- How To Change Axis Scale, Value Display Range And Datetimes Displayed Adaptively In Matplotlib
- 1. How To Change The Matplotlib Plot Axis Scale.
- 2. How To Change The Matplotlib Plot Axis Value Display Range.
- 3. How To Make Datetimes Displayed Adaptively In Matplotlib Axis.
- How to Set Axis Range (xlim, ylim) in Matplotlib
- Creating a Plot
- Setting Axis Range in Matplotlib
- How to Set X-Limit (xlim) in Matplotlib
- How to Set Y-Limit (ylim) in Matplotlib
- Conclusion
- Data Visualization in Python
- Free eBook: Git Essentials
How To Change Axis Scale, Value Display Range And Datetimes Displayed Adaptively In Matplotlib
This article will show you 3 examples. The first example tells you how to change the Matplotlib plot axis scale, the second example tells you how to change the axis range, and the third example tells you how to make the DateTime value displayed on the axis adaptively.
1. How To Change The Matplotlib Plot Axis Scale.
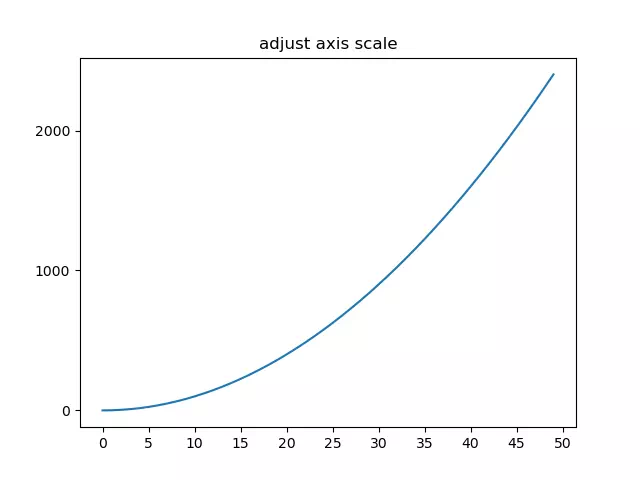
- You can use the matplotlib.pyplot module’s locator_params() method to change the axis scale.
- You can adjust the x-axis and y-axis at the same time with the code plt.locator_params(nbins = 10).
- You can also adjust only the x-axis with plt.locator_params (‘x ‘, nbins = 10) or only adjust the y-axis with plt.locator_params(‘y’,nbins = 10).
- Below is the example.
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt def change_axis_scale(): # create a numpy array. x=np.arange(0,50,1) # plot the curve by x value. plt.plot(x,x*x) # set the plot title. plt.title('adjust axis scale') # get the axes object. ax=plt.gca() # adjust the y axis scale. ax.locator_params('y', nbins=5) # adjust the x axis scale. plt.locator_params('x', nbins=20) # show the final figure. plt.show() if __name__ == '__main__': change_axis_scale() 2. How To Change The Matplotlib Plot Axis Value Display Range.
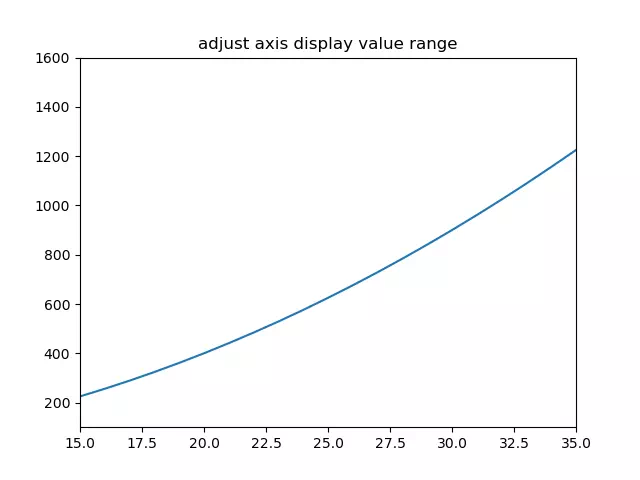
- Use the matplotlib.pyplot module’s xlim(xmin, xmax), ylim(ymin, ymax) method to adjust the axis value display range.
- Below is the example source code.
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt def change_axis_range(): # create an integer number array. x=np.arange(0,50,1) # plot the curve. plt.plot(x,x*x) # set the plot title. plt.title('adjust axis display value range') # only show 15 - 35 on x-axis. plt.xlim(xmin=15,xmax=35) # only show 100 - 1600 on y-axis. plt.ylim(ymin=100,ymax=1600) # show the plot. plt.show() if __name__ == '__main__': change_axis_range() 3. How To Make Datetimes Displayed Adaptively In Matplotlib Axis.
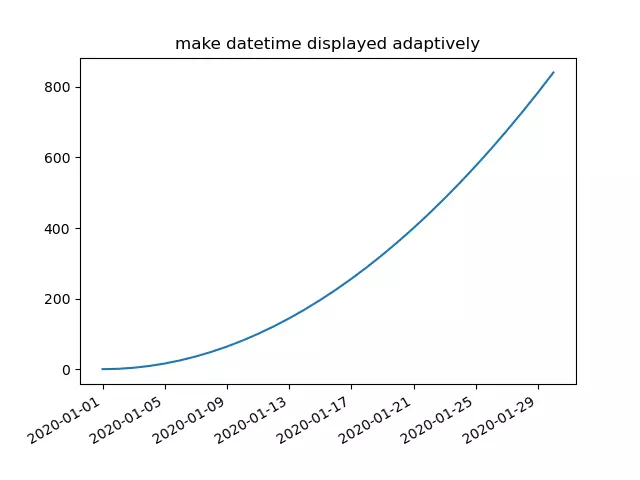
- You can call the matplotlib.pyplot module’s gcf() method to get the current figure object.
- Then call the current figure object’s autofmt_xdate() method to make the date times string displayed adaptively on the related axis. Below is the example, you can remove the code ( current_figure.autofmt_xdate() ) to see the difference.
import pandas as pd import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt def change_datetime_adaptively(): # create a date range (30 days) array. x=pd.date_range('2020/01/01',periods=30) print(x) # create a numpy array. y=np.arange(0,30,1) # plot the curve, the x-axis is date and the y-axis is integer number. plt.plot(x,y*y) # set the plot title. plt.title('make datetime displayed adaptively') # get the current figure. current_figure = plt.gcf() # make the datetime displayed adaptively. current_figure.autofmt_xdate() # show the plot. plt.show() if __name__ == '__main__': change_datetime_adaptively() How to Set Axis Range (xlim, ylim) in Matplotlib
Matplotlib is one of the most widely used data visualization libraries in Python. Much of Matplotlib’s popularity comes from its customization options — you can tweak just about any element from its hierarchy of objects.
In this tutorial, we’ll take a look at how to set the axis range (xlim, ylim) in Matplotlib, to truncate or expand the view to specific limits. This can be useful when you want to focus on a particular portion of your data or to ensure consistency across multiple plots.
Creating a Plot
Let’s first create a simple plot to work with:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 6)) x = np.arange(0, 10, 0.1) y = np.sin(x) z = np.cos(x) ax.plot(y, color='blue', label='Sine wave') ax.plot(z, color='black', label='Cosine wave') plt.show() In the above code, we create a figure and axis object with plt.subplots() , generate x , y , and z data points using numpy, and then plot the sine and cosine waves on the same axis. Optionally, you could add ax.legend() to display the labels for each wave.
In this example, we’ve plotted the values created by applying a sine and cosine function to the sequence generated using Numpy’s arange() Function. The sequence starts at 0 and ends at 10 with a step of 0.1 . Running this code produces the following plot:
The x-axis currently ranges from 0 to 100 , and the y-axis ranges from -1 to 1 . However, you might want to modify the axis range for better visualization or to focus on a specific region of the plot.
Setting Axis Range in Matplotlib
To adjust the axis range, you can use the xlim and ylim functions. These functions can be accessed either through the PyPlot instance or the Axes instance.
How to Set X-Limit (xlim) in Matplotlib
To set the x-axis range, you can use the xlim function, which takes two arguments: the lower and upper limits of the x-axis. For example, if you want to focus on the range from 2 to 8 , you can set the x-axis limits as follows:
Let’s first set the X-limit using both the PyPlot and Axes instances. Both of these methods accept a tuple containing the left and right limits. For example, if we wanted to truncate the view to only show the data in the range of 25-50 on the X-axis, we’d use xlim([25, 50]) :
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 6)) x = np.arange(0, 10, 0.1) y = np.sin(x) z = np.cos(x) ax.plot(y, color='blue', label='Sine wave') ax.plot(z, color='black', label='Cosine wave') plt.xlim([25, 50]) plt.show() This code limits the view on the X-axis to the data between 25 and 50 , as shown in the resulting plot:
The same effect can be achieved by setting the limit via the ax object. This way, if we have multiple Axes , we can set the limit for them separately:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6)) x = np.arange(0, 10, 0.1) y = np.sin(x) z = np.cos(x) ax = fig.add_subplot(121) ax2 = fig.add_subplot(122) ax.set_title('Full view') ax.plot(y, color='blue', label='Sine wave') ax.plot(z, color='black', label='Cosine wave') ax2.set_title('Truncated view') ax2.plot(y, color='blue', label='Sine wave') ax2.plot(z, color='black', label='Cosine wave') ax2.set_xlim([25, 50]) plt.show() In this example, the first subplot ( ax ) displays the full range of data, while the second subplot ( ax2 ) has a truncated view of the data between 25 and 50 on the X-axis.
How to Set Y-Limit (ylim) in Matplotlib
Now, let’s set the Y-limit for better visualization and understanding of the data. This can be achieved with the same two approaches as we used for setting the X-limit:
ax.plot(y, color='blue', label='Sine wave') ax.plot(z, color='black', label='Cosine wave') plt.ylim([-1, 0]) ax.plot(y, color='blue', label='Sine wave') ax.plot(z, color='black', label='Cosine wave') ax.set_ylim([-1, 0]) Both of these approaches result in the following graph with a customized Y-axis range:
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we’ve gone over how to set the axis range (i.e., the X and Y limits) using Matplotlib in Python. Setting axis ranges can help improve the readability and understanding of your plots by focusing on the relevant data. Remember, you can use either the plt.xlim() and plt.ylim() functions or the ax.set_xlim() and ax.set_ylim() methods to achieve this customization.
If you’re interested in Data Visualization and are unsure where to begin, we highly recommend our bundle of books on Data Visualization in Python:
Data Visualization in Python
Master the art of Data Visualization
Free eBook: Git Essentials
Check out our hands-on, practical guide to learning Git, with best-practices, industry-accepted standards, and included cheat sheet. Stop Googling Git commands and actually learn it!
✅ 30-day no-question money-back guarantee
✅ Regularly updated for free (latest update in April 2021)
✅ Includes bonus resources and guides
Data Visualization in Python with Matplotlib and Pandas is a comprehensive book designed to guide absolute beginners with basic Python knowledge in mastering Pandas and Matplotlib. It builds a strong foundation for advanced work with these libraries, covering a wide range of plotting techniques — from simple 2D plots to animated 3D plots with interactive buttons.
This in-depth guide will teach you everything you need to know about Pandas and Matplotlib, including how to create custom plot types that aren’t readily available within the library itself.
Data Visualization in Python, a book designed for beginner to intermediate Python developers, provides comprehensive guidance on data manipulation using Pandas and thoroughly explains core plotting libraries such as Matplotlib and Seaborn. Additionally, it delves into declarative and experimental libraries like Altair. Spanning 11 chapters, this book covers a total of 9 essential Python libraries: Pandas, Matplotlib, Seaborn, Bokeh, Altair, Plotly, GGPlot, GeoPandas, and VisPy.
This book serves as a unique, practical guide to Data Visualization, offering in-depth knowledge of a wide range of tools that you may encounter and utilize throughout your career. By learning how to effectively set axis ranges (xlim, ylim) in Matplotlib, you will be able to create visually appealing and informative plots, enhancing your data analysis and presentation skills.