- Python list comprehension using if-else
- Python list comprehension using if statement
- Python list comprehension using if without else
- Python list comprehension using nested if statement
- Python list comprehension using multiple if statement
- Python list comprehension using nested for loop
- Python list comprehension transposes rows and columns
- Python if statement with list
- # Table of Contents
- # Using elif statement in a List comprehension in Python
- # If you only have an if statement, specify it at the end
- # List comprehension with if-else statement in Python
- # Additional Resources
Python list comprehension using if-else
In this Python tutorial, we will learn python list comprehension using if-else, and also we will cover these topics:
- Python list comprehension using if statement
- Python list comprehension using if without else
- Python list comprehension using nested if statement
- Python list comprehension using multiple if statement
- Python list comprehension with if-else
- Python list comprehension using nested for loop
- Python list comprehension transposes rows and columns
Python list comprehension using if statement
Here, we can see list comprehension using if statement in Python.
In this example, I have taken a variable as num and I have used for loop for iteration and assigned a range of 10, and if condition is used as if i%2==0. To get the output, I have used print(num).
num = [i for i in range(10) if i%2==0 ] print(num)In the output, you can see the numbers in the form of a list up to the range of 10. You can refer to the below screenshot for the output.
Python list comprehension using if without else
Now, we can see list comprehension using if without else in Python.
In this example, I have taken a variable as num, The num = [i for i in range(10) if i>=5] is used and for iteration, I have used for loop and assigned a range of 10 and then if condition is used as if>=5. To get the output I have used print(num).
num = [i for i in range(10) if i>=5] print(num)The output is in the form of a list where you can see the numbers in the list which are greater than or equal to 5. You can refer to the below screenshot for the output.
Python list comprehension using nested if statement
Now, we can see list comprehension using nested if statement in Python.
- In this example, I have taken a variable num. The num = [i for i in range(50) if i%2==0 if i%3==0 if i%3==0] is used. For iteration, I have used for loop
- And assigned a range of 50 and multiple if conditions are used as ifi%2==0 if i%3==0 if i%3==0, to print the numbers I have used print(num).
num = [i for i in range(50) if i%2==0 if i%3==0 if i%3==0] print(num)Here, the numbers which satisfy all the three if conditions from the given range will be the output in the list format. The below screenshot shows the output.
Python list comprehension using multiple if statement
Now, we can see list comprehension using multiple if statement in Python.
- In this example, I have taken a variable = num, Here, the for loop is used for iterations, and assigned a range of 30.
- The multiple if statements are used as num = [i for i in range(30) if i>=2 if i. To print the numbers I have used print(num).
num = [i for i in range(30) if i>=2 if iThe number from the given range which satisfys all the multiple if conditions are printed as the output in the list format. The below screenshot shows the output.
Python list comprehension with if-else
Here, we can see list comprehension with if else in Python.
- In this example, I have a variable as fruits and the if-else condition is used as i%3==0, if the condition is true then the result will be mango else orange.
- Here, for loop is used for iteration, and to get the output I have used print(fruits).
fruits = ["mango" if i%3==0 else "orange" for i in range(10)] print(fruits)We can see the output as mango when the if condition is true and orange when the else condition is true in the list format as the output. You can refer to the below screenshot for the output.
Python list comprehension using nested for loop
Now, we can see list comprehension using nested for loop in Python.
- In this example, multiple for loops are used. The range is given from 2 to 4, and for loop is used for iteration.
- The first for loop is taken as for i in range(2,4): and another for loop as for j in range(1,5):
- The addition operation is performed for these two loops as a print(f”+=”).
- To print the added numbers I have used print(f”+=”).
for i in range(2,4): for j in range(1,5): print(f"+=")In the output, you can see the numbers are added from the given range. You can refer to the below screenshot for the output.
Python list comprehension transposes rows and columns
Here, we can see list comprehension transposes rows and columns in Python.
- In this example, I have taken a list as list = [[2,4,6,8]] and to transpose this matrix into rows and columns. I have used for loop for iteration.
- I have taken matrix = [[row[i] for row in list] for i in range(4)] and range is given up to 4.
- To get the matrix output, I have used print(matrix).
list = [[2,4,6,8]] matrix = [[row[i] for row in list] for i in range(4)] print(matrix)We can see the four matrices as the output in the below screenshot.
You may like the following Python tutorials:
In this tutorial, we have learned about Python list comprehension using if-else, and also we have covered these topics:
- Python list comprehension using if statement
- Python list comprehension using if without else
- Python list comprehension using nested if statement
- Python list comprehension using multiple if statement
- Python list comprehension with if-else
- Python list comprehension using nested for loop
- Python list comprehension transposes rows and columns
I am Bijay Kumar, a Microsoft MVP in SharePoint. Apart from SharePoint, I started working on Python, Machine learning, and artificial intelligence for the last 5 years. During this time I got expertise in various Python libraries also like Tkinter, Pandas, NumPy, Turtle, Django, Matplotlib, Tensorflow, Scipy, Scikit-Learn, etc… for various clients in the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, Australia, New Zealand, etc. Check out my profile.
Python if statement with list
Last updated: Feb 23, 2023
Reading time · 6 min
# Table of Contents
# Using elif statement in a List comprehension in Python
To use an elif statement in a list comprehension:
- Use an if statement to check for a condition.
- Use an else statement to implement an elif clause.
- Use a second else statement to return a value if neither condition is met.
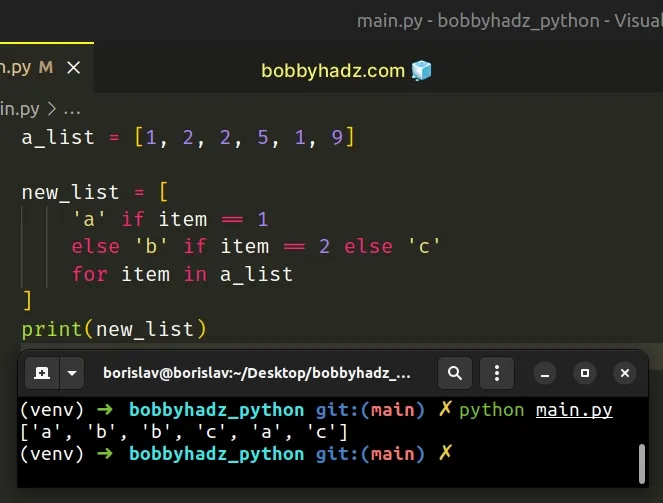
Copied!a_list = [1, 2, 2, 5, 1, 9] new_list = [ 'a' if item == 1 else 'b' if item == 2 else 'c' for item in a_list ] print(new_list) # 👉️ ['a', 'b', 'b', 'c', 'a', 'c']
List comprehensions are used to perform some operation for every element or select a subset of elements that meet a condition.
We used an else statement to implement an elif clause in a list comprehension.
The if statement checks if the current item is equal to 1 and if the condition is met, a is returned.
The else statement returns another condition. The condition checks if the item is equal to 2 . If the condition is met, b is returned.
If neither condition is met, c is returned.
In pseudo-code, the syntax looks as follows.
Copied!new_list = [ return A if condition_is_met else return B if condition_is_met else return C for item in a_list ]
Notice that the if and else statements are at the beginning of the list comprehension.
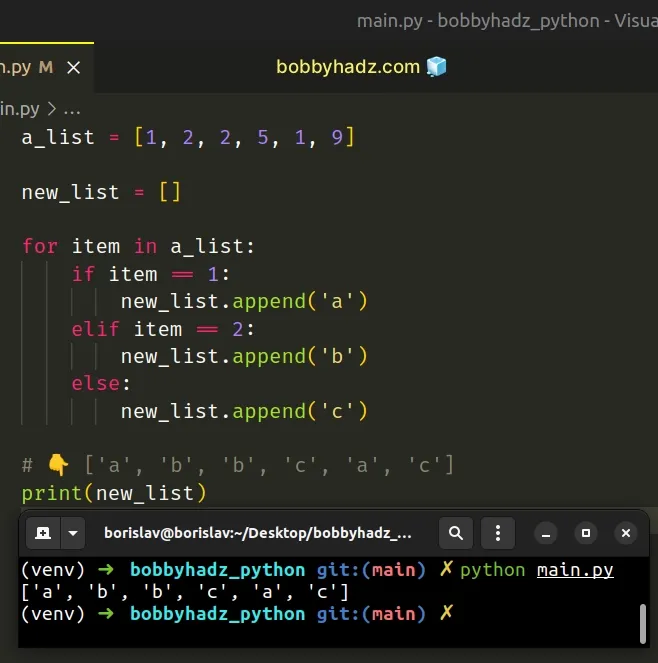
Here is how we would implement the list comprehension from the example using a for loop.
Copied!a_list = [1, 2, 2, 5, 1, 9] new_list = [] for item in a_list: if item == 1: new_list.append('a') elif item == 2: new_list.append('b') else: new_list.append('c') # 👇️ ['a', 'b', 'b', 'c', 'a', 'c'] print(new_list)
The for loop from the code sample is equivalent to the list comprehension.
Here is another example of using an elif statement in a list comprehension.
Copied!a_list = [1, 2, 2, None, 1, None] new_list = [ 0 if item is None else item if item % 2 == 0 else item + 11 for item in a_list ] print(new_list) # 👉️ [12, 2, 2, 0, 12, 0]
The if statement checks if the current item is None and if the condition is met, 0 is returned.
The else statement implements another condition. The condition checks if the number divided by 2 has a remainder of 0 .
If the condition is met, the item is returned, otherwise, the item + 11 is returned.
The same approach can be used if you only need to implement an if-else statement in a list comprehension.
Copied!a_list = [1, 2, 2, None, 1, None] new_list = [ 0 if item is None else item for item in a_list ] print(new_list) # 👉️ [1, 2, 2, 0, 1, 0]
The if statement checks if the item is None. If the condition is met, 0 is returned, otherwise, the item is returned.
The syntax in pseudo-code looks as follows.
Copied!new_list = [ return A if condition_is_met else return B for item in list ]
Notice that the if and else statements are specified at the beginning of the list comprehension.
# If you only have an if statement, specify it at the end
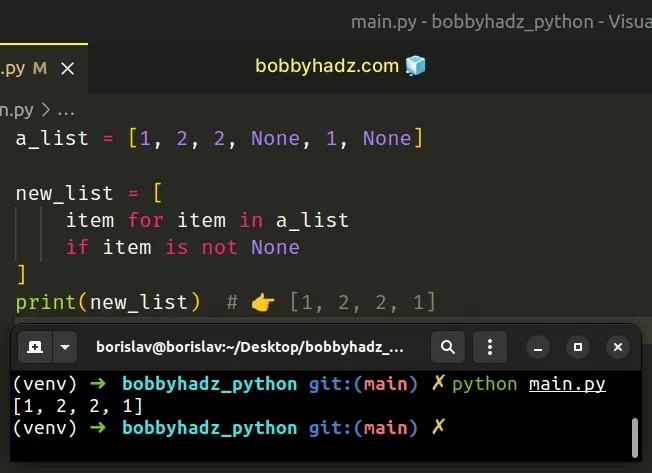
If you only have an if statement in a list comprehension, make sure to specify it at the end.
Copied!a_list = [1, 2, 2, None, 1, None] new_list = [ item for item in a_list if item is not None ] print(new_list) # 👉️ [1, 2, 2, 1]
Implementing an if-elif-else statement in a list comprehension might make your code more difficult to read.
If that's the case, simply use a for loop.
Copied!a_list = [1, 2, 2, None, 1, None] new_list = [] for item in a_list: if item is None: new_list.append(0) elif item % 2 == 0: new_list.append(item) else: new_list.append(item + 11) print(new_list) # 👉️ [12, 2, 2, 0, 12, 0]
The for loop approach is a bit more verbose but in my opinion, it is more readable and intuitive.
# List comprehension with if-else statement in Python
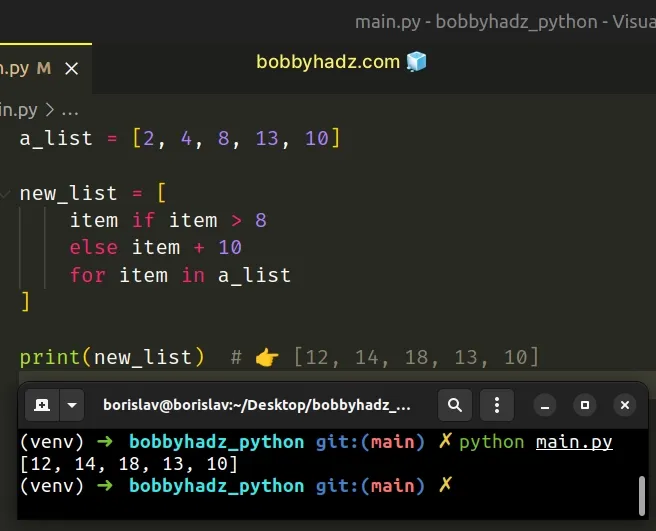
To use a list comprehension with if-else:
- Specify the if statement first in the list comprehension.
- Specify the else statement after the if .
- Iterate over a collection in the list comprehension.
Copied!a_list = [2, 4, 8, 13, 10] new_list = [ item if item > 8 else item + 10 for item in a_list ] print(new_list) # 👉️ [12, 14, 18, 13, 10]
List comprehensions are used to perform some operation for every element or select a subset of elements that meet a condition.
The syntax for using if-else in a list comprehension is as follows.
Copied!new_list = [ return A if condition_is_met else return B for item in list ]
The syntax a if condition else b is called the ternary operator.
Copied!site = 'bobbyhadz.com' result = 'a' if len(site) > 1 else 'b' print(result) # 👉️ 'a'
The ternary operator returns the value to the left if the condition is met, otherwise, the value to the right is returned.
If you only have an if statement in your list comprehension, specify the condition at the end.
Copied!a_list = [2, 4, 8, 13, 10] new_list = [ item for item in a_list if item > 8 ] print(new_list) # 👉️ [13, 10]
However, you can't have an if/else statement at the end of a list comprehension as it is invalid syntax.
Copied!a_list = [2, None, 4, None, 8] new_list = [ item if item is not None else 0 for item in a_list ] print(new_list) # 👉️ [2, 0, 4, 0, 8]
We used a list comprehension to iterate over the list.
The if statement checks if the current item is not None and if the condition is met, the item is returned.
Otherwise, the else statement returns 0 .
The list comprehension is equivalent to the following for loop.
Copied!a_list = [2, None, 4, None, 8] new_list = [] for item in a_list: if item is not None: new_list.append(item) else: new_list.append(0) print(new_list) # 👉️ [2, 0, 4, 0, 8]
You can also use an if with multiple else statements in a list comprehension to implement an elif condition.
Copied!a_list = [2, 4, 8, 4, 19] new_list = ['a' if item == 4 else 'b' if item == 8 else 'c' for item in a_list] print(new_list) # 👉️ ['c', 'a', 'b', 'a', 'c']
The if statement checks if the current item is equal to 4 and if the condition is met, the letter a is returned.
The else statement returns another condition.
The condition checks if the item is equal to 8 . If the condition is met, the letter b is returned, otherwise, the letter c is returned.
In pseudo-code, the syntax looks as follows.
Copied!new_list = [ return A if condition_is_met else return B if condition_is_met else return C for item in a_list ]
Here is how you'd implement the list comprehension from the previous example using a for loop.
Copied!a_list = [2, 4, 8, 4, 19] new_list = [] for item in a_list: if item == 4: new_list.append('a') elif item == 8: new_list.append('b') else: new_list.append('c') print(new_list) # 👉️ ['c', 'a', 'b', 'a', 'c']
We check if the item is equal to 4 and append a to a new list if the condition is met.
Otherwise, the elif statement checks if the current item is equal to 8 . If the condition is met, we append b to the new list.
If the conditions aren't met, the else statement runs and we append c to the list.
Checking for too many conditions in list comprehensions might get more complicated than necessary.
In these cases, you can use a simple for loop for readability purposes.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
I wrote a book in which I share everything I know about how to become a better, more efficient programmer.