- Clear figure subplots matplotlib python
- 2 Answers 2
- How to Clear Plot in Matplotlib Using clear() Method
- Syntax of Matplotlib clear plot in Python
- Parameter
- Return type
- Example of Matplotlib Figure clear plot
- Explanation:
- Example of Matplotlib Axis clear plot
- Explanation:
- Must Read
- Conclusion
- When to use cla(), clf() or close() for clearing a plot
- pyplot interface
- methods of the Figure class
- How To Clear A Plot In Python
- How to Clear a Pyplot Figure
- How to Clear Pyplot Axes
- Use ActiveState Python and accelerate your Python Data Science projects.
Clear figure subplots matplotlib python
I wrote a simple Python function to generate a matplotlib figure. I call plotData multiple times from a separate script, but each time it generates a new plot. What I would like is to always have just one plot with something like subplot.clear() to clear the subplots between data changes. I need a way to identify the figure from outside plotData so that I can clear the plots for new data. What would be the best way to accomplish this?
## Plot Data Function def plotData(self): # Setup figure to hold subplots f = Figure(figsize=(10,8), dpi=100) # Setup subplots subplot1=f.add_subplot(2,1,1) subplot2=f.add_subplot(2,1,2) # Show plots dataPlot = FigureCanvasTkAgg(f, master=app) dataPlot.show() dataPlot.get_tk_widget().pack(side=RIGHT, fill=BOTH, expand=1) 2 Answers 2
I’m not sure if I fully understand where the problem lies. If you want to update the plot you would need a function that does this. I would call this function plotData . Before that you also need to set the plot up. That is what you currently have in plotData . So let’s rename that to generatePlot .
class SomeClass(): . def generatePlot(self): # Setup figure to hold subplots f = Figure(figsize=(10,8), dpi=100) # Setup subplots self.subplot1=f.add_subplot(2,1,1) self.subplot2=f.add_subplot(2,1,2) # Show plots dataPlot = FigureCanvasTkAgg(f, master=app) dataPlot.show() dataPlot.get_tk_widget().pack(side=RIGHT, fill=BOTH, expand=1) ## Plot Data Function def plotData(self, data, otherdata): #clear subplots self.subplot1.cla() self.subplot2.cla() #plot new data to the same axes self.subplot1.plot(data) self.subplot2.plot(otherdata) Now you need to call generatePlot only once at the beginning. Afterwards you can update your plot with new data whenever you want.
How to Clear Plot in Matplotlib Using clear() Method
Hello programmers, in today’s article, we will discuss Matplotlib clear plot in python. Matplotlib is a library in Python, which is a numerical – mathematical extension for NumPy library. The figure module of the Matplotlib library provides the top-level Artist, the Figure, which contains all the plot elements. The figure module is used to control the subplots’ default spacing and top-level container for all plot elements.
The Axes Class contains the figure elements: Axis, Tick, Line2D, Text, Polygon, etc., and sets the coordinate system. The instances of Axes supports callbacks through a callbacks attribute. The Axes.clear() in the axes module of the matplotlib library is used to clear the axes. Thus, the Matplotlib figure.clear() and axes.clear() is used to clear figure and axes, respectively. Here are the syntax and parameters of the Matplotlib clear plot function.
Syntax of Matplotlib clear plot in Python
clear(self, keep_observers=False)Parameter
The axis.clear() function accepts no parameters.
The ‘keep_observers’ parameter in figure.clear() function is a boolean value.
Return type
The clear() function does not return any value. It is used in python programs to clear plots.
Example of Matplotlib Figure clear plot
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt fig, ax = plt.subplots() ax.set_xlabel('x-axis') ax.set_ylabel('y-axis') ax.plot([1, 2, 3]) ax.grid(True) fig.clear(True) fig.suptitle('matplotlib.figure.Figure.clear() \ function Example\n\n', fontweight ="bold") plt.show() Explanation:
In the above example, we first create a plot as per data values given as input.The xlabel is ‘x-axis,’ and the ylabel is ‘y-axis.’ The title of the figure is ‘matplotlib.figure.Figure.clear() function Example’. The gridlines are also plotted for the figure by setting ax.grid(True). But before the plt.show() statement that shows the plotted figure, we use the fig.clear() function. The fig.clear() function clears the figure plot when ‘True’ is an argument. Thus, in this example, since fig.clear(True) is before the plt.show(), the output is the entire clear current figure except the figure title.
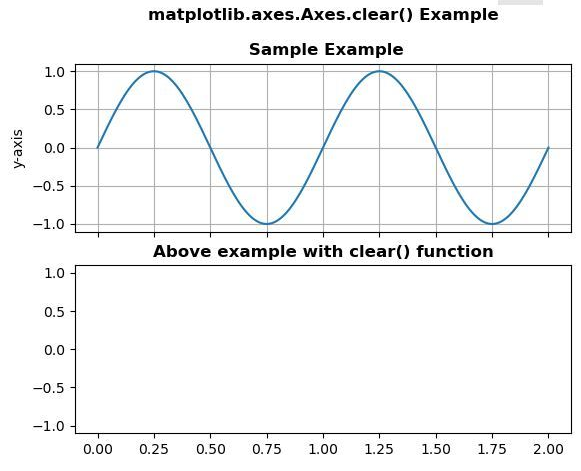
Example of Matplotlib Axis clear plot
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt t = np.linspace(0.0, 2.0, 201) s = np.sin(2 * np.pi * t) fig, [ax, ax1] = plt.subplots(2, 1, sharex = True) ax.set_ylabel('y-axis') ax.plot(t, s) ax.grid(True) ax.set_title('matplotlib.axes.Axes.clear() Example\n\n Sample Example', fontsize = 12, fontweight ='bold') ax1.set_ylabel('y-axis') ax1.plot(t, s) ax1.grid(True) ax1.clear() ax1.set_title('Above example with clear() \ function', fontsize = 12, fontweight ='bold') plt.show() Explanation:
In the above example, the two plots ‘ax’ and ‘ax1’ are created. The ylabel of figure 1 is ‘y-axis.’ The Matplotlib grid() is also ‘True,’ which returns grid lines for the figure. Also, the title of the figure is mentioned. But, we do not use the Matplotlib clear() function with the ‘ax’ plot. For the second figure, we plot it as per the given input values. But since the ax2.clear() is used, the current ‘ax2’ figure plot is cleared except for its title. Finally, the plt.show() statement gives the ‘ax’ figure and clears the ‘ax2’ figure with just its title.
Must Read
Conclusion
In this article, we have discussed ways of Matplotlib clear plot in Python. The clear() function as axes.clear() or figure.clear() clears the axes and figure of the plot, respectively. We have discussed both axes clearly and figure clear with examples and explanations. The Matplotlib cla() function can be used as axes.clear() function. Similarly, the clf() function makes figure clear. Both cla() and clf() clears plot in Matplotlib.
However, if you have any doubts or questions, do let me know in the comment section below. I will try to help you as soon as possible.
Happy Pythoning!
When to use cla(), clf() or close() for clearing a plot
They all do different things, since matplotlib uses a hierarchical order in which a figure window contains a figure which may consist of many axes. Additionally, there are functions from the pyplot interface and there are methods on the Figure class. I will discuss both cases below.
pyplot interface
pyplot is a module that collects a couple of functions that allow matplotlib to be used in a functional manner. I here assume that pyplot has been imported as import matplotlib.pyplot as plt . In this case, there are three different commands that remove stuff:
- plt.cla() clears an axis, i.e. the currently active axis in the current figure. It leaves the other axes untouched.
- plt.clf() clears the entire current figure with all its axes, but leaves the window opened, such that it may be reused for other plots.
- plt.close() closes a window, which will be the current window, if not specified otherwise.
Which functions suits you best depends thus on your use-case.
The close() function furthermore allows one to specify which window should be closed. The argument can either be a number or name given to a window when it was created using figure(number_or_name) or it can be a figure instance fig obtained, i.e., using fig = figure() . If no argument is given to close() , the currently active window will be closed. Furthermore, there is the syntax close(‘all’) , which closes all figures.
methods of the Figure class
Additionally, the Figure class provides methods for clearing figures. I’ll assume in the following that fig is an instance of a Figure :
fig.clf() clears the entire figure. This call is equivalent to plt.clf() only if fig is the current figure.
fig.clear() is a synonym for fig.clf()
Note that even del fig will not close the associated figure window. As far as I know the only way to close a figure window is using plt.close(fig) as described above.
How To Clear A Plot In Python
Before we start: This Python tutorial is a part of our series of Python Package tutorials. You can find other Matplotlib related topics too!
Matplotlib is a data visualization and graphical plotting library for Python. Matplotlib’s pyplot API is stateful, which means that it stores the state of objects until a method is encountered that will clear the current state.
This article focuses on how to clear a plot by clearing the current Axes and Figure state of a plot, without closing the plot window. There are two methods available for this purpose:
- clf() | class: matplotlib.pyplot.clf() . Used to clear the current Figure’s state without closing it.
- cla() | class: matplotlib.pyplot.cla() . Used to clear the current Axes state without closing it.
How to Clear a Pyplot Figure
Figure is the top-level container object in a matplotlib plot. Figure includes everything visualized in a plot, including one or more Axes .
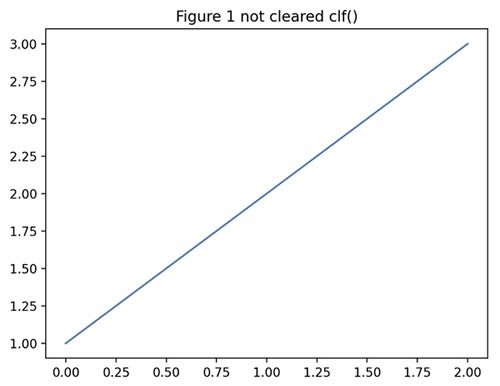
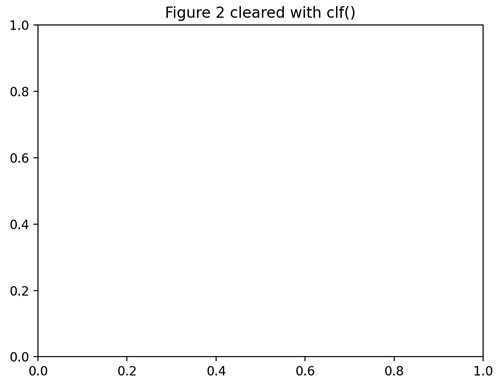
You can use the matplotlib.pyplot.clf() function to clear the current Figure’s state. The following example shows how to create two identical Figures simultaneously, and then apply the clf() function only to Figure 2:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt f1 = plt.figure() plt.plot([1, 2, 3]) plt.title("Figure 1 not cleared clf()") f2 = plt.figure() plt.plot([1,2,3]) # Clear Figure 2 with clf() function: plt.clf() plt.title("Figure 2 cleared with clf()") plt.show() Figure 1. A Figure not cleared with the clf() function:
Figure 2. A Figure with the same elements cleared with the clf() function:
How to Clear Pyplot Axes
Axes is a container class within the top-level Figure container. It is the data plotting area in which most of the elements in a plot are located, including Axis, Tick, Line2D, Text, etc., and it also sets the coordinates. An Axes has at least an X-Axis and a Y-Axis, and may have a Z-Axis.
The matplotlib.pyplot.cla() function clears the current Axes state without closing the Axes . The elements within the Axes are not dropped, however the current Axes can be redrawn with commands in the same script.
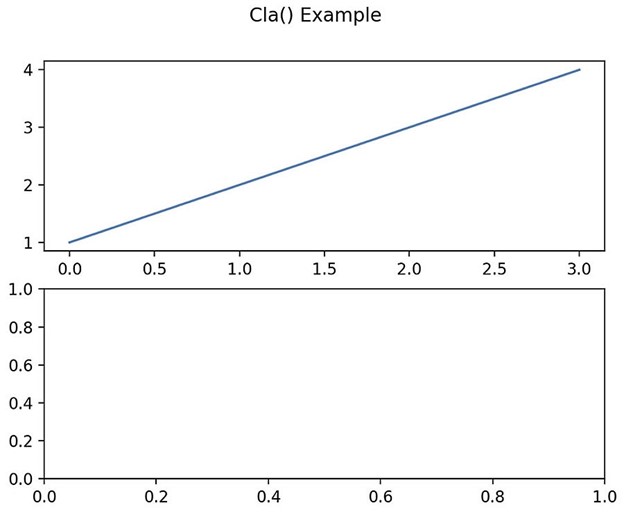
The following example creates a Figure and then plots two Axes in two different subplots. Only the second Axes is cleared with the cla() function:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt fig, [ax, ax1] = plt.subplots(2, 1) ax.plot([1, 2, 3, 4]) ax1.plot([1, 2, 3, 4]) # cla() function clears the 2nd Axe: ax1.cla() fig.suptitle('Cla() Example') plt.show() Figure 3. A Figure containing two Axes in different subplots. The first Axes is not cleared with the cla() function. The second Axes is cleared with cla():
The following tutorials will provide you with step-by-step instructions on how to work with Matplotlib, including:
Use ActiveState Python and accelerate your Python Data Science projects.
ActiveState Python is 100% compatible with the open source Python distribution, and provides the security and commercial support that your organization requires.
With ActiveState Python you can explore and manipulate data, run statistical analysis, and deliver visualizations to share insights with your business users and executives sooner–no matter where your data lives.
- Download and install the pre-built “Data Plotting” runtime environment for Windows 10 or CentOS 7, or
- Build your own custom Python runtime with just the packages you’ll need for your Data Science / Machine Learning project, by creating a free ActiveState Platform account.