- Формат данных JSON в Python
- JSON в Python
- Конвертируем JSON в объекты Python
- Конвертируем объекты Python в JSON
- Кортеж Python — в массив JSON
- Список Python — в массив JSON
- Строка Python — в строку JSON
- Булевы значения Python — в булевы значения JSON
- Запись в файл JSON
- Чтение файлов JSON
- json.load vs json.loads
- json.dump vs json.dumps
- Работа с данными JSON в Data Science
- Ограничения имплементации
- Формат JSON в разработке API
- Заключение
- Python JSON to List
- Syntax
- Examples
- 1. Convert JSON array string to Python list
- 2. Convert JSON array of arrays string to Python list
- Summary
- Python json loads array
- # Table of Contents
- # How to filter a JSON array in Python
- # How to filter a JSON array using a for loop
- # Filter a JSON array that is stored in a file in Python
- # Filter a JSON array using the filter() function
- # Additional Resources
Формат данных JSON в Python
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) это легковесный формат обмена данными. Людям его легко читать и вести в нем записи, а компьютеры запросто справляются с его синтаксическим анализом и генерацией.
JSON основан на языке программирования JavaScript. Но этот текстовый формат не зависит от языка и среди прочих может использоваться в Python и Perl. В основном его применяют для передачи данных между сервером и веб-приложением.
JSON построен на двух структурах:
- Набор пар «имя-значение». Они могут быть реализованы как объект, запись, словарь, хеш-таблица, список «ключей-значений» или ассоциативный массив.
- Упорядоченный список значений. Его реализуют в виде массива, вектора, списка или последовательности.
JSON в Python
В Python есть ряд пакетов, поддерживающих JSON, в частности metamagic.json, jyson, simplejson, Yajl-Py, ultrajson, и json. В этом руководстве мы будем использовать json, имеющий «родную» поддержку в Python. Для проверки данных JSON мы можем воспользоваться этим сайтом, предоставляющим JSON-линтер.
Ниже приведен пример записи JSON. Как видим, представление данных очень похоже на словари Python.
Конвертируем JSON в объекты Python
Вышеуказанную JSON-строку мы можем спарсить при помощи метода json.loads() из модуля json . В итоге получим словарь Python.
import json my_json_string = """< "article": [ < "id":"01", "language": "JSON", "edition": "first", "author": "Derrick Mwiti" >, < "id":"02", "language": "Python", "edition": "second", "author": "Derrick Mwiti" >], "blog":[ < "name": "Datacamp", "URL":"datacamp.com" >] > """ to_python = json.loads(my_json_string)
Конвертируем объекты Python в JSON
Используя json.dumps() , мы можем сконвертировать объекты Python в формат JSON.
blog = to_json= json.dumps(blog)
Теперь давайте сравним типы данных в Python и JSON.
| Python | JSON |
| dict | Object |
| list | Array |
| tuple | Array |
| str | String |
| int | Number |
| float | Number |
| True | true |
| False | false |
| None | null |
Ниже мы покажем, как сконвертировать некоторые объекты Python в типы данных JSON.
Кортеж Python — в массив JSON
tuple_example = 'Mango', 'Banana', 'Apple' print(json.dumps(tuple_example))
Список Python — в массив JSON
list_example = ["Mango", 1, 3, 6, "Oranges"] print(json.dumps(list_example))
Строка Python — в строку JSON
string_example = "This is a cool example." print(json.dumps(string_example))
Булевы значения Python — в булевы значения JSON
boolean_value = False print(json.dumps(boolean_value))
Запись в файл JSON
Модуль json позволяет также записывать данные JSON в файл. Такие файлы сохраняют с расширением .json .
Давайте посмотрим, как это сделать. Для этого воспользуемся функцией open() с параметром w , сигнализирующим о том, что мы хотим записать в файл.
my_json_string = """< "article": [ < "id":"01", "language": "JSON", "edition": "first", "author": "Derrick Mwiti" >, < "id":"02", "language": "Python", "edition": "second", "author": "Derrick Mwiti" >], "blog":[ < "name": "Datacamp", "URL":"datacamp.com" >] > """ with open('test_file.json', 'w') as file: json.dump(my_json_string, file) Чтение файлов JSON
Теперь продемонстрируем, как прочитать только что созданный нами файл JSON. Для его загрузки вызовем json.load() .
with open('test_file.json', 'r') as j: json_data = json.load(j) print(json_data) json.load vs json.loads
json.load используют для загрузки файла, а json.loads – для загрузки строки (loads расшифровывается как «load string»).
json.dump vs json.dumps
Аналогично, json.dump применяется, если нужно сохранить JSON в файл, а json.dumps (dump string) – если данные JSON нам нужны в виде строки для парсинга или вывода.
Работа с данными JSON в Data Science
Иногда при работе над проектами, связанными с data science, требуется загрузить данные в формате JSON. Библиотека для анализа данных Pandas предоставляет для этого функцию .read_json . Как только данные загружены, мы конвертируем их в объект dataframe при помощи атрибута pandas.DataFrame .
import pandas as pd data = pd.read_json("https://api.github.com/users") df = pd.DataFrame(data) Ограничения имплементации
Процесс кодирования в JSON называется сериализацией, а декодирования – десериализацией. Некоторые реализации десериализаторов имеют ограничения на:
- размер принимаемых текстов JSON
- максимальный уровень вложенности объектов и массивов JSON
- диапазон точности чисел JSON
- содержание и максимальную длину строк JSON.
Впрочем, подобные ограничения связаны только с типами данных Python и работой самого интерпретатора Python.
Формат JSON в разработке API
Одно из важнейших применений JSON – для разработки API в веб-приложениях. Этот формат очень полезен, ведь позволяет коллегам-разработчикам строить систему на основе наших API, используя любой язык, поддерживающий JSON. А такой поддержкой обладают практически все современные языки. На простом примере покажем, как вернуть JSON при разработке приложения на Python с фреймворком Flask. Flask предоставляет для этого модуль jsonify .
from flask import jsonify @app.route('/_get_current_user') def get_current_user(): return jsonify(username=g.user.username, email=g.user.email, > Эта программа отправит в браузер что-то вроде следующего: Заключение
В этом уроке мы сделали небольшое введение в особенности работы с JSON в Python. Рассмотрели использование различных методов из модуля json, таких как json.load и json.dumps . Кроме того, мы разобрали, как загрузить данные в формате JSON для работы в проектах data science и как возвращать JSON при разработке API. Узнать больше о модуле json можно на его официальной странице на сайте Python.
Python JSON to List
To convert a JSON String to Python List, use json.loads() function. loads() function takes JSON Array string as argument and returns a Python List.
Syntax
The syntax to use json.loads() method is
import json aList = json.dumps(jsonString)We have to import json package to use json.dumps() function.
Note: Please note that dumps() function returns a Python List, only if the JSON string is a JSON Array.
Examples
1. Convert JSON array string to Python list
In this example, we will take a JSON Array string and convert it into Python List. The JSON Array has two elements, with each element containing two key:value pairs of each.
After loading the JSON string to list, we shall print the value for key “b”.
Python Program
import json jsonStr = '[, ]' aList = json.loads(jsonStr) print(aList[0]['b'])2. Convert JSON array of arrays string to Python list
In this example, we will take a JSON String with Array of Arrays and convert it to Python List of Lists.
After parsing the JSON string to Python List, we shall access the first element of first first in the whole list.
Python Program
import json jsonStr = '[[], []]' aList = json.loads(jsonStr) print(aList[0][0])Summary
In this Python JSON Tutorial, we learned how to load a JSON Array string to Python List.
Python json loads array
Last updated: Feb 23, 2023
Reading time · 4 min
# Table of Contents
# How to filter a JSON array in Python
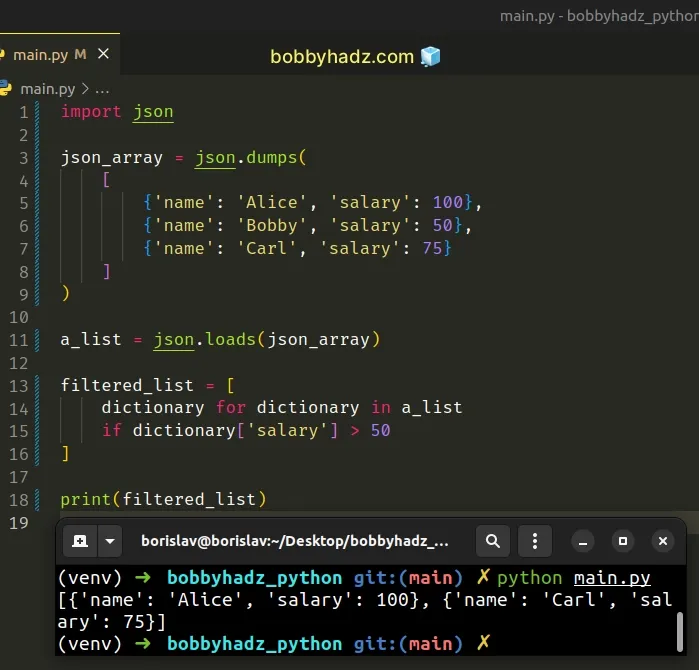
To filter a JSON array in Python:
- Use the json.loads() method to convert the JSON array to a Python list.
- Use a list comprehension to iterate over the list.
- Check if each item in the list meets a certain condition and return the result.
Copied!import json json_array = json.dumps( [ 'name': 'Alice', 'salary': 100>, 'name': 'Bobby', 'salary': 50>, 'name': 'Carl', 'salary': 75> ] ) a_list = json.loads(json_array) filtered_list = [ dictionary for dictionary in a_list if dictionary['salary'] > 50 ] # 👇️ [, ] print(filtered_list)
The json.dumps method converts a Python object to a JSON formatted string.
Conversely, the json.loads method parses a JSON string into a native Python object.
We then used a list comprehension to iterate over the list.
On each iteration, we check if a certain condition is met and return the result.
The code sample checks if each dictionary has a salary key with a value greater than 50 .
Copied!import json json_array = json.dumps( [ 'name': 'Alice', 'salary': 100>, 'name': 'Bobby', 'salary': 50>, 'name': 'Carl', 'salary': 75> ] ) a_list = json.loads(json_array) filtered_list = [ dictionary for dictionary in a_list if dictionary['salary'] > 50 ] # 👇️ [, ] print(filtered_list)
The new list only contains the dictionaries that meet the condition.
You can use this approach to check for any condition.
Alternatively, you can use a for loop.
# How to filter a JSON array using a for loop
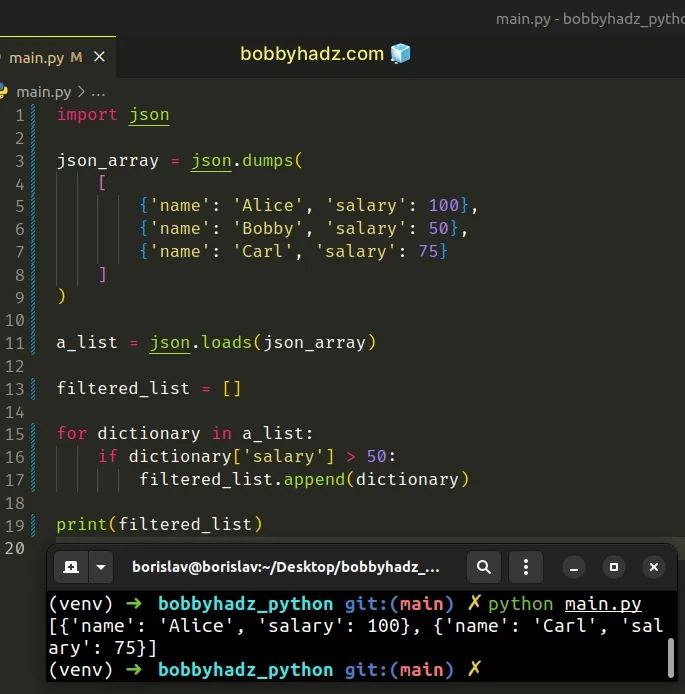
This is a four-step process:
- Use the json.loads() method to convert the JSON array to a Python list.
- Use a for loop to iterate over the list.
- Check if each list item meets a certain condition.
- Append the matching items to a new list.
Copied!import json json_array = json.dumps( [ 'name': 'Alice', 'salary': 100>, 'name': 'Bobby', 'salary': 50>, 'name': 'Carl', 'salary': 75> ] ) a_list = json.loads(json_array) filtered_list = [] for dictionary in a_list: if dictionary['salary'] > 50: filtered_list.append(dictionary) # 👇️ [, ] print(filtered_list)
We used a for loop to iterate over the list.
On each iteration, we check if the current dictionary has a salary key with a value greater than 50 .
If the condition is met, we use the list.append() method to append the dictionary to a new list.
The list.append() method adds an item to the end of the list.
The new list only contains the items of the original list that meet the condition.
You can use the same approach to filter a JSON array stored in a file.
# Filter a JSON array that is stored in a file in Python
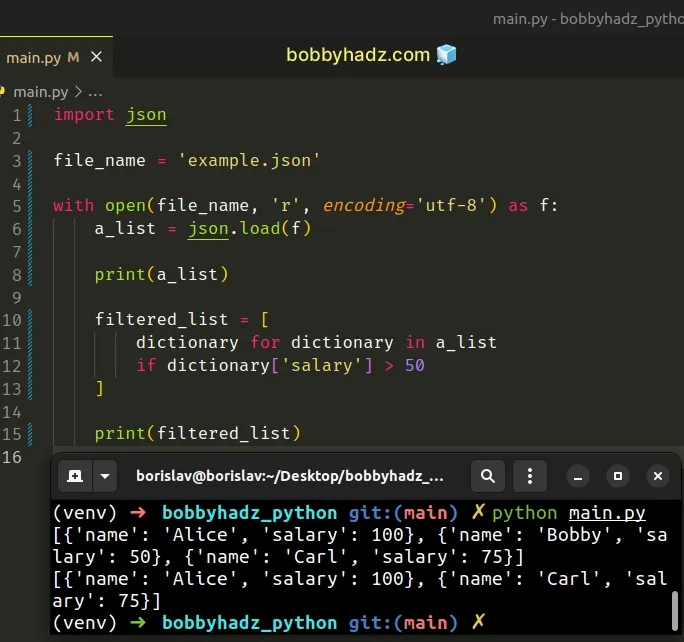
To filter a JSON array that is stored in a file:
- Open the JSON file in reading mode.
- Use the JSON.load() method to deserialize the file to a Python list.
- Use a list comprehension to filter the list.
Copied!import json file_name = 'example.json' with open(file_name, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f: a_list = json.load(f) # 👇️ [, , ] print(a_list) filtered_list = [ dictionary for dictionary in a_list if dictionary['salary'] > 50 ] # 👇️ [, ] print(filtered_list)
The code sample assumes that you have an example.json file stored in the same directory as your main.py script.
Copied![ "name": "Alice", "salary": 100>, "name": "Bobby", "salary": 50>, "name": "Carl", "salary": 75> ]
The json.load method is used to deserialize a file to a Python object.
On the other hand, the json.loads method is used to deserialize a JSON string to a Python object.
The json.load() method expects a text file or a binary file containing a JSON document that implements a .read() method.
Once we have the data from the JSON file parsed to a native Python list, we can use a list comprehension or a for loop to filter the list.
You can also use the filter() function to filter a JSON array.
# Filter a JSON array using the filter() function
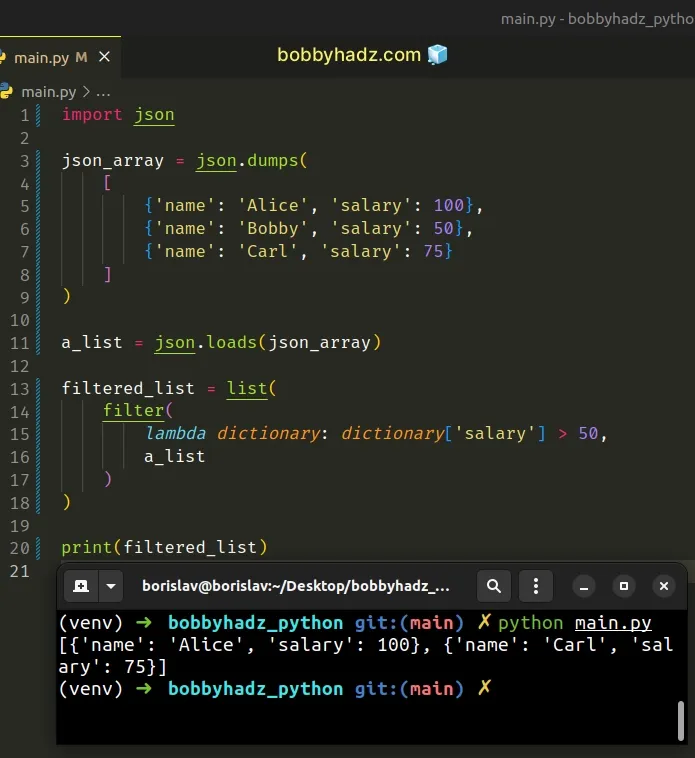
This is a three-step process:
- Use the json.loads() function to parse the JSON array into a Python list.
- Pass a lambda function and the list to the filter() function.
- The lambda function should check if each list item meets a condition.
Copied!import json json_array = json.dumps( [ 'name': 'Alice', 'salary': 100>, 'name': 'Bobby', 'salary': 50>, 'name': 'Carl', 'salary': 75> ] ) a_list = json.loads(json_array) filtered_list = list( filter( lambda dictionary: dictionary['salary'] > 50, a_list ) ) # 👇️ [, ] print(filtered_list)
The filter function takes a function and an iterable as arguments and constructs an iterator from the elements of the iterable for which the function returns a truthy value.
The function checks if the dictionary meets a certain condition and returns the result.
The last step is to use the list() class to convert the filter object to a list.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- How to Convert JSON NULL values to None using Python
- How to convert a Tuple to JSON in Python
- How to Delete a JSON object from a List in Python
- ImportError: cannot import name ‘json’ from ‘itsdangerous’
- ValueError: malformed node or string in Python [Solved]
- Check the syntax of a Python script without executing it
- Mock multiple return values in a Python unit Test
- Python: Assert that Mock was called with specific Arguments
- Python: Sending multipart/form-data request with requests
- Python: Don’t run a module’s code when it is imported
- How to keep a Python script output Window open
- How to merge multiple JSON files in Python [3 Ways]
I wrote a book in which I share everything I know about how to become a better, more efficient programmer.