- IndentationError: expected an indented block
- Python block
- Indentation in Python
- Tabbed indentation
- Docstring Indentation
- How to Fix IndentationError: expected an indented block
- Reproduce the error
- Other causes of the error
- How to Fix IndentationError: expected an indented block
- Python cares about indention
- Python unexpected indent
- How to Fix the “IndentationError: expected an indented block” Error in Your Python Code
- Why Do You Get the IndentationError in Python?
- Common Cases of Correct Indentation
- If statements
- Functions
IndentationError: expected an indented block
In documentation terminology, indentation means the space from margin to the begin of characters in a line. In most popular programming languages, spaces or indentation are just used to make the code look better and be easier to read. In Python , it is actually part of this programming language. Because the Python language is a very sensitive language for indentation, it has caused confusion for many beginners. Putting in an extra space or leaving one out where it is needed will surely generate an error message . Some common causes of this error include:
- Forgetting to indent the statements within a compound statement
- Forgetting to indent the statements of a user-defined function.
The error message IndentationError: expected an indented block would seem to indicate that you have an indentation error. It is probably caused by a mix of tabs and spaces . There are two main reasons why you could have such an error:
output
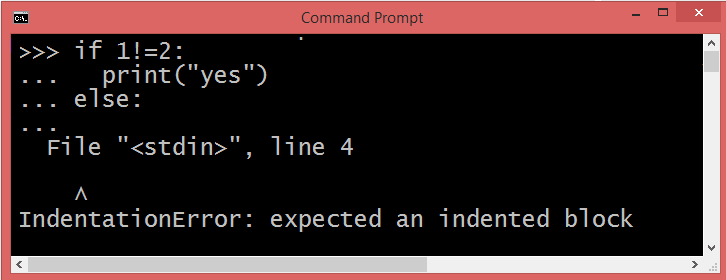
The above example fails to indent after the if statement and the output states that you need to have an indented block on line 2.
example 2:
The output states that you need to have an indented block on line 4, after the else: statement
Python block
Here you can see, what follows the colon (:) is a line-break and an indented block . Python uses white-space to distinguish code blocks. You can use spaces or tabs to create a Python block . When several statements use the same indentation , they are considered as a block. Python in fact insists that separate statements use the same indentation in a block. It would complain if you forget to indent when a block is expected, as well as if you use varying indentations.
Indentation in Python
The indentation can be any consistent white space . It is recommended to use 4 spaces for indentation in Python, tabulation or a different number of spaces may work, but it is also known to cause trouble at times. 4 spaces are a good compromise between small indentation (allows greater nesting depth) and large indentation (easier to read). Using only spaces is generally the better choice. Most editors have an option for automatically converting tabs to spaces. If your editor has this option, turn it on.
Tabbed indentation
Tabs are a bad idea because they may create different amount if spacing in different editors . They’re also potentially confusing if you mix tabbed indentation with spaced indentation. If you’re using an IDE like Eclipse , you can configure how many spaces the IDE will insert when you press tab. It’s important to note that most modern IDEs help you keep indentation using tabs or spaces , but since whitespace characters are not visible in some editors, you should take care to properly indent blocks .
Docstring Indentation
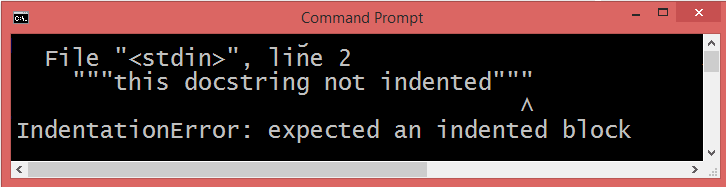
This error IndentationError: expected an indented block can also come up if the programmer forgets to indent a docstring. Docstrings must be in line with the rest of the code in a function. Docstring processing tools will strip a uniform amount of indentation from the second and further lines of the docstring, equal to the minimum indentation of all non-blank lines after the first line.
output
To fix this issue, indent the docstring .
How to Fix IndentationError: expected an indented block
IndentationError: expected an indented block error occurs in Python when the code is not indented correctly.
To fix the IndentationError: expected an indented block error in Python, “indent the code block correctly to align it with its surrounding code.”
In Python, whitespace (indentation) is significant and determines the scope of a code block.
An “IndentationError: expected an indented block” means a block of code that is supposed to be indented at all or not indented enough, leading the interpreter to believe that the block of code is not part of the current scope.
Before Python runs any code in your program, it will first discover each line’s correct parent and children. Then, Python throws an Indentation whenever it comes across a line for which it cannot define the right parent to assign.
Reproduce the error
def compare(num): if num >= 1: print("It is positive number") elif num < 0: print("It is negative number") else: print("It is zero") compare(1)If you run the above file, your output looks like the one below.
File "/Users/krunal/Desktop/code/pyt/database/app.py", line 3 print("It is positive number") ^ IndentationError: expected an indented blockOther causes of the error
The causes of the IndentationError: expected an indented block error include:
- Incorrect indentation levels: T he code is not indented to the proper level
- Mixing tabs and spaces for indentation causes inconsistencies, leading to the error message.
- Improper use of white space characters: Using extra spaces or the wrong type of white space character can result in an error.
How to Fix IndentationError: expected an indented block
Python cares about indention
In Python, indentation replaces the keyword begin / end or < >and is therefore necessary.
This is verified before the execution of the code; therefore, even if the code with the indentation error is never reached, it won’t work.
From the above example, you can check if you have left alone an elif: part of an if-condition, and check if the indentation is missing after conditions, loops, etc.
In our example, there should be an indentation before starting a new statement after the if, elif, and else blocks.
Still, we did not put any whitespace, and that caused an indentation error. So let’s resolve the error by providing whitespaces.
def compare(num): if num >= 1: print("It is positive number") elif num < 0: print("It is negative number") else: print("It is zero") compare(1)And the IndentationError is successfully resolved.
For example, Python statements start with def or must have at least one child. This means that a function must have at least one line of code. It also means that a conditional must have at least one line of code to run if the condition is True.
Let’s see the example in which we don’t write anything after the first if statement.
def compare(num): if num >= 1: elif num < 0: print("It is negative number") else: print("It is zero") compare(1)File "/Users/krunal/Desktop/code/pyt/database/app.py", line 4 elif num < 0: ^ IndentationError: expected an indented blockAfter Python reads the if statement, it expects to see at least one child line following it. However, since the next non-empty line reads it is the elif statement, which means the if statement has no children, Python reports that it expected some indented lines.
To fix this IndentationError, either place at least one line of code as the if statement’s child or remove them entirely.
def compare(num): if num >= 1: print("It is positive number") elif num < 0: print("It is negative number") else: print("It is zero") compare(1)If you run the above code, you will get the expected output.
Python unexpected indent
Python throws an IndentationError when it finds a line indented as if the line had some parent line, but it couldn’t get any lines above to be its parent.
For example, you face this unexpected indent error when a line is indented by one or more spaces more than the previous line, and the previous line isn’t def, if, elif, else, for, or while loop.
That is it for IndentationError in Python and how to resolve it.
How to Fix the “IndentationError: expected an indented block” Error in Your Python Code
Indentation is more important in Python than many languages, so much so that it can cause errors. Learn how to deal with the most common problem.
Readers like you help support MUO. When you make a purchase using links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. Read More.
Indentation is a vital feature of readable, maintainable code, but few languages enforce it. Python is one of those few.
If Python determines your code is indented incorrectly, you’ll be seeing the “IndentationError” message when you run your code. But how do you fix this, and how do you prevent it in the future?
Why Do You Get the IndentationError in Python?
The “IndentationError: expected an indented block” error is something you’re likely to see when you first start using Python, especially if you’ve come from another programming language.
The specifics of Python’s indentation rules are complex, but they boil down to one thing: indent code in blocks. This goes for functions, if clauses, and so on. Here’s an example of incorrectly formatted Python code:
fname = "Gaurav"
lname = "Siyal"
if fname == "Gaurav" and lname == "Siyal":
print("You're Gaurav")
else:
print("You're somebody else") When you try to run the above code, you’ll get a message like this:
File «tmp.py», line 5
print(«You’re Gaurav»)
^
IndentationError: expected an indented block
Instead, you should add either a tab or a series of spaces at the start of the two lines that represent blocks:
fname = "Gaurav"
lname = "Siyal"
if fname == "Gaurav" and lname == "Siyal":
print("You're Gaurav")
else:
print("You're somebody else") If you indent with spaces, you can actually use any number you like, so long as you’re consistent and unambiguous. Most programmers use two, four, or eight spaces.
Common Cases of Correct Indentation
Here are some examples that you can refer to, so you can ensure you’re indenting correctly.
If statements
Indent the block that follows an if statement:
if my_name == "Gaurav":
print("My name is Gaurav")
return True Functions
The body of a function is a block. You should indent this entire block: