- Robert Heaton
- Is Python pass-by-reference or pass-by-value?
- Useful links
- More on Programming
- Python pass by reference or value with examples
- Python pass by reference vs pass by value
- Call by reference vs call by value
- Python pass by reference example
- Python pass by value example
- Pass by reference vs value in python
- Python function arguments pass by reference or value
- Python pass string by value
- Python — pass by reference
- Table of Contents
- What is pass by reference?
- Pass by reference vs value in Python
- Pass by value
- Input:
- Output:
- Pass by reference
- Input:
- Output:
- Python Object Model
- Closing Thoughts
Robert Heaton
Is Python pass-by-reference or pass-by-value?
“Suppose I say to Fat, or Kevin says to Fat, “You did not experience God. You merely experienced something with the qualities and aspects and nature and powers and wisdom and goodness of God.” This is like the joke about the German proclivity toward double abstractions; a German authority on English literature declares, “Hamlet was not written by Shakespeare; it was merely written by a man named Shakespeare.” In English the distinction is verbal and without meaning, although German as a language will express the difference (which accounts for some of the strange features of the German mind).”
Philip K. Dick is not known for his light or digestible prose. The vast majority of his characters are high. Like, really, really, really high. And yet, in the above quote from Valis (published in 1981), he gives a remarkably foresighted explanation of the notoriously misunderstood Python parameter passing paradigm. Plus ça change, plus c’est omnomnomnom drugs.
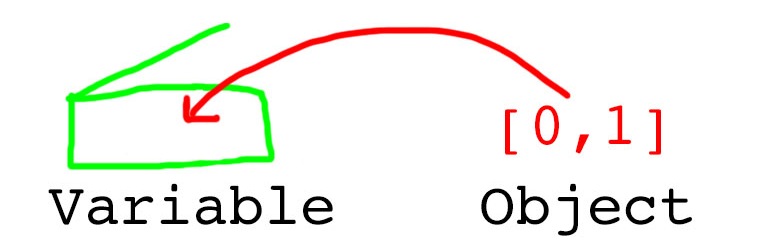
The two most widely known and easy to understand approaches to parameter passing amongst programming languages are pass-by-reference and pass-by-value. Unfortunately, Python is “pass-by-object-reference”, of which it is often said:
“Object references are passed by value.”
When I first read this smug and overly-pithy definition, I wanted to punch something. After removing the shards of glass from my hands and being escorted out of the strip club, I realised that all 3 paradigms can be understood in terms of how they cause the following 2 functions to behave:
You may also want to read about the interesting interactions these concepts have with mutable and immutable types. But those are stories for another day. Now if you’ll excuse me, I’m going to read “Do Androids Dream Of Electric Sheep?” — my meta-programming is a little rusty.
Useful links
More on Programming
Python pass by reference or value with examples
In this Python tutorial, let us discuss on Python pass by reference or value with a few examples.
- Python pass by reference vs pass by value
- Python call by reference vs call by value
- Python pass by reference example
- Python pass by value example
- Pass by reference vs value in python
- Python function arguments pass by reference or value
- Python pass string by value
Python pass by reference vs pass by value
Pass by reference – It is used in some programming languages, where values to the argument of the function are passed by reference which means that the address of the variable is passed and then the operation is done on the value stored at these addresses.
Pass by value – It means that the value is directly passed as the value to the argument of the function. Here, the operation is done on the value and then the value is stored at the address. Pass by value is used for a copy of the variable.
Call by reference vs call by value
| Call by reference | Call by value |
| While calling a function, in a programming language instead of copying the values of variables, the address of the variables is used, it is known as “Call By Reference.” | While calling a function, when we pass values by copying variables, it is known as “Call By Values.” |
| In this method, a variable itself is passed. | A copy of the variable is passed in a call by value. |
| Change in the variable also affects the value of the variable outside the function. | Changes made in a copy of a variable never modify the value of the variable outside the function. |
| Allows you to make changes in the values of variables by using function calls. | Does not allow you to make any changes in the actual variables. |
| The original value is modified. | Original value not modified. |
Python pass by reference example
When we pass something by reference any change we make to the variable inside the function then those changes are reflected to the outside value as well.
student = def test(student): new = student.update(new) print("Inside the function", student) return test(student) print("Outside the function:", student)After writing the above code, Once you will print “student” then the output will appear. Here, we created a dictionary called student, and test(student) is the function. Then two more students joined so we created the variable as “new” and the student.update(new) is used to update the dictionary, also the print will display the output.
You can refer to the below screenshot for python pass by reference example
Python pass by value example
When we pass something by value then the changes made to the function or copying of the variable are not reflected back to the calling function.
student = def test(student): student = print("Inside the function", student) return test(student) print("Outside the function:", student)After writing the above code, Once you will print “student” then the output will appear. Here, we created a dictionary called student, and test(student) is the function. Then two more students joined so we created the variable as “new” and the print will display the output. We can see that the inside and outside function remains the same.
You can refer to the below screenshot for the python pass by value example
Pass by reference vs value in python
In the below example, we can see that all the parameters in the python language are passed by reference. So, if we change what a parameter refers to within a function, the change also reflects back in the calling function.
def marks(list): list.append([11, 12, 13, 14, 15]) print("Value inside the function: ", list) return list = [10,20] marks(list) print("Value outside the function: ", list)In this output, we can see that we are maintaining the reference of the passed object, and values are appending in the same object. So, you can see the output of the inside function and outside function.
You can refer to the below screenshot pass by reference vs value in python
Python function arguments pass by reference or value
The parameters in the python language are passed by reference. Which mean if we change what parameter refers to within the function, the change also reflect black in the calling function.
teacher = def test(teacher): new = teacher.update(new) print("Inside the function",teacher) return test(teacher) print("Outside the function:",teacher)After writing the above code, Once you will print “teacher” then the output will appear. Here, we created a dictionary called teacher, and the def test(teacher) is the function. Then two more teachers joined so we created the variable as “new” and the print will display the output. We can see that the inside and outside function remains the same.
You can refer to the below screenshot python function arguments pass by reference or value.
Python pass string by value
In this example, we have passed strings to a function, and the string value is an immutable object which is being passed to the function. So, the changes made to the function or copying of the variable are not reflected back to the calling function.
my_string = "Python" def test(my_string): my_string = "PythonGuides" print("Inside the function:",my_string) test(my_string) print("Outside the function:",my_string)In this output, once you will print “my_string” then the output will appear. Here, we created the function called def test(my_string). Here, the passing is like a pass string by the value as we can not change the value of the immutable object.
You can refer to the below screenshot python pass string by value.
You may like the following Python tutorials:
In this Python tutorial, we have learned about the python pass by reference or value. Also, We covered these below topics:
- Python pass by reference vs pass by value
- Python call by reference vs call by value
- Python pass by reference example
- Python pass by value example
- Pass by reference vs value in python
- Python function arguments pass by reference or value
- Python pass string by value
I am Bijay Kumar, a Microsoft MVP in SharePoint. Apart from SharePoint, I started working on Python, Machine learning, and artificial intelligence for the last 5 years. During this time I got expertise in various Python libraries also like Tkinter, Pandas, NumPy, Turtle, Django, Matplotlib, Tensorflow, Scipy, Scikit-Learn, etc… for various clients in the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, Australia, New Zealand, etc. Check out my profile.
Python — pass by reference
In this tutorial, we will learn how to use pass by reference in Python. Variables work differently in Python than in any other programming language known to us. It is a memory location with a unique address whereas in Python, variables are not declared beforehand but the data decides the data type.
Table of Contents
- What is pass by reference
- Pass by reference vs value in Python
- Python Object Model
- Closing Thoughts
What is pass by reference?
Before we jump into the technical details, let’s first see what does pass and by reference actually mean.
By pass we mean to provide an argument to a function. Whereas by reference means that the argument that has been passed to the function is a reference to a variable that is already existing in the memory. Now that we have cleared that, now we can learn about pass by reference.
In pass by reference, the variable is passed into the function directly while the variable acts as a Package that comes with the objects. Because you’ve given the function a reference to an existing variable, any operations you execute on it will have a direct effect on the variable it refers to.
Pass by reference vs value in Python
When you give function parameters via reference, you’re just passing references to values that already exist. When you pass arguments by value, on the other hand, the arguments become independent copies of the original values.
Pass by value
Any other operation performed will not have any effect on the original value as the argument passed to the function is copied. It only changes the value of the copy created within the function.
Input:
def function(int): int+=100 print("Inside function call ",int) int=100 print("Before function call ",int) function(int) print("After function call ",int) Here, a copy of the argument is created, and changes are made to that copy such that the original value is not affected. As a result, the original value is printed after the function call.
Output:
Before function call 100 Inside function call 200 After function call 100 In this, we assigned the variable the value ‘100’ and changed it to ‘200’, but the change was not seen outside the function i.e. int is still ‘100’. Hence proved, it is pass by value method.
Pass by reference
This method passes a reference to the original arguments, and any operation performed on the parameter affects the actual value. It alters the value in both function and globally.
Input:
def function(int): int.append('B')print("Inside function call",int) int=['A'] print("Before function call",int) function(int) print("After function call",int)When a list is used, its reference is supplied into the function, and any modifications to the list have an effect even after the method has been called.
Output:
Before function call ['A'] Inside function call ['A', 'B'] After function call ['A', 'B']In the above example, function() returns a string and also modifies the value of int. This shows that Python supports the pass by reference method.
Python Object Model
It’s best if we first understand what Python objects are and how to characterize them. In Python, everything is an object. Object’s identity, data type and object’s content characterize every object.
# the identity of `int` id(int) 3578332784044 # the type of `int` type(int) # the contents of `int` int [1, 2, 3] As we can see above, id is the built-in function you use to query the identity of an object, and type is the built-in function you use to query the type of an object.
Closing Thoughts
Python operates differently than the other programming languages when it comes to the moving of the arguments. Since you’re giving the function a reference to an existing variable, all operations performed on this reference will directly affect the variable to which it refers. One can learn about other Python-related concepts here.