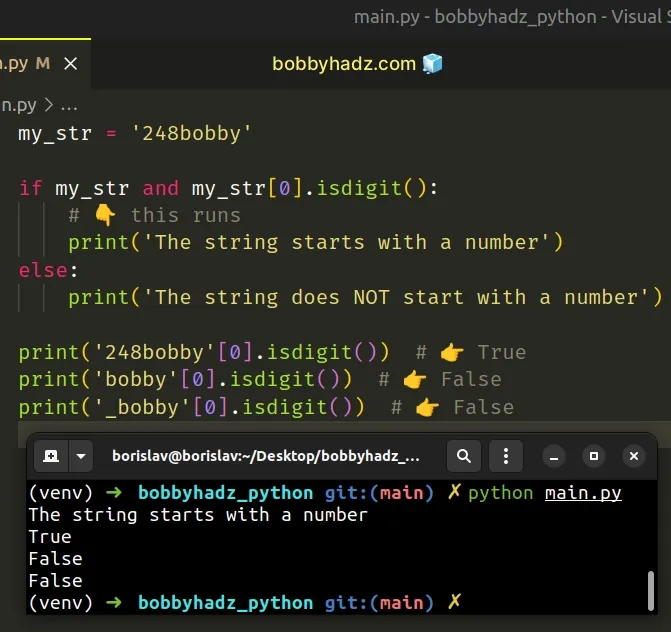
To check if a string starts with a number:
- Access the first character in the string.
- Use the str.isdigit() method to check if the character is a number.
- The str.isdigit() method will return True if the string starts with a number.
Copied!my_str = '248bobby' if my_str and my_str[0].isdigit(): # 👇️ this runs print('The string starts with a number') else: print('The string does NOT start with a number') print('248bobby'[0].isdigit()) # 👉️ True print('bobby'[0].isdigit()) # 👉️ False print('_bobby'[0].isdigit()) # 👉️ False
If you need to check if a string starts with a letter, click on the following subheading:
We first make sure that the string is not empty before accessing the character at index 0 .
Python indexes are zero-based, so the first character in a string has an index of 0 , and the last character has an index of -1 or len(my_str) — 1 .
The str.isdigit method returns True if all characters in the string are digits and there is at least 1 character, otherwise False is returned.
Copied!print('123'.isdigit()) # 👉️ True print('1.23'.isdigit()) # 👉️ False (contains period) print('-123'.isdigit()) # 👉️ False (contains minus)
If the character at index 0 is a digit, then the string starts with a number.
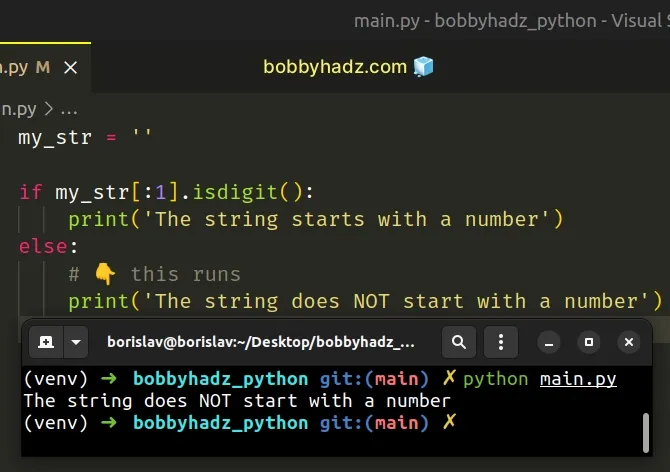
# Handling a scenario where the string is empty
If you try to access the character at index 0 of an empty string, you’d get an error.
You can either use the boolean and operator as we did in the first example or use string slicing to avoid the error.
Copied!my_str = '' if my_str[:1].isdigit(): print('The string starts with a number') else: # 👇️ this runs print('The string does NOT start with a number')
The syntax for string slicing is my_str[start:stop:step] .
The slice selects the first character in the string if it exists, otherwise an empty string is returned.
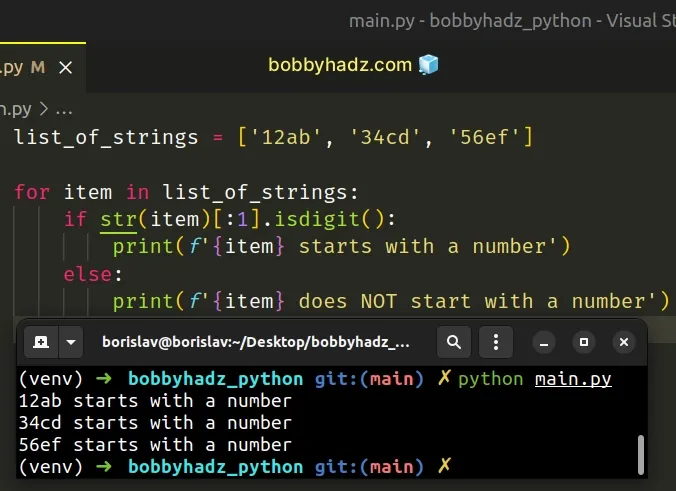
# Check if each String in a List starts with a Number
If you need to check if each string in a list starts with a number, use a for loop.
Copied!list_of_strings = ['12ab', '34cd', '56ef'] for item in list_of_strings: if str(item)[:1].isdigit(): print(f'item> starts with a number') else: print(f'item> does NOT start with a number') # Output: # 12ab starts with a number # 34cd starts with a number # 56ef starts with a number
# Check if all Strings in a List start with a Number
If you need to check if all strings in a list start with a number, use the all() function.
Copied!list_of_strings = ['12ab', '34cd', '56ef'] if all(str(item)[:1].isdigit() for item in list_of_strings): # 👇️ this runs print('All strings start with a number') else: print('NOT all strings start with a number')
The all() function will only return True if the condition is met for all strings in the list.
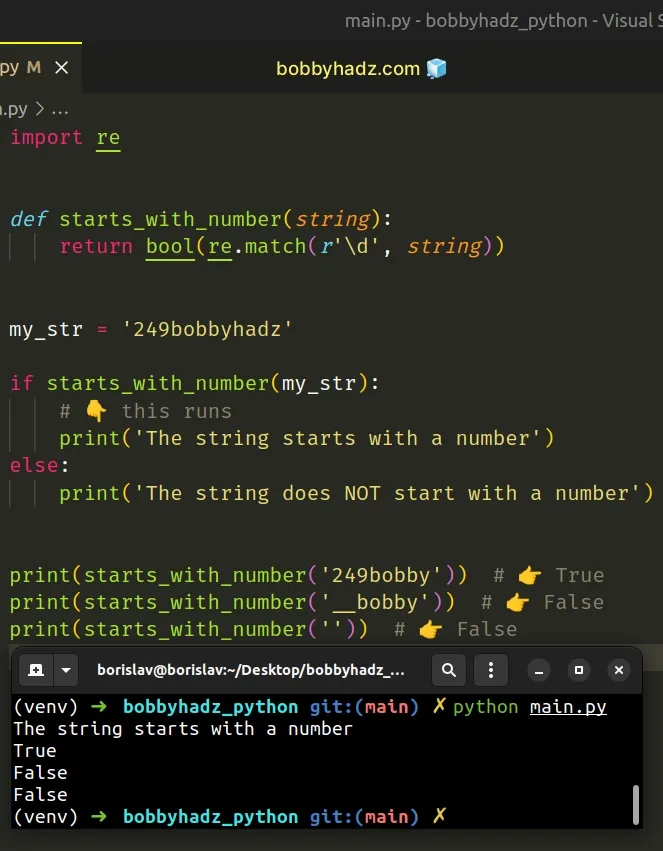
# Check if a string starts with a Number using re.match()
Alternatively, you can use the re.match() method.
The re.match() method will return a match object if the string starts with a number, otherwise, None is returned.
Copied!import re def starts_with_number(string): return bool(re.match(r'\d', string)) my_str = '249bobbyhadz' if starts_with_number(my_str): # 👇️ this runs print('The string starts with a number') else: print('The string does NOT start with a number') print(starts_with_number('249bobby')) # 👉️ True print(starts_with_number('__bobby')) # 👉️ False print(starts_with_number('')) # 👉️ False
The re.match method returns a match object if the provided regular expression is matched in the string.
The match() method returns None if the string doesn’t match the regex pattern.
The first argument we passed to the re.match() method is a regular expression.
Copied!import re def starts_with_number(string): return bool(re.match(r'\d', string))
The \d character matches the digits 6 (and many other digit characters).
The re.match() method only checks if the characters at the beginning of the string match the regular expression, so it does exactly what we need.
If you ever need help reading or writing a regular expression, consult the regular expression syntax subheading in the official docs.
The page contains a list of all of the special characters with many useful examples.
# Check if a string starts with a Number using str.startswith()
You can also use the str.startswith() method to check if a string starts with a specific number.
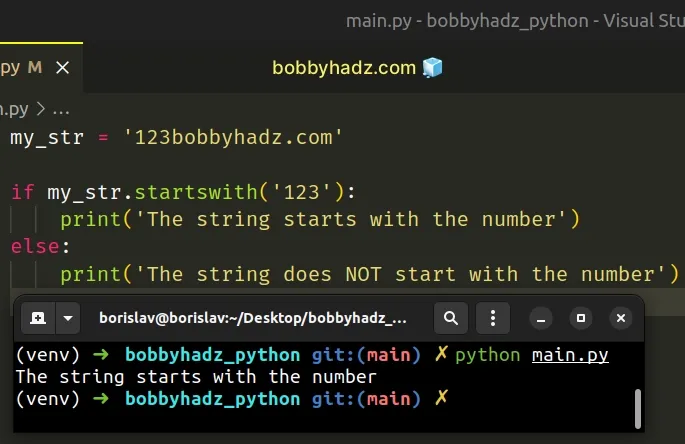
Copied!my_str = '123bobbyhadz.com' if my_str.startswith('123'): print('The string starts with the number') else: print('The string does NOT start with the number')
The str.startswith method returns True if the string starts with the provided prefix, otherwise the method returns False .
If the string starts with the number 123 , then True is returned, otherwise, False is returned.
Copied!my_str = '123bobbyhadz.com' print(my_str.startswith('123')) # 👉️ True print(my_str.startswith('456')) # 👉️ False
# Check if a string starts with a Letter in Python
To check if a string starts with a letter:
- Access the first character in the string.
- Use the str.isalpha() method to check if the character is a letter.
- The str.isalpha() method will return True if the string starts with a letter.
Copied!my_str = 'bobby hadz' if my_str and my_str[0].isalpha(): # 👇️ this runs print('The string starts with a letter') else: print('The string does NOT start with a letter') print('bobby'[0].isalpha()) # 👉️ True print('_bobby'[0].isalpha()) # 👉️ False
We first make sure that the string is not empty before accessing the character at index 0 .
Python indexes are zero-based, so the first character in a string has an index of 0 , and the last character has an index of -1 or len(my_str) — 1 .
The str.isalpha() method returns True if all characters in the string are alphabetic and there is at least one character, otherwise False is returned.
Copied!print('BOBBY'.isalpha()) # 👉️ True print('_BOBBY'.isalpha()) # 👉️ False
The str.isalpha method considers alphabetic characters the ones that are defined in the Unicode character database as «Letter».
# Check if a string starts with an ASCII letter
This is a three-step process:
- Use the string.ascii_letters attribute to get a string containing the ASCII letters.
- Access the first character in the original string.
- Use the in operator to check if the string starts with an ASCII letter.
Copied!import string my_str = 'bobby hadz' ascii_letters = string.ascii_letters # 👇️ abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ print(ascii_letters) if my_str and my_str[0] in ascii_letters: # 👇️ this runs print('The string starts with an ASCII letter') else: print('The string does NOT start with an ASCII letter') print('bobby'[0] in ascii_letters) # 👉️ True print('ффф bobby'[0] in ascii_letters) # 👉️ False
The string.ascii_letters attribute returns a string containing the lowercase and uppercase ASCII letters.
The in operator tests for membership. For example, x in s evaluates to True if x is a member of s , otherwise it evaluates to False .
# Check if a string starts with a Letter using re.match()
Alternatively, you can use the re.match() method.
The re.match() method will return a match object if the string starts with a letter, otherwise None is returned.
Copied!import re def starts_with_letter(string): return bool(re.match(r'[a-zA-Z]', string)) if starts_with_letter('bhadz'): print('The string starts with a letter') else: print('The string does NOT start with a letter') print(starts_with_letter('bhadz')) # 👉️ True print(starts_with_letter('__bhadz')) # 👉️ False print(starts_with_letter('444bhadz')) # 👉️ False print(starts_with_letter('ФФ bhadz')) # 👉️ False
The re.match method returns a match object if the provided regular expression is matched in the string.
The match() method returns None if the string doesn’t match the regex pattern.