- How to Play Sound, Audio or MP3 Files in Python
- Playing Sound, Audio, or MP3 Files in Python on Windows
- Using Playsound
- Using VLC
- Using Pygame
- Playing Sound, Audio, or MP3 Files in Python on Linux
- Using Playsound
- Using os and mpg123
- Playing Sound, Audio, or MP3 Files in Python on macOS
- Using Afplay and os
- Conclusion
- Play sound in Python
- Play sound in Python
- playsound module
- pydub
- snack sound kit
- native player
- How to Play and Record Audio in Python?
- How to Play and Record Audio in Python?
- Install Required Libraries
- 1) Python playsound library
- 2) Python sounddevice library
- Python Program to Play Audio Files
- How to Record Audio in Python?
- #Python program to record an audio file.
- Conclusion
How to Play Sound, Audio or MP3 Files in Python
There are numerous ways for us to play sound, audio, or MP3 files using the Python programming language. These include modules such as playsound , VLC , pygame , mpg123 , etc. We can also play it natively on macOS and Linux as we will see later on.
Most of the modules that we will be using don’t come pre-installed with Python, which means we will have to install them ourselves. Therefore, you need to have Python and PIP installed on your system, before installing these Python modules.
Luckily, playing audio in Python is straightforward and can be done with a few lines of code. In this guide, we will be going over the steps to play sound, audio, or MP3 files in Python on Windows , Linux , and macOS .
Note: In this guide, a 4-second MP3 file is used named testaudio.mp3 and it is located in the same directory as the .py file which we will be using to run the code.
Table of Contents
Playing Sound, Audio, or MP3 Files in Python on Windows
Using Playsound
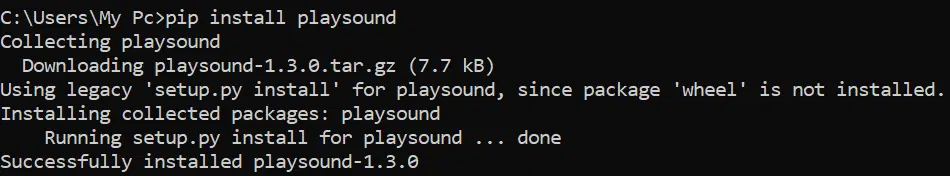
Playsound is a cross-platform Python module with no dependencies and a single function.
So, to use playsound to play audio:
If you would like to double-check that you’ve properly installed the module, enter python in the terminal to access the python terminal and then import playsound . If playsound is installed, there should be no errors in the output.
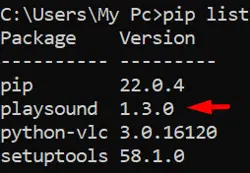
You can also enter pip list in the terminal to have a look at all the installed packages and their versions.
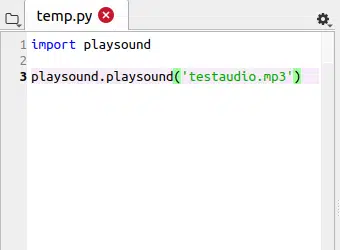
import playsound playsound.playsound('testaudio.mp3') - After running the code, your audio will begin playing and will stop automatically depending on the length of your mp3 file.
Using VLC
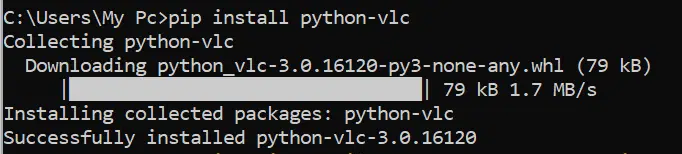
VLC is an open-source and cross-platform media player that can be used to play audio and video files. VLC has a python module that enables us to play mp3 files.
Hence, to use VLC to play audio:
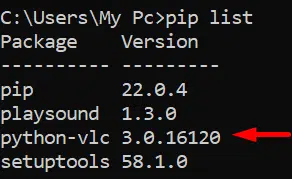
Confirm the installation by entering:
- We will be using another module alongside the Python VLC module in order to delay the execution of the file. The time module enables us to determine how long we want the file to delay execution so we can hear our audio being played. Otherwise, the file will finish executing immediately without our audio being played.
- In your code editor, enter the following:
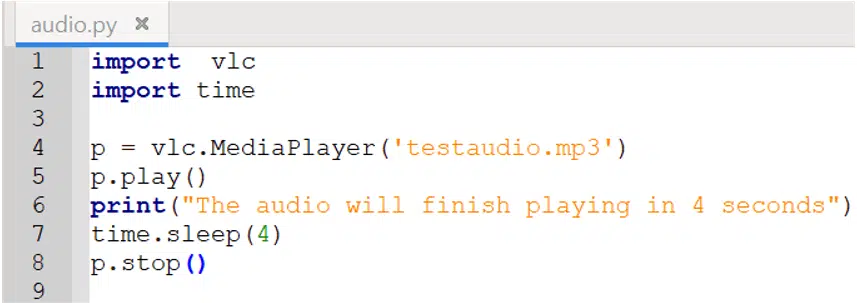
import vlc import time p = vlc.MediaPlayer(‘testaudio.mp3’) p.play() print("The audio will finish playing in 4 seconds") time.sleep(4) p.stop()
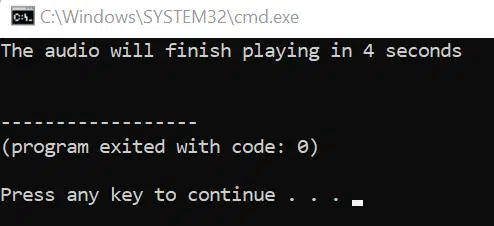
The time.sleep(4) function tells the program to delay execution for 4 seconds before we call the p.stop() function. When running the program, it should look something like this:
A terminal window will appear and your audio should start playing. At the same time, the result of the print function is shown to indicate that the audio is 4 seconds long. The program will finish executing right after as that is the time we specify in time.sleep(4) .
Using Pygame
Pygame is a game development module that is cross-platform and enables us to use Python for graphics and audio purposes.
To use pygame to play audio:
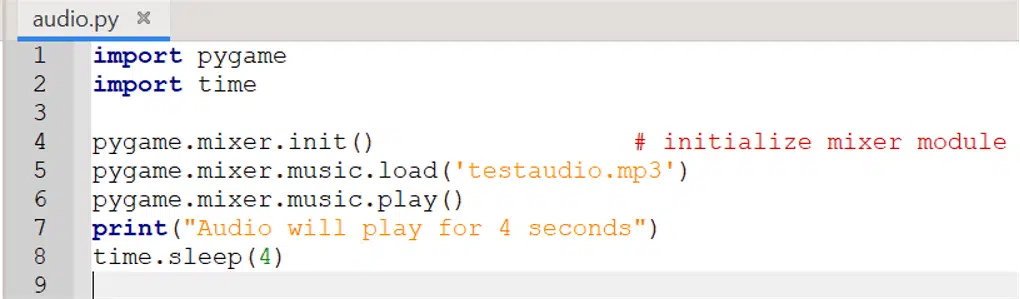
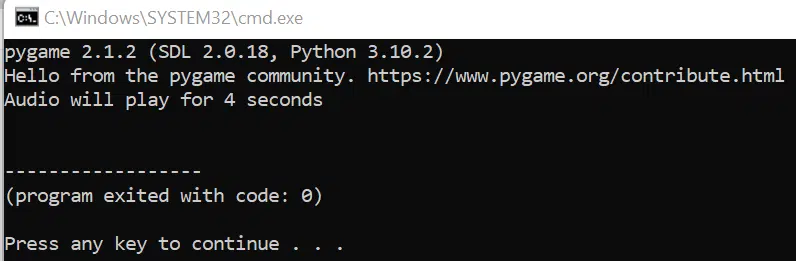
import pygame import time pygame.mixer.init() # initialize mixer module pygame.mixer.music.load('testaudio.mp3') pygame.mixer.music.play() print("Audio will play for 4 seconds") time.sleep(4)
The result will look like this:
First, the audio will start playing, and the result of the print function will be shown on the screen. Then, the program will finish executing after 4 seconds as specified by the time.sleep() function.
Playing Sound, Audio, or MP3 Files in Python on Linux
Using Playsound
import playsound playsound.playsound(‘testaudio.mp3’)
Using os and mpg123
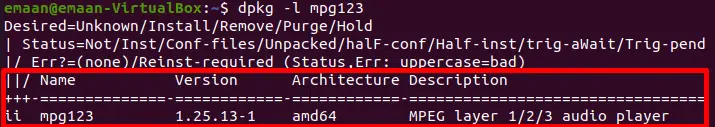
os is a standard Python module that doesn’t need to be installed. It allows us to interact with our Operating System through its functions. mpg123 is an open-source mp3 player for Linux systems.
So, we can use methods from both these functions to play audio files with Python through the following steps:
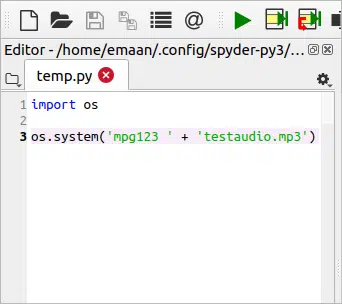
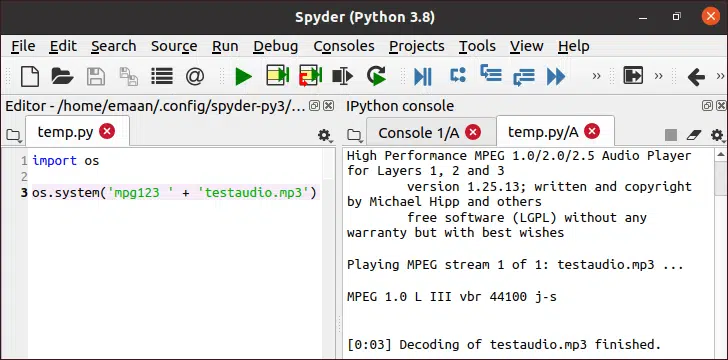
import os os.system(‘mpg123 ‘ + ‘testaudio.mp3’)
Playing Sound, Audio, or MP3 Files in Python on macOS
Using Afplay and os
To play audio on a macOS-based machine, we will be using afplay and os . Afplay is a tool that allows us to play audio from a file on macOS.
import os os.system(“afplay ” + “testaudio.mp3”)
Conclusion
Learning how to play audio, sounds, and MP3 files in Python can be quite useful in many circumstances. There are a number of reasons why someone may want to play music or audio in Python.
These include wanting to add to their programming skills, adding music to a game, adding sound effects to an app, and many more!
With that said, in this article, we looked at the steps to play sound , audio , or MP3 files in Python on Windows , Linux , and macOS machines . We hope you’ve found this guide helpful when it comes to playing audio in Python.
Feel free to share this post with your fellow coders to guide them through playing sound, audio, or MP3 files with Python on Windows, Linux, and macOS!
Play sound in Python
Play sound on Python is easy. There are several modules that can play a sound file (.wav).
These solutions are cross platform (Windows, Mac, Linux).
The main difference is in the ease of use and supported file formats. All of them should work with Python 3. The audio file should be in the same directory as your python program, unless you specify a path.
Play sound in Python
playsound module
The playsound module is a cross platform module that can play audio files. This doesn’t have any dependencies, simply install with pip in your virtualenv and run!
from playsound import playsound
playsound(‘audio.mp3’)
Implementation is different on platforms. It uses windll.winm on Windows, AppKit.NSSound on Apple OS X and GStreamer on Linux.
I’ve tested this with Python 3.5.3. This should work with both WAV and MP3 files.
pydub
You can play sound files with the pydub module. It’s available in the pypi repository (install with pip).
This module can use PyAudio and ffmpeg underneath.
from pydub import AudioSegment
from pydub.playback import play
song = AudioSegment.from_wav(«sound.wav»)
play(song)
snack sound kit
The module snack sound kit can play several audio files: WAV, AU, AIFF, MP3, CSL, SD, SMP, and NIST/Sphere.
You can install it with your package manager: ‘apt install python3-tksnack’. For old versions there’s ‘python-tksnack’.
This module depends on Tkinter. That means that to play sound with this module, you’d also have to import the gui module Tkinter. The module doesn’t seem to have been updated in a while.
from Tkinter import *
import tkSnack
root = Tk()
tkSnack.initializeSnack(root)
snd = tkSnack.Sound()
snd.read(‘sound.wav’)
snd.play(blocking=1)
native player
You can also play sounds natively on your system. This requires you to have some kind of audio player installed on the terminal. On Linux you can use mpg123 for that.
This simply plays the mp3 file with an external player.
# apt install mpg123
import os
file = «file.mp3»
os.system(«mpg123 « + file)
Create a Python Web Server
How to Play and Record Audio in Python?
There are many applications out there on the internet that can play and record audio files such as mp3, wav, and mp4. If you are a Python developer and wish to write code that can record or play audio for you, then continue reading this article.
In this Python tutorial, I will walk you through two Python programs that can play and record audio.
How to Play and Record Audio in Python?
Install Required Libraries
Before we can code in Python to play and record audio, we need to install three Python libraries, namely playsound, sounddevice, and Scipy.
1) Python playsound library
As the library name suggests, the playsound library is used to play different types of audio files. It is an open-source Python library, and you can install it using the following pip command:
2) Python sounddevice library
The Python sounddevice library is another open-source library that is used to play and record NumPy arrays containing sound singles. This means it uses NumPy arrays to generate and structure audio file data. To install the sounddevice library, run the following pip command on your terminal or command prompt:
3) Python Scipy library
Scipy is a scientific computing library for Python, and in this tutorial, we will be using this library to save or write the data generated by the sounddevice library. Install the Python library using the following command:
Python Program to Play Audio Files
Playing an audio file is very straightforward with the Python playsound library. Check out the following code:
from playsound import playsound filename = "music.mp3" print(f"Playing . ") playsound(filename) #play audioIn this example, the music.mp3 audio file is located in the same directory where the Python script is, and that’s why we have only specified the file name, not the complete path.
Thus, if your audio file is located in some directory other than the directory having the Python script, then you need to specify the full path, like: filename =r»C:\Users\tsmehra\music\music.mp3″
How to Record Audio in Python?
Now you know how to play audio in Python using the Python playsound library. Next, let’s write a Python program that will record audio from your mic. Let’s start with importing the required modules.
import sounddevice as sd from scipy.io.wavfile import write from playsound import playsound import timeWith the sounddevice module, we will record the audio in the wav format. Using the scipy.io.wavfile write module, we will save the recorded wav audio file locally, and the playsound module will allow us to play the recorded file. With the time module, we will create a recording timer.
Now, let’s define a timer function that will print the timer while the audio is recording.
def timer(duration): while duration: mins, secs = divmod(duration, 60) timer = f" mins: seconds Left" print(timer, end=" \r") time.sleep(1) duration -= 1Next, let’s define the audio_record function that will record the audio and save it locally:
def record_audio(filename): #frequency fs=44100 #frames per second duration = 10 # seconds in integer print("Recording. ") #start recording myrecording = sd.rec(int(duration * fs), samplerate=fs, channels=2) timer(duration) #call timer function sd.wait() #write the data in filename and save it write(filename, fs, myrecording)The fs variable specifies the frequency of the audio in frames per second, and its value could either be 44,100 or 48,000. The duration variable defines the recording duration in seconds.
rec() initializes the recording object while the wait() function holds the recording screen for the specified duration . Also, the write() function writes the recorded data and saves it in the same directory where the Python script is located, with the specified filename .
Now, let’s declare a variable that represents the recorded audio file name and calls the record_audio function.
filename ="new_record.wav" record_audio(filename) listen = input("Do you want to listen the recorded audio? [y/n]") if listen.lower() =="y": playsound(filename)Finally, let’s put all the code together and execute it.
#Python program to record an audio file.
import sounddevice as sd from scipy.io.wavfile import write from playsound import playsound import time def timer(duration): while duration: mins, secs = divmod(duration, 60) timer = f" mins: seconds Left" print(timer, end=" \r") time.sleep(1) duration -= 1 def record_audio(filename): #frequency fs=44100 #frames per second duration = 10 # seconds in integer print("Recording. ") #start recording myrecording = sd.rec(int(duration * fs), samplerate=fs, channels=2) timer(duration) #call timer function sd.wait() #write the data in filename and save it write(filename, fs, myrecording) filename ="new_record.wav" record_audio(filename) listen = input("Do you want to listen the recorded audio? [y/n]") if listen.lower() =="y": playsound(filename)When you execute the program, look in the directory where your Python script is located. There you will find a new wav audio file with the name new_record.wav .
Conclusion
In this Python tutorial, you learned » How to Play audio in Python? » and » How to Record Audio in Python? » In this tutorial, we have used three Python libraries, which are playsound , sounddevice , and Scipy .
We would recommend you read the official documentation of these three libraries if you want to perform more audio-related functions in Python. Let us know in the comments if you come across any issues.
People are also reading: