- Python Write Text File
- TL;DR
- Steps for writing to text files
- Writing text file examples
- Appending text files
- Writing to a UTF-8 text file
- Summary
- Writing to a File with Python’s print() Function
- Redirecting a Python’s Script Output in the Terminal
- Redirecting the Standard Output Stream
- Free eBook: Git Essentials
- Redirecting the Standard Error Stream
- Print Using the «file» Parameter
- Conclusion
- About the Author
Python Write Text File
Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn various ways to write text files in Python.
TL;DR
The following illustrates how to write a string to a text file:
with open('readme.txt', 'w') as f: f.write('readme')Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Steps for writing to text files
To write to a text file in Python, you follow these steps:
- First, open the text file for writing (or append) using the open() function.
- Second, write to the text file using the write() or writelines() method.
- Third, close the file using the close() method.
The following shows the basic syntax of the open() function:
The open() function accepts many parameters. But you’ll focus on the first two:
- The file parameter specifies the path to the text file that you want to open for writing.
- The mode parameter specifies the mode for which you want to open the text file.
For writing to a text file, you use one of the following modes:
| Mode | Description |
|---|---|
| ‘w’ | Open a text file for writing. If the file exists, the function will truncate all the contents as soon as you open it. If the file doesn’t exist, the function creates a new file. |
| ‘a’ | Open a text file for appending text. If the file exists, the function append contents at the end of the file. |
| ‘+’ | Open a text file for updating (both reading & writing). |
The open() function returns a file object that has two useful methods for writing text to the file: write() and writelines() .
- The write() method writes a string to a text file.
- The writelines() method write a list of strings to a file at once.
The writelines() method accepts an iterable object, not just a list, so you can pass a tuple of strings, a set of strings, etc., to the writelines() method.
To write a line to a text file, you need to manually add a new line character:
f.write('\n') f.writelines('\n')Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Writing text file examples
The following example shows how to use the write() function to write a list of texts to a text file:
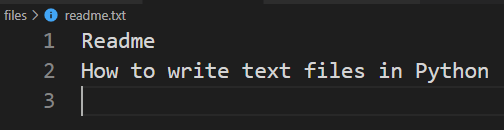
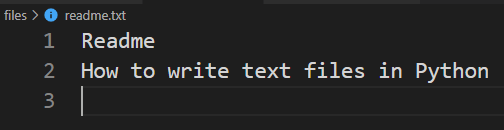
lines = ['Readme', 'How to write text files in Python'] with open('readme.txt', 'w') as f: for line in lines: f.write(line) f.write('\n')Code language: JavaScript (javascript)If the readme.txt file doesn’t exist, the open() function will create a new file.
The following shows how to write a list of text strings to a text file:
lines = ['Readme', 'How to write text files in Python'] with open('readme.txt', 'w') as f: f.writelines(lines)Code language: JavaScript (javascript)If you treat each element of the list as a line, you need to concatenate it with the newline character like this:
lines = ['Readme', 'How to write text files in Python'] with open('readme.txt', 'w') as f: f.write('\n'.join(lines))Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Appending text files
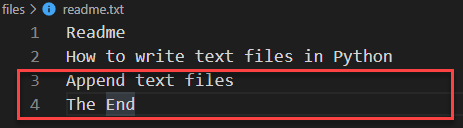
To append to a text file, you need to open the text file for appending mode. The following example appends new lines to the readme.txt file:
more_lines = ['', 'Append text files', 'The End'] with open('readme.txt', 'a') as f: f.write('\n'.join(more_lines))Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Writing to a UTF-8 text file
If you write UTF-8 characters to a text file using the code from the previous examples, you’ll get an error like this:
UnicodeEncodeError: 'charmap' codec can't encode characters in position 0-44: character maps to undefined>Code language: HTML, XML (xml)To open a file and write UTF-8 characters to a file, you need to pass the encoding=’utf-8′ parameter to the open() function.
The following example shows how to write UTF-8 characters to a text file:
quote = '成功を収める人とは人が投げてきたレンガでしっかりした基盤を築くことができる人のことである。' with open('quotes.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f: f.write(quote) Code language: JavaScript (javascript) Summary
- Use the open() function with the w or a mode to open a text file for appending.
- Always close the file after completing writing using the close() method or use the with statement when opening the file.
- Use write() and writelines() methods to write to a text file.
- Pass the encoding=’utf-8′ to the open() function to write UTF-8 characters into a file.
Writing to a File with Python’s print() Function
Python’s print() function is typically used to display text either in the command-line or in the interactive interpreter, depending on how the Python program is executed. However, we can change its behavior to write text to a file instead of to the console.
In this article, we’ll examine the many ways we can write to a file with the print() function.
Redirecting a Python’s Script Output in the Terminal
The quick and dirty way to redirect a Python script’s output is directly from the command-line while executing the script.
For example, if we had a Python file called hello.py with the following contents:
print("Hallo") # Deliberately in German We can redirect the output of the file in the shell using a single right angle bracket:
$ python3 hello.py > output.txt If we open our newly created output.txt , we’ll see the following contents:
However, with this method, all output of the script is written to a file. It is often more flexible to perform this redirection from within the Python script itself.
Redirecting the Standard Output Stream
In Python, the print() function is more flexible than you might think. It was not hard-coded in such a way that specified text can only be written to the display. Instead, it sends text to a location called the standard output stream, also known as stdout .
All UNIX systems have three main pipes — standard input pipe ( stdin ), standard output pipe ( stdout ) and standard error pipe ( stderr ).
By default, the standard output pipe points to the interactive window used to execute the program, so we normally see text printed out on the screen. However, the standard output can be redirected to other locations, such as files, for convenience.
If the standard output is redirected to a specific file, the text specified in the print() function will be written to that file instead of being displayed on the screen.
In Python, a reference to the standard output can be obtained using the stdout object of the sys module. It is a file-like object, meaning it has methods that allow Python to read and write from it like an actual file.
Let’s see an example where we change stdout to be a file:
import sys print('This message will be displayed on the screen.') original_stdout = sys.stdout # Save a reference to the original standard output with open('filename.txt', 'w') as f: sys.stdout = f # Change the standard output to the file we created. print('This message will be written to a file.') sys.stdout = original_stdout # Reset the standard output to its original value The print() function takes the supplied string argument, appends a newline character to the end, and calls the stdout.write() method to write it to standard output.
In the example above, we first print a line of text as we’re accustomed to, which will be displayed in the console when we run the file. We then reassigned stdout to our custom file object — f . Since a file object has a perfectly valid write() method, our printed value gets written to the file without a problem.
Note that it is good practice to store the original value of the standard output in a variable before changing it. This way we can reset the standard output to its original value after we’re done, which can help avoid confusion.
Let’s save the code to a new file, printToFile.py . And then, let’s execute it:
We’ll see the following output in the Terminal:
This message will be displayed on the screen. And the script will create a new file called filename.txt with the following contents:
Free eBook: Git Essentials
Check out our hands-on, practical guide to learning Git, with best-practices, industry-accepted standards, and included cheat sheet. Stop Googling Git commands and actually learn it!
This message will be written to a file. You successfully redirected data from the standard output stream to a file. Let’s see how we can do this to another popular file-like object that’s dedicated to programming errors.
Redirecting the Standard Error Stream
In Python, errors are written to the standard error stream, also known as stderr . This also defaults to the interactive window but can be changed via the sys.stderr object. If we wanted to print values to the stderr , we could simply redirect the sys.stdout to point to the sys.stderr .
Create a file called printToStderr.py and add the following code:
import sys print('This message will be displayed via standard output.') original_stdout = sys.stdout # Save a reference to the original standard output sys.stdout = sys.stderr # Redirect the standard output to the standard error. print('This message will be displayed via the standard error.') sys.stdout = original_stdout # Reset the standard output to its original value This example is almost identical to the previous one, except that instead of redirecting the standard output stream to a file, we redirect it to the standard error stream. If the standard error stream was also redirected somewhere else, the output would be sent to that location instead of to the screen.
This message will be displayed via standard output. This message will be displayed via the standard error. While it may appear like regular output to us, for the computer it is displayed through different pipelines.
Print Using the «file» Parameter
In the previous examples, we explicitly redirected the standard output to another file-like object by changing the stdout object. However, for convenience we can do this directly from within the print() function by specifying the output location with the file parameter:
For example, if we wanted to print directly to a file without changing the entire script’s stdout , we would write:
import sys print('This message will be displayed on the screen.') with open('filename.txt', 'w') as f: print('This message will be written to a file.', file=f) As we did not fiddle with redirecting the standard output explicitly, we no longer have to reset it to its initial value. As a result, this is the preferred way to write to a file with the print() function.
Note: Although the parameter’s name is file , remember that it works with any file-like object. If you wanted to print to stderr , for example, you would change the print() statement to:
print('This message will be written to stderr.', file=sys.stderr) Conclusion
In this article, we discussed redirecting Python’s print() function output using various methods. These methods included redirecting the output of a Python script from the command-line, redirecting the standard output within Python scripts, and specifying a file-like object in the file parameter directly in the print() function.
About the Author
This article was written by Jacob Stopak, a software developer and consultant with passion for helping others improve their lives through code. Jacob is the author of the Coding Essentials Guidebook for Developers, an introductory book that covers essential coding concepts and tools. It contains chapters on basic computer architecture, the Internet, Command Line, HTML, CSS, JavaScript, Python, Java, databases/SQL, Git, and more.