- crypto 1.4.1
- Install
- Upgrade
- Usage
- Encryption (crypto)
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Issue Reporting
- pycrypto 2.6.1
- Installation
- ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘Crypto’ in Python
- Reason: ‘Crypto’ Module is Not Installed
- Solution (For Windows): Install the Python ‘Crypto’ Module
- How to Uninstall Crypto/pycryptodome Module in Python?
- Install the ‘Crypto’ Module in Anaconda
- Install the ‘Crypto’ Module in Jupyter Notebook
- Solution (For Linux): Install Python ‘Crypto’ Module
- For Ubuntu 22.04
- Conclusion
crypto 1.4.1
crypto provides a simple interface to symmetric Gnu Privacy Guard (gpg) encryption and decryption for one or more files on Unix and Linux platforms. It runs on top of gpg and requires a gpg install on your system. Encryption is performed with the AES256 cipher algorithm. Benchmarks relative to default gpg settings are available for text and binary file mime types.
crypto provides a number of options including automated tar archives of multiple files prior to encryption, portable ASCII armored encryption formatting, and SHA256 hash digest generation for your encrypted files. You can view all available options in the usage documentation or with the —help option.
Tested in cPython 2.7.x, 3.4.x, and pypy 2.6.x (Python version 2.7.9)
Install
Install with pip using the command:
or download the source repository, unpack it, and navigate to the top level of the repository. Then enter:
Upgrade
You can upgrade your crypto version with the command:
$ pip install --upgrade cryptoUsage
Encryption (crypto)
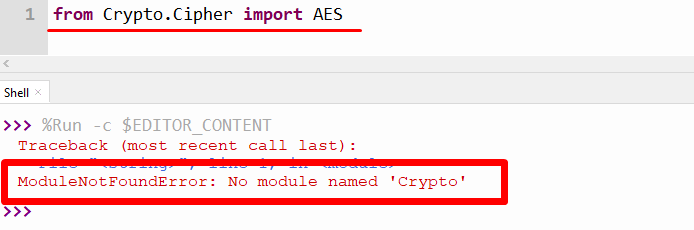
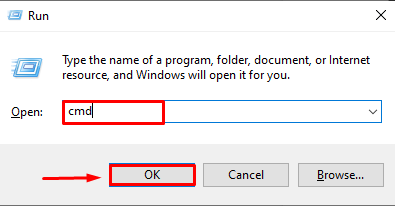
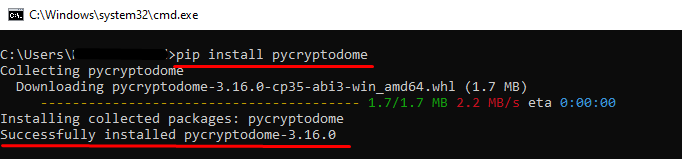
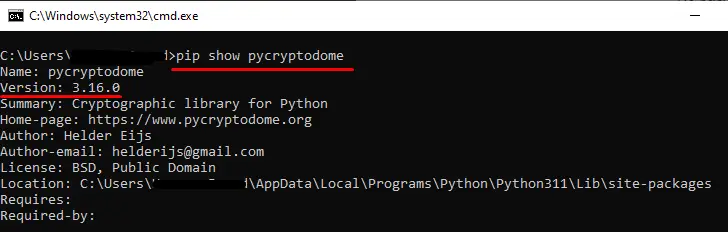
$ crypto path Issue reporting is available on the GitHub repository This is a collection of both secure hash functions (such as SHA256 and RIPEMD160), and various encryption algorithms (AES, DES, RSA, ElGamal, etc.). The package is structured to make adding new modules easy. This section is essentially complete, and the software interface will almost certainly not change in an incompatible way in the future; all that remains to be done is to fix any bugs that show up. If you encounter a bug, please report it in the Launchpad bug tracker at An example usage of the SHA256 module is: An example usage of an encryption algorithm (AES, in this case) is: One possible application of the modules is writing secure administration tools. Another application is in writing daemons and servers. Clients and servers can encrypt the data being exchanged and mutually authenticate themselves; daemons can encrypt private data for added security. Python also provides a pleasant framework for prototyping and experimentation with cryptographic algorithms; thanks to its arbitrary-length integers, public key algorithms are easily implemented. As of PyCrypto 2.1.0, PyCrypto provides an easy-to-use random number generator: A stronger version of Python’s standard “random” module is also provided: Caveat: For the random number generator to work correctly, you must call Random.atfork() in both the parent and child processes after using os.fork() PyCrypto is written and tested using Python version 2.1 through 3.3. Python 1.5.2 is not supported. The modules are packaged using the Distutils, so you can simply run “python setup.py build” to build the package, and “python setup.py install” to install it. If the setup.py script crashes with a DistutilsPlatformError complaining that the file /usr/lib/python2.2/config/Makefile doesn’t exist, this means that the files needed for compiling new Python modules aren’t installed on your system. Red Hat users often run into this because they don’t have the python2-devel RPM installed. The fix is to simply install the requisite RPM. On Debian/Ubuntu, you need the python-dev package. To verify that everything is in order, run “python setup.py test”. It will test all the cryptographic modules, skipping ones that aren’t available. If the test script reports an error on your machine, please report the bug using the bug tracker (URL given above). If possible, track down the bug and include a patch that fixes it, provided that you are able to meet the eligibility requirements at http://www.pycrypto.org/submission-requirements/. It is possible to test a single sub-package or a single module only, for instance when you investigate why certain tests fail and don’t want to run the whole suite each time. Use “python setup.py test –module=name”, where ‘name’ is either a sub-package (Cipher, PublicKey, etc) or a module (Cipher.DES, PublicKey.RSA, etc). To further cut test coverage, pass also the option “–skip-slow-tests”. To install the package under the site-packages directory of your Python installation, run “python setup.py install”. If you have any comments, corrections, or improvements for this package, please report them to our mailing list, accessible via the PyCrypto website: Python supports extensive modern libraries such as NumPy, pandas, sklearn, etc. that help developers to complete complex tasks easily. The “PyCrypto” module, replaced by “PyCryptodome”, is used for cryptography and security engineering. To access this module in Python, you must import them at the beginning. If the “PyCrypto” module is imported without installation, then the “ModuleNotFoundError” arises in Python. The Python post will demonstrate the reason and solutions for the “no module named Crypto” error using the following contents: First, let’s dig into the first reason. The primary reason which causes this “ModuleNotFoundError” in Python is when the user imports the “Crypto” module in Python without installing it. Here is an example of this error The above output shows an error because the “Crypto” module is not found in Python. Note: This error also occurs when we use the name “Crypto” for modules such as “Crypto.py” or initialize a variable with the name “Crypto”. The best way to resolve this error is by installing the module in Python. To install the module, we use the “pip” package manager. The pip module comes with Python; if you don’t have a pip, you can install it by following this tutorial. For an installation of the “Crypto” module, you can use the given below steps: Step 1: Open CMD To open the command prompt terminal, simply press the “Windows key + R” button and type the “cmd” command in the run dialog box: Note: If you are using the Python editor that uses a virtual environment then it is recommended to open the editor shell rather than cmd and install the module on the IDE terminal. Step 2: Install the ‘Crypto’ Module Using pip To install the “Crypto” module using the “pip”, you can type the below command in the terminal: The above snippet shows that the module named “pycryptodome” successfully installed in Python. If you get a permission error, then you can use the following command: Step 3: Verification of ‘Crypto’ Module in Python To verify the “Crypto” module installation in Python, you can type the below code in terminal: The above snippet shows the “pycryptodome” module name, version, and location. To uninstall the “pycryptodome” module, you can type the following command in the terminal: The above snippet shows that the module has been successfully installed from Python using the “pip” command. To install the “Crypto” module in Anaconda Environment; you can use the following command: To install the “Crypto” module in Jupyter Notebook you can use the following code: To install the “Crypto” module in Python Linux you can use the pip package manager, you can type the given below command in the terminal to install the “Crypto” module: To install the “Crypto” module in Ubuntu 22.04, you first need to update the repository by typing the below command: After updating now you can type the given below command to install the “Crypto” module in Ubuntu 22.04: That’s all from this crypto module not found error. The “ModuleNotFoundError” occurs when we try to import the “Crypto” module without installing it in Python. The error occurs when we install the module in an incorrect Python version. To resolve this error, install the module using the “pip” and “apt” commands. This article demonstrated a detailed guide on resolving Python’s “no module named Crypto” error.$ decrypto path
$ crypto --help decrypto --helpFrequently Asked Questions
Issue Reporting
pycrypto 2.6.1
>>> from Crypto.Hash import SHA256 >>> hash = SHA256.new() >>> hash.update('message') >>> hash.digest() '\xabS\n\x13\xe4Y\x14\x98+y\xf9\xb7\xe3\xfb\xa9\x94\xcf\xd1\xf3\xfb"\xf7\x1c\xea\x1a\xfb\xf0+F\x0cm\x1d' >>> from Crypto.Cipher import AES >>> obj = AES.new('This is a key123', AES.MODE_CBC, 'This is an IV456') >>> message = "The answer is no" >>> ciphertext = obj.encrypt(message) >>> ciphertext '\xd6\x83\x8dd!VT\x92\xaa`A\x05\xe0\x9b\x8b\xf1' >>> obj2 = AES.new('This is a key123', AES.MODE_CBC, 'This is an IV456') >>> obj2.decrypt(ciphertext) 'The answer is no' >>> from Crypto import Random >>> rndfile = Random.new() >>> rndfile.read(16) '\xf7.\x838#>\xc6\xc2jJU'
>>> from Crypto.Random import random >>> random.choice(['dogs', 'cats', 'bears']) 'bears'
Installation
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘Crypto’ in Python
Reason: ‘Crypto’ Module is Not Installed
Solution (For Windows): Install the Python ‘Crypto’ Module
> pip install pycryptodome --user
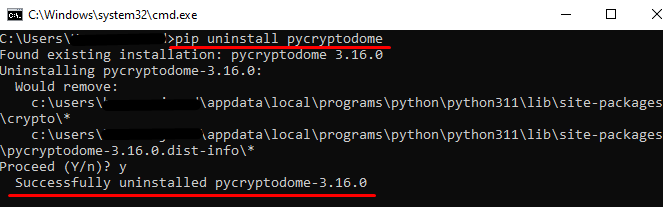
How to Uninstall Crypto/pycryptodome Module in Python?
> pip uninstall pycryptodome
Install the ‘Crypto’ Module in Anaconda
> conda install -c conda-forge pycryptodome
Install the ‘Crypto’ Module in Jupyter Notebook
Solution (For Linux): Install Python ‘Crypto’ Module
$ sudo pip install pycryptodome
For Ubuntu 22.04
$ sudo apt -y install python3-pycryptodome
Conclusion