- Примеры работы функции format() в Python
- Форматирование индекса
- Передача значений аргументам
- Заполнение форматированной строки функцией format()
- Передача dict в качестве параметра
- Передача комплексного числа в качестве аргумента
- С использованием запятой в качестве значения разделителя
- Форматирование чисел
- Python format() function
- Getting started with the Python format() function
- Index formatting with Python format()
- Passing values to the arguments in format() function
- Padding a formatted string with Python format() function
- Passing dict as parameter to Python format() function
- Passing complex number as an argument to the format() function
- Python format() function using comma as separator value
- Formatting numbers using format() function
- Conclusion
- References
Примеры работы функции format() в Python
В этой статье мы сосредоточимся на форматировании строки и значений с помощью функции Python format().
Функция Python format() — это встроенная функция String, используемая для форматирования строк.
Функция Python format() function форматирует строки в соответствии с положением. Таким образом, пользователь может изменить положение строки в выводе с помощью функции format().
- <> : Эти фигурные скобки действуют как средство форматирования, и при вызове функции они заменяются строкой, которая должна быть помещена в определенную позицию.
- value : этот параметр может быть строкой, числом или даже целым числом с плавающей запятой. Он представляет собой значение, которое будет заменено средством форматирования в выходных данных.
s1 = 'Python' s2 = 'with' s4 = 'JournalDev' s3 = "<> <> <>".format(s1, s2, s4) print(s3)
Форматирование индекса
Функция format() также служит для форматирования строки в определенных пользователем позициях, то есть мы можем изменить положение строки или значения, которое будет помещено в вывод, указав значения индекса внутри фигурных скобок.
s1 = 'Python' s2 = 'with' s4 = 'Data Science' res = " ".format(s1, s2, s4) print(res)
В приведенном выше фрагменте кода формат (s1, s2, s4) внутренне присваивает им значения индекса как 0, 1, 2 и т. д. значениям, передаваемым в функцию.
То есть s1 присваивается индексу 0, s2 назначается индексу 1, а s4 присваивается индексу 2.
Таким образом, передав значение индекса строки в <>, мы можем изменить положение строки с помощью значений индекса.
Передача значений аргументам
Мы можем присвоить значения переменным, которые мы хотим отображать внутри списка параметров самой функции.
res = " ".format(s1 = 'Python',s2 = 'with',s4 = 'Data Science') print(res)
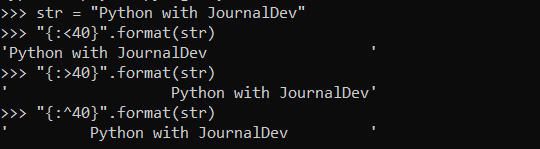
Заполнение форматированной строки функцией format()
Строки также могут быть отформатированы с точки зрения выравнивания и заполнения.
#left padding "number>".format(value) #right padding "".format(value) #centre padding "".format(value)
Передавая конкретное число, оно служит количеством символов, добавляемых в строку.
Передача dict в качестве параметра
Словарь Python также может быть передан в format() как значение для форматирования.
Ключ передается в <>, а функция format() используется для замены ключа его значением соответственно.
Поскольку мы передаем ключи dict в качестве аргументов, чтобы заменить ключи их значениями, нам нужно распаковать словарь. Таким образом, для распаковки словаря используется Python «**» operator .
dict1 = res = " ".format(**dict1) print(res)
Передача комплексного числа в качестве аргумента
Данная функция может использоваться для доступа к действительным и мнимым значениям из комплексного числа.
num = 20-3j res = "Real-part:, Imaginary-part:".format(num) print(res)
Real-part:20.0, Imaginary-part:-3.0
С использованием запятой в качестве значения разделителя
Позволяет нам разделять числовые значения, используя «,» as a separator .
Разделитель, то есть «,» добавляется после трех цифр таким образом, чтобы он работал с разрядами тысяч в системе счисления.
num = 10000000000 res = "".format(num) print(res)
Форматирование чисел
Помимо форматирования числовых значений, можно использовать для представления числовых значений в соответствии с различными системами счисления, такими как двоичная, восьмеричная, шестнадцатеричная и т. д.
#Hexadecimal representation "".format(value) #Octal representation "".format(value) #Decimal representation "".format(value) #Binary representation "".format(value)
num = 10 binary = "".format(num) print("Binary representation:", binary) hexadecimal = "".format(num) print("Hexadecimal representation:", hexadecimal) octal = "".format(num) print("Octal Decimal representation:", octal) decimal = "".format(num) print("Decimal representation:", decimal) Binary representation: 1010 Hexadecimal representation: a Octal Decimal representation: 12 Decimal representation: 10
Python format() function
Hello! In this article, we will be focusing on formatting string and values using Python format() function.
Getting started with the Python format() function
Python format() function is an in-built String function used for the purpose of formatting of strings.
The Python format() function formats strings according to the position. Thus, the user can alter the position of the string in the output using the format() function.
- <> : These curly braces act as a formatter and when the function is called they are replaced with the string to be placed at the defined position.
- value : This parameter can be a string or a number or even a floating point integer. It represents the value to be replaced by the formatter in the output.
s1 = 'Python' s2 = 'with' s4 = 'JournalDev' s3 = "<> <> <>".format(s1, s2, s4) print(s3)
Index formatting with Python format()
The format() function also serves the purpose of formatting string at user defined positions i.e. we can change the position of the string or value to be placed in the output by specifying the index values inside the curly braces.
s1 = 'Python' s2 = 'with' s4 = 'Data Science' res = " ".format(s1, s2, s4) print(res)
In the above snippet of code, the format(s1, s2, s4) internally assigns them index values as 0, 1, 2, and so on to the values passed to the function.
That is, s1 is assigned to index 0, s2 is assigned to index 1 and s4 is assigned to index 2.
So, by passing the index value of the string in the <>, we can alter the position of the string by the index values.
Passing values to the arguments in format() function
Using Python format() function, we can assign values to the variables we want to be displayed inside the parameter list of the function itself.
res = " ".format(s1 = 'Python',s2 = 'with',s4 = 'Data Science') print(res)
Padding a formatted string with Python format() function
The strings can also be formatted in terms of the alignment and padding using the format() function.
#left padding "number>".format(value) #right padding "".format(value) #centre padding "".format(value)
By passing a particular number, it serves as the number of characters to be padded around the string.
Passing dict as parameter to Python format() function
Python Dictionary can also be passed to format() function as a value to be formatted.
The key is passed to the <> and the format() function is used to replace the key by it’s value, respectively.
Since, we are passing the dict keys as arguments, in order to replace the keys with their values we need to unpack the dictionary. Thus, Python «**» operator is used to unpack the dictionary.
dict1 = res = " ".format(**dict1) print(res)
Passing complex number as an argument to the format() function
Python format() function can be used to access the Real and the Imaginary values from a complex number.
num = 20-3j res = "Real-part:, Imaginary-part:".format(num) print(res)
Real-part:20.0, Imaginary-part:-3.0
Python format() function using comma as separator value
Python format() function enables us to separate the numeric values using «,» as a separator .
The separator i.e. “,” is added after three digits in a manner that it works for the thousands place in the number system.
num = 10000000000 res = "".format(num) print(res)
Formatting numbers using format() function
Python format() function has the feature of formatting numbers too.
In addition to formatting the numeric values, the format() function can be used to represent the numeric values according to the different number systems such as binary, octal, hexadecimal, etc.
#Hexadecimal representation "".format(value) #Octal representation "".format(value) #Decimal representation "".format(value) #Binary representation "".format(value)
num = 10 binary = "".format(num) print("Binary representation:", binary) hexadecimal = "".format(num) print("Hexadecimal representation:", hexadecimal) octal = "".format(num) print("Octal Decimal representation:", octal) decimal = "".format(num) print("Decimal representation:", decimal) Binary representation: 1010 Hexadecimal representation: a Octal Decimal representation: 12 Decimal representation: 10
Conclusion
Thus, in this article, we have looked at the working of Python format() function along with the various uses of the function with strings, numbers, etc.
To know more about formatting of Strings, I would strongly recommend the readers to learn about Python f-string.