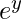- Python Math Module
- Constants provided by the math module
- Euler’s Number
- Python3
- Pi
- Python3
- Python3
- Tau
- Python3
- Infinity
- Python3
- Python3
- NaN
- Python3
- Numeric Functions
- Finding the ceiling and the floor value
- Python3
- Finding the factorial of the number
- Python3
- Finding the GCD
- Python3
- Finding the absolute value
- Python3
- Logarithmic and Power Functions
- Finding the power of exp
- Python3
- Finding the power of a number
- Python3
- Finding the Logarithm
- Python3
- Finding the Square root
- Python3
- Trigonometric and Angular Functions
- Finding sine, cosine, and tangent
- Python3
- Converting values from degrees to radians and vice versa
- Python3
- Special Functions
- Finding gamma value
- Python3
- Check if the value is infinity or NaN
- Python3
- Python3
Python Math Module
Sometimes when working with some kind of financial or scientific projects it becomes necessary to implement mathematical calculations in the project. Python provides the math module to deal with such calculations. Math module provides functions to deal with both basic operations such as addition(+), subtraction(-), multiplication(*), division(/) and advance operations like trigonometric, logarithmic, exponential functions.
In this article, we learn about the math module from basics to advance using the help of a huge dataset containing functions explained with the help of good examples.
Constants provided by the math module
Math module provides various the value of various constants like pi, tau. Having such constants saves the time of writing the value of each constant every time we want to use it and that too with great precision. Constants provided by the math module are –
Let’s see each constant in detail.
Euler’s Number
The math.e constant returns the Euler’s number: 2.71828182846.
Python3
Pi
You all must be familiar with pi. The pi is depicted as either 22/7 or 3.14. math.pi provides a more precise value for the pi.
Python3
Example 2: Let’s find the area of the circle
Python3
Tau
Tau is defined as the ratio of the circumference to the radius of a circle. The math.tau constant returns the value tau: 6.283185307179586.
Python3
Infinity
Infinity basically means something which is never-ending or boundless from both directions i.e. negative and positive. It cannot be depicted by a number. The math.inf constant returns of positive infinity. For negative infinity, use -math.inf.
Python3
Example 2: Comparing the values of infinity with the maximum floating point value
Python3
NaN
The math.nan constant returns a floating-point nan (Not a Number) value. This value is not a legal number. The nan constant is equivalent to float(“nan”).
Python3
Numeric Functions
In this section, we will deal with the functions that are used with number theory as well as representation theory such as finding the factorial of a number.
Finding the ceiling and the floor value
Ceil value means the smallest integral value greater than the number and the floor value means the greatest integral value smaller than the number. This can be easily calculated using the ceil() and floor() method respectively.
Python3
The ceil of 2.3 is : 3 The floor of 2.3 is : 2
Finding the factorial of the number
Using the factorial() function we can find the factorial of a number in a single line of the code. An error message is displayed if number is not integral.
Python3
The factorial of 5 is : 120
Finding the GCD
gcd() function is used to find the greatest common divisor of two numbers passed as the arguments.
Python3
The gcd of 5 and 15 is : 5
Finding the absolute value
fabs() function returns the absolute value of the number.
Python3
The absolute value of -10 is : 10.0
Refer to the below article to get detailed information about the numeric functions.
Logarithmic and Power Functions
Power functions can be expressed as x^n where n is the power of x whereas logarithmic functions are considered as the inverse of exponential functions.
Finding the power of exp
exp() method is used to calculate the power of e i.e. or we can say exponential of y.
Python3
54.598150033144236 0.049787068367863944 1.0
Finding the power of a number
pow() function computes x**y. This function first converts its arguments into float and then computes the power.
Python3
Finding the Logarithm
- log() function returns the logarithmic value of a with base b. If the base is not mentioned, the computed value is of the natural log.
- log2(a) function computes value of log a with base 2. This value is more accurate than the value of the function discussed above.
- log10(a) function computes value of log a with base 10. This value is more accurate than the value of the function discussed above.
Python3
The value of log 2 with base 3 is : 0.6309297535714574 The value of log2 of 16 is : 4.0 The value of log10 of 10000 is : 4.0
Finding the Square root
sqrt() function returns the square root of the number.
Python3
Refer to the below article to get detailed information about the Logarithmic and Power Functions
Trigonometric and Angular Functions
You all must know about Trigonometric and how it may become difficult to find the values of sine and cosine values of any angle. Math module provides built-in functions to find such values and even to change the values between degrees and radians.
Finding sine, cosine, and tangent
sin(), cos(), and tan() functions returns the sine, cosine, and tangent of value passed as the argument. The value passed in this function should be in radians.
Python3
The value of sine of pi/6 is : 0.49999999999999994 The value of cosine of pi/6 is : 0.8660254037844387 The value of tangent of pi/6 is : 0.5773502691896257
Converting values from degrees to radians and vice versa
- degrees() function is used to convert argument value from radians to degrees.
- radians() function is used to convert argument value from degrees to radians.
Python3
The converted value from radians to degrees is : 29.999999999999996 The converted value from degrees to radians is : 0.5235987755982988
Refer to the below articles to get detailed information about the trigonometric and angular functions.
Special Functions
Besides all the numeric, logarithmic functions we have discussed yet, the math module provides some more useful functions that does not fall under any category discussed above but may become handy at some point while coding.
Finding gamma value
The gamma() function is used to return the gamma value of the argument.
Python3
The gamma value of the given argument is : 120.0
Check if the value is infinity or NaN
isinf() function is used to check whether the value is infinity or not.
Python3
isnan() function returns true if the number is “NaN” else returns false.
Python3
Refer to the below article to get detailed information about the special functions.
List of Mathematical function in Python
| Function Name | Description |
|---|---|
| ceil(x) | Returns the smallest integral value greater than the number |
| copysign(x, y) | Returns the number with the value of ‘x’ but with the sign of ‘y’ |
| fabs(x) | Returns the absolute value of the number |
| factorial(x) | Returns the factorial of the number |
| floor(x) | Returns the greatest integral value smaller than the number |
| gcd(x, y) | Compute the greatest common divisor of 2 numbers |
| fmod(x, y) | Returns the remainder when x is divided by y |
| frexp(x) | Returns the mantissa and exponent of x as the pair (m, e) |
| fsum(iterable) | Returns the precise floating-point value of sum of elements in an iterable |
| isfinite(x) | Check whether the value is neither infinity not Nan |
| isinf(x) | Check whether the value is infinity or not |
| isnan(x) | Returns true if the number is “nan” else returns false |
| ldexp(x, i) | Returns x * (2**i) |
| modf(x) | Returns the fractional and integer parts of x |
| trunc(x) | Returns the truncated integer value of x |
| exp(x) | Returns the value of e raised to the power x(e**x) |
| expm1(x) | Returns the value of e raised to the power a (x-1) |
| log(x[, b]) | Returns the logarithmic value of a with base b |
| log1p(x) | Returns the natural logarithmic value of 1+x |
| log2(x) | Computes value of log a with base 2 |
| log10(x) | Computes value of log a with base 10 |
| pow(x, y) | Compute value of x raised to the power y (x**y) |
| sqrt(x) | Returns the square root of the number |
| acos(x) | Returns the arc cosine of value passed as argument |
| asin(x) | Returns the arc sine of value passed as argument |
| atan(x) | Returns the arc tangent of value passed as argument |
| atan2(y, x) | Returns atan(y / x) |
| cos(x) | Returns the cosine of value passed as argument |
| hypot(x, y) | Returns the hypotenuse of the values passed in arguments |
| sin(x) | Returns the sine of value passed as argument |
| tan(x) | Returns the tangent of the value passed as argument |
| degrees(x) | Convert argument value from radians to degrees |
| radians(x) | Convert argument value from degrees to radians |
| acosh(x) | Returns the inverse hyperbolic cosine of value passed as argument |
| asinh(x) | Returns the inverse hyperbolic sine of value passed as argument |
| atanh(x) | Returns the inverse hyperbolic tangent of value passed as argument |
| cosh(x) | Returns the hyperbolic cosine of value passed as argument |
| sinh(x) | Returns the hyperbolic sine of value passed as argument |
| tanh(x) | Returns the hyperbolic tangent of value passed as argument |
| erf(x) | Returns the error function at x |
| erfc(x) | Returns the complementary error function at x |
| gamma(x) | Return the gamma function of the argument |
| lgamma(x) | Return the natural log of the absolute value of the gamma function |