- Python MySQL – Insert Data Into a Table
- Insert one row into a table
- Insert multiple rows into a table
- Python MySQL Insert Into Table
- Example
- Insert Multiple Rows
- Example
- Get Inserted ID
- Example
- Python – MySQL Insert Data
- Insert Data into Table
- Python-MySQL Insert Data
- Insert a Single Row
- Insert Multiple Rows
- Get the id of Inserted Record
- Conclusion
Python MySQL – Insert Data Into a Table
Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to insert data into a table using MySQL Connector/Python API.
To insert new rows into a MySQL table, you follow these steps:
- Connect to the MySQL database server by creating a new MySQLConnection object.
- Initiate a MySQLCursor object from the MySQLConnection object.
- Execute the INSERT statement to insert data into the table.
- Close the database connection.
MySQL Connector/Python provides API that allows you to insert one or multiple rows into a table at a time. Let’s examine at each method in more detail.
Insert one row into a table
The following method inserts a new book into the books table:
from mysql.connector import MySQLConnection, Error from python_mysql_dbconfig import read_db_config def insert_book(title, isbn): query = "INSERT INTO books(title,isbn) " \ "VALUES(%s,%s)" args = (title, isbn) try: db_config = read_db_config() conn = MySQLConnection(**db_config) cursor = conn.cursor() cursor.execute(query, args) if cursor.lastrowid: print('last insert id', cursor.lastrowid) else: print('last insert id not found') conn.commit() except Error as error: print(error) finally: cursor.close() conn.close() def main(): insert_book('A Sudden Light','9781439187036') if __name__ == '__main__': main()Code language: Python (python)- First, import MySQLConnection and Error objects from the MySQL Connector/Python package and read_db_config() function from the python_mysql_dbconfig module.
- Next, define a new function named insert_book() that accepts two arguments: title and isbn. Inside the insert_book() function, construct an INSERT statement ( query ) and data ( args ) for inserting into the books table. Notice that the data passing to the function is a tuple.
- Then, create a new connection, execute the statement, and commit the change in the try except block. Note that you have to explicitly call the commit() method in order to make the changes to the database. In case a new row is inserted successfully, you can retrieve the last insert id of the AUTO_INCREMENT column by using the lastrowid property of the MySQLCursor object.
- After that, close the cursor and database connection at the end of the insert_book() function.
- Finally, call the insert_book() function to insert a new row into the books table in the main() function.
Insert multiple rows into a table
The following INSERT statement allows you to insert multiple rows into the books table:
INSERT INTO books(title,isbn) VALUES('Harry Potter And The Order Of The Phoenix', '9780439358071'), ('Gone with the Wind', '9780446675536'), ('Pride and Prejudice (Modern Library Classics)', '9780679783268');Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)To insert multiple rows into a table in Python, you use the executemany() method of the MySQLCursor object. See the following code:
from mysql.connector import MySQLConnection, Error from python_mysql_dbconfig import read_db_config def insert_books(books): query = "INSERT INTO books(title,isbn) " \ "VALUES(%s,%s)" try: db_config = read_db_config() conn = MySQLConnection(**db_config) cursor = conn.cursor() cursor.executemany(query, books) conn.commit() except Error as e: print('Error:', e) finally: cursor.close() conn.close() def main(): books = [('Harry Potter And The Order Of The Phoenix', '9780439358071'), ('Gone with the Wind', '9780446675536'), ('Pride and Prejudice (Modern Library Classics)', '9780679783268')] insert_books(books) if __name__ == '__main__': main()Code language: Python (python)The logic in this example is similar to the logic in the first example. However, instead of calling the execute() method, we call executemany() method.
In the main() function, we pass a list of tuples, each contains title and isbn of the book to the insert_books() function.
By calling the executemany() method of the MySQLCursor object, the MySQL Connector/Python translates the INSERT statement into the one that contains multiple lists of values.
In this tutorial, you have learned how to insert one or more rows into a table in Python.
Python MySQL Insert Into Table
To fill a table in MySQL, use the «INSERT INTO» statement.
Example
Insert a record in the «customers» table:
mydb = mysql.connector.connect(
host=»localhost»,
user=»yourusername«,
password=»yourpassword«,
database=»mydatabase»
)
sql = «INSERT INTO customers (name, address) VALUES (%s, %s)»
val = («John», «Highway 21»)
mycursor.execute(sql, val)
mydb.commit()
print(mycursor.rowcount, «record inserted.»)
Important!: Notice the statement: mydb.commit() . It is required to make the changes, otherwise no changes are made to the table.
Insert Multiple Rows
To insert multiple rows into a table, use the executemany() method.
The second parameter of the executemany() method is a list of tuples, containing the data you want to insert:
Example
Fill the «customers» table with data:
mydb = mysql.connector.connect(
host=»localhost»,
user=»yourusername«,
password=»yourpassword«,
database=»mydatabase»
)
sql = «INSERT INTO customers (name, address) VALUES (%s, %s)»
val = [
(‘Peter’, ‘Lowstreet 4’),
(‘Amy’, ‘Apple st 652’),
(‘Hannah’, ‘Mountain 21’),
(‘Michael’, ‘Valley 345’),
(‘Sandy’, ‘Ocean blvd 2’),
(‘Betty’, ‘Green Grass 1’),
(‘Richard’, ‘Sky st 331’),
(‘Susan’, ‘One way 98’),
(‘Vicky’, ‘Yellow Garden 2’),
(‘Ben’, ‘Park Lane 38’),
(‘William’, ‘Central st 954’),
(‘Chuck’, ‘Main Road 989’),
(‘Viola’, ‘Sideway 1633’)
]
print(mycursor.rowcount, «was inserted.»)
Get Inserted ID
You can get the id of the row you just inserted by asking the cursor object.
Note: If you insert more than one row, the id of the last inserted row is returned.
Example
Insert one row, and return the ID:
mydb = mysql.connector.connect(
host=»localhost»,
user=»yourusername«,
password=»yourpassword«,
database=»mydatabase»
)
sql = «INSERT INTO customers (name, address) VALUES (%s, %s)»
val = («Michelle», «Blue Village»)
mycursor.execute(sql, val)
print(«1 record inserted, ID:», mycursor.lastrowid)
Python – MySQL Insert Data
In the previous tutorial, we have seen how to create a database and connect it to the python program. In this tutorial, we will see how to insert a single row as well as multiple rows using the python program. Apart from this, we will see how we can get the id of the last inserted row. So, let’s get started!
Insert Data into Table
We already know that the INSERT statement is used to insert the data into the table. However, let’s revise it one more time-
To insert a single row of data in all columns of the table-
INSERT INTO table VALUES(val1, val2, val3. );Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Note that, when you want to insert the data into all columns of the row, there is no need to mention the column names in the insert statement.
To insert a single row of data in particular columns of the table-
INSERT INTO table(col1,col2. ) VALUES(val1,val2. );Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)INSERT INTO table(col1,col2) VALUES(val1,val2), (val1,val2), (val1,val2);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Python-MySQL Insert Data
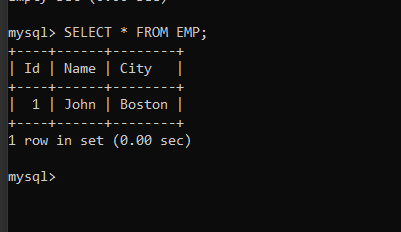
In the examples below, we will use a table that we have already created using the MySQL CLI. Following is the table description of the ’emp’ table-
Insert a Single Row
import mysql.connector mydb = mysql.connector.connect( host="localhost", user="root", passwd="1234", database="journaldev" ) mycursor = mydb.cursor() sql = "INSERT INTO emp (name, city) VALUES (%s, %s)" val = ("John", "Boston") mycursor.execute(sql, val) mydb.commit() print(mycursor.rowcount, "record inserted successfully")Code language: Python (python)Here, we have first established the connection with the database. Then we created a cursor and wrote an insert query. Using the cursor, we execute that query.
Note that, even if you execute the query, the changes won’t be made in the table unless you write a statement mydb.commit().
the mycursor.rowcount statement returns how many rows are inserted into the table.
Let’s run the python program and check the emp table to see if the data is inserted into it.
SELECT * FROM EMP;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Insert Multiple Rows
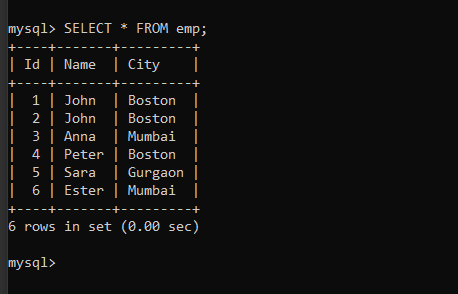
import mysql.connector mydb = mysql.connector.connect( host="localhost", user="root", passwd="1234", database="journaldev" ) mycursor = mydb.cursor() sql = "INSERT INTO emp (name, city) VALUES (%s, %s)" val = [ ("John", "Boston"), ("Anna", "Mumbai"), ("Peter", "Boston"), ("Sara", "Gurgaon"), ("Ester", "Mumbai") ] mycursor.executemany(sql, val) mydb.commit() print(mycursor.rowcount, " records inserted successfully") Code language: Python (python)Here, instead of writing multiple values in the insert statement, we have only specified the type of data that we will insert.
Then, we have created the list of values that we want to insert.
Note that, we must use the executemany() method when there are multiple rows has to be inserted into the table.
Finally, we make changes in the table using the commit() method.
Let’s run the program and check the table to see if all values are inserted correctly.
SELECT * FROM emp;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Get the id of Inserted Record
By using the cursor object, we can get the id of the row that we have just inserted.
If we insert multiple rows, the object will return the id of the last inserted row.
import mysql.connector mydb = mysql.connector.connect( host="localhost", user="root", passwd="1234", database="journaldev" ) mycursor = mydb.cursor() sql = "INSERT INTO emp (name, city) VALUES (%s, %s)" val = ("Sean", "San Jose") mycursor.execute(sql, val) mydb.commit() print("id of the last record is ", mycursor.lastrowid) Code language: Python (python)Here, have a look at the last line of the code. The lastrowid property returns the id of the last inserted row.
Till now, we have six records present in the table. When we execute the above program, we must get the if 7 in the output.
As you can see, we have got the correct output.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we have learned how to insert a single row as well as multiple rows into the MySQL table using the python program. We have learned to get the id of the last inserted row which is quite useful when you want to assign a unique id based on the auto_increment id such as student PRN number, employee number or order id, etc. In the next tutorial, we will learn to fetch the data from the MySQL table.