- How do I get the filename without the extension from a path in Python?
- Python file without extension
- # Table of Contents
- # Remove the extension from a Filename in Python
- # Remove the extension from a Filename using pathlib.Path
- # Remove the extension from a Filename using removesuffix()
- # Remove the extension from a Filename using str.rsplit()
- # Additional Resources
- Python Get Filename Without Extension From Path
- Get Filename Without Extension From Path Using pathlib.path().stem Method in Python
- Get Filename Without Extension From Path Using os.path.splitext() and string.split() Methods in Python
- Get Filename From Path Using os.path.basename() and os.path.splitext() Methods in Python
- Related Article — Python File
How do I get the filename without the extension from a path in Python?
To get the filename without the extension from a file path in Python, you can use the os.path.splitext() function. This function returns a tuple containing the file name and the file extension. You can then use string slicing to get just the file name.
import os file_path = '/path/to/file.txt' # Use os.path.splitext to split the file name and extension filename, file_ext = os.path.splitext(file_path) # Use slicing to get the file name without the extension filename_without_ext = filename[:-len(file_ext)] print(filename_without_ext) # Output: '/path/to/file'Alternatively, you can use the os.path.basename() function to get the base name of the file, and then use string slicing to remove the extension. Here’s an example:
import os file_path = '/path/to/file.txt' # Get the base name of the file filename = os.path.basename(file_path) # Use slicing to remove the extension filename_without_ext = filename[:filename.rindex('.')] print(filename_without_ext) # Output: 'file'Both of these methods assume that the file extension is separated from the rest of the file name by a period ( . ). If this is not the case, then you will need to use a different approach to split the file name and extension.
Python file without extension
Last updated: Feb 20, 2023
Reading time · 4 min
# Table of Contents
# Remove the extension from a Filename in Python
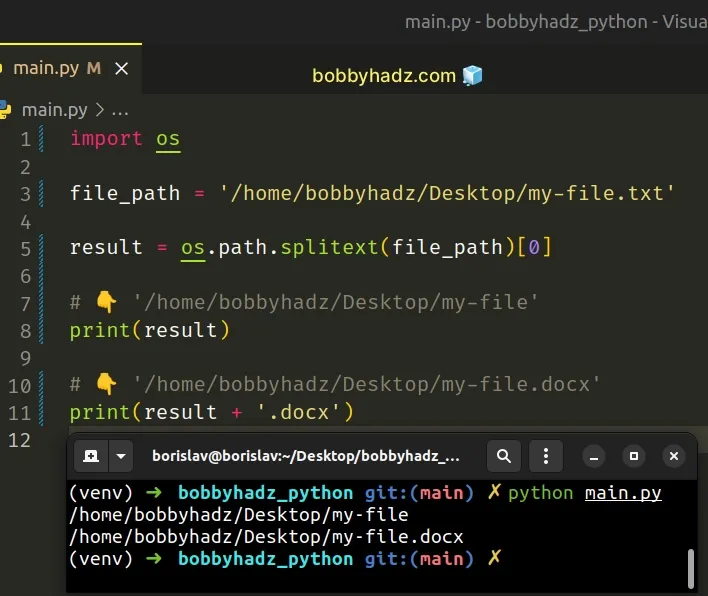
Use the os.path.splitext() method to remove the extension from a filename.
The os.path.splitext method will return a tuple that contains the filename without the extension as its first element.
Copied!import os file_path = '/home/bobbyhadz/Desktop/my-file.txt' result = os.path.splitext(file_path)[0] # 👇️ '/home/bobbyhadz/Desktop/my-file' print(result) # 👇️ '/home/bobbyhadz/Desktop/my-file.docx' print(result + '.docx')
If you need to split the filename on name and extension, use the following code sample instead.
Copied!import os file_path = '/home/bobbyhadz/Desktop/file.txt' filename, extension = os.path.splitext(file_path) print(filename) # 👉️ '/home/bobbyhadz/Desktop/file' print(extension) # 👉️ '.txt'
We used the os.path.splitext method to remove the extension from a filename.
The os.path.splitext method splits the path into a tuple that contains the root and the extension.
Copied!import os file_path = '/home/bobbyhadz/Desktop/my-file.txt' # 👇️ ('/home/bobbyhadz/Desktop/my-file', '.txt') print(os.path.splitext(file_path))
To get the filename without the extension, access the first element in the tuple.
If the specified path doesn’t contain an extension, the second element in the tuple is an empty string.
Copied!import os file_path = '/home/bobbyhadz/Desktop/my-file' # 👇️ ('/home/bobbyhadz/Desktop/my-file', '') print(os.path.splitext(file_path))
If the provided path doesn’t have an extension, we return the string as is.
Previous periods are ignored if the path contains multiple.
Copied!import os import pathlib file_path = '/home/bobby.hadz/Desktop/my-file.txt' # 👇️ ('/home/bobby.hadz/Desktop/my-file', '.txt') print(os.path.splitext(file_path))
Alternatively, you can use the pathlib.Path() class.
# Remove the extension from a Filename using pathlib.Path
This is a two-step process:
- Instantiate the pathlib.Path() class to create a Path object.
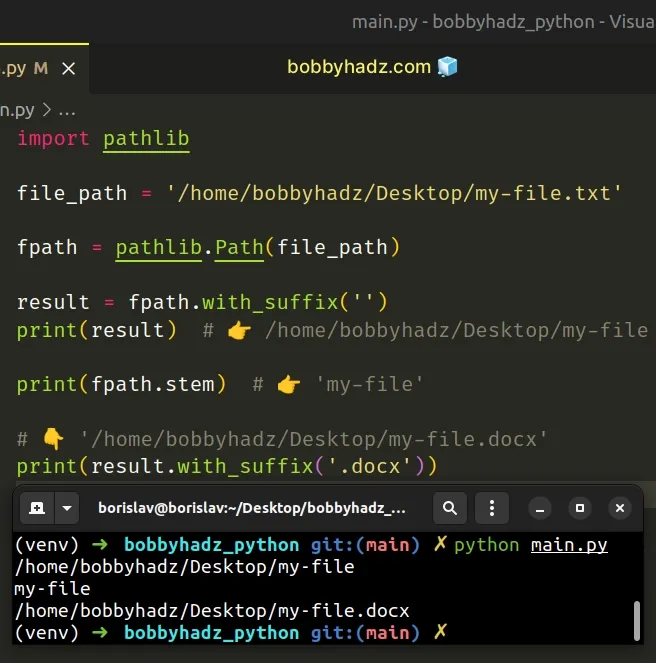
- Use the with_suffix() method to remove the extension from the filename.
Copied!import pathlib file_path = '/home/bobbyhadz/Desktop/my-file.txt' fpath = pathlib.Path(file_path) result = fpath.with_suffix('') print(result) # 👉️ /home/bobbyhadz/Desktop/my-file print(fpath.stem) # 👉️ 'my-file' # 👇️ '/home/bobbyhadz/Desktop/my-file.docx' print(result.with_suffix('.docx'))
If you need to split the filename on the name and the extension, use the following code sample instead.
Copied!import pathlib file_path = '/home/bobbyhadz/Desktop/file.txt' fpath = pathlib.Path(file_path) print(fpath.suffix) # 👉️ '.txt' print(fpath.suffixes) # 👉️ ['.txt'] print(fpath.stem) # 👉️ 'file' print(fpath.parent) # 👉️ '/home/bobbyhadz/Desktop'
The pathlib.Path class is used to create a PosixPath or a WindowsPath object depending on your operating system.
The with_suffix method takes a suffix and changes the suffix of the path.
We first passed an empty string to the method to remove the extension from the filename.
You can optionally call the method with a different extension if you need to add one.
Copied!import pathlib file_path = '/home/bobbyhadz/Desktop/my-file.txt' fpath = pathlib.Path(file_path) result = fpath.with_suffix('') print(result) # 👉️ /home/bobbyhadz/Desktop/my-file print(fpath.stem) # 👉️ 'my-file' # 👇️ '/home/bobbyhadz/Desktop/my-file.docx' print(result.with_suffix('.docx'))
You can use the stem attribute on the Path object if you need to get only the filename without the extension.
# Remove the extension from a Filename using removesuffix()
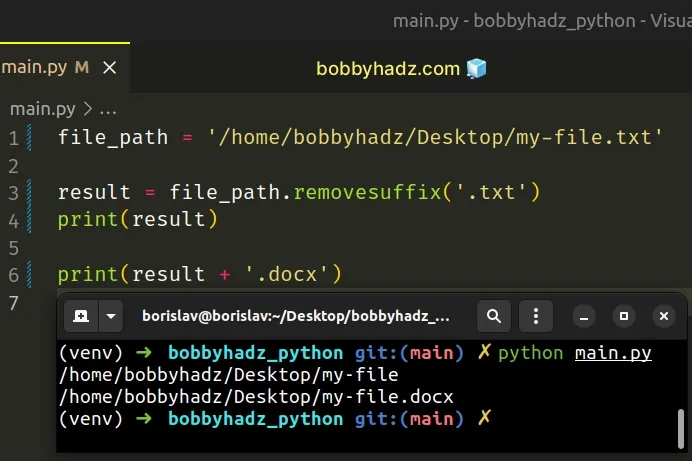
Alternatively, you can use the removesuffix() method.
Copied!file_path = '/home/bobbyhadz/Desktop/my-file.txt' result = file_path.removesuffix('.txt') print(result) # 👉️ '/home/bobbyhadz/Desktop/my-file' print(result + '.docx') # 👉️ '/home/bobbyhadz/Desktop/my-file.docx'
The str.removesuffix() method is available in Python 3.9+.
The str.removesuffix method checks if the string ends with the specified suffix and if it does, the method returns a new string excluding the suffix, otherwise it returns a copy of the original string.
Copied!# 👇️ '/home/bobbyhadz/Desktop/my-file' print('/home/bobbyhadz/Desktop/my-file.txt'.removesuffix('.txt')) # 👇️ '/home/bobbyhadz/Desktop/my-file' print('/home/bobbyhadz/Desktop/my-file'.removesuffix('.txt'))
If the string doesn’t contain the specified suffix, the method returns the string as is.
Make sure you are running Python version 3.9 or newer to be able to use the str.removesuffix method.
Alternatively, you can use the str.rsplit() method.
# Remove the extension from a Filename using str.rsplit()
This is a three-step process:
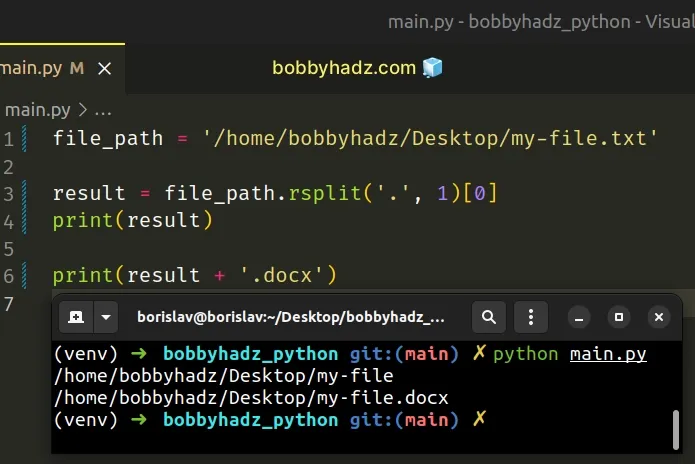
- Use the str.rsplit() method to split the filename on a period, once, from the right.
- Access the list item at index 0 .
- The list item at index 0 will contain the filename without the extension.
Copied!file_path = '/home/bobbyhadz/Desktop/my-file.txt' result = file_path.rsplit('.', 1)[0] print(result) # 👉️ '/home/bobbyhadz/Desktop/my-file' print(result + '.docx') # 👉️ '/home/bobbyhadz/Desktop/my-file.docx'
The str.rsplit method returns a list of the words in the string using the provided separator as the delimiter string.
Copied!file_path = '/home/bobbyhadz/Desktop/my-file.txt' # 👇️ ['/home/bobbyhadz/Desktop/my-file', 'txt'] print(file_path.rsplit('.', 1))
The method takes the following 2 arguments:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| separator | Split the string into substrings on each occurrence of the separator |
| maxsplit | At most maxsplit splits are done, the rightmost ones (optional) |
Except for splitting from the right, rsplit() behaves like split() .
We split the filename, once, on a period, from the right.
This approach handles the scenario where the filename doesn’t contain any periods.
Copied!file_path = '/home/bobbyhadz/Desktop/my-file' result = file_path.rsplit('.', 1)[0] print(result) # 👉️ '/home/bobbyhadz/Desktop/my-file'
However, it leads to confusing behavior if the filename contains a period, but doesn’t contain an extension.
Copied!file_path = '/home/bobby.hadz/Desktop/my-file' # 👇️ ['/home/bobby', 'hadz/Desktop/my-file'] print(file_path.rsplit('.', 1)) result = file_path.rsplit('.', 1)[0] print(result) # 👉️ '/home/bobby'
The previously covered approaches are more forgiving in this scenario.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Remove all Non-Numeric characters from a String in Python
- Remove everything Before or After a Character in Python
- Remove First and Last Characters from a String in Python
- Remove first occurrence of character from String in Python
- Remove the First N characters from String in Python
- Remove the last N characters from a String in Python
- Remove Newline characters from a List or a String in Python
- Remove non-alphanumeric characters from a Python string
- Remove non-ASCII characters from a string in Python
- Remove the non utf-8 characters from a String in Python
- Remove characters matching Regex from a String in Python
- Remove special characters except Space from String in Python
- How to unzip a .gz file using Python [5 simple Ways]
- How to merge text files in Python [5 simple Ways]
- OSError [Errno 22] invalid argument in Python [Solved]
- How to create a Zip archive of a Directory in Python
- How to recursively delete a Directory in Python
- How to open an HTML file in the Browser using Python
I wrote a book in which I share everything I know about how to become a better, more efficient programmer.
Python Get Filename Without Extension From Path
- Get Filename Without Extension From Path Using pathlib.path().stem Method in Python
- Get Filename Without Extension From Path Using os.path.splitext() and string.split() Methods in Python
- Get Filename From Path Using os.path.basename() and os.path.splitext() Methods in Python
This tutorial will demonstrate various methods to get filename without extension from the file path in Python. Suppose the goal is to get the name of files from the list of file paths available in the form of a string, like from the path Desktop/folder/myfile.txt , we get only the filename myfile without .txt extension.
Get Filename Without Extension From Path Using pathlib.path().stem Method in Python
The path().stem method takes the file path as input and returns the file name by extracting it from the file path. For example, from the path Desktop/folder/myfile.txt , it will return myfile without the .txt extension.
The code example below demonstrates how to use the path().stem to get file name without the file extension from the file path:
from pathlib import Path file_path = "Desktop/folder/myfile.txt" file_name = Path(file_path).stem print(file_name) Get Filename Without Extension From Path Using os.path.splitext() and string.split() Methods in Python
The path.splitext() method of the os module takes the file path as string input and returns the file path and file extension as output.
As we want to get the file name from the file path, we can first remove the file extension from the file path using the os.path.splitext() method. The first element of the splitting result is the file path without extension. This result is further split it using / as the separator. The last element will be the filename without extension. The code example below demonstrates how to get filename without extension from the file path using path.splitext() and string.split() methods.
import os file_path = "Desktop/folder/myfile.txt" file_path = os.path.splitext(file_path)[0] file_name = file_path.split('/')[-1] print(file_name) Get Filename From Path Using os.path.basename() and os.path.splitext() Methods in Python
In Python the path.basename() method of the os module takes the file path as input and returns the basename extracted from the file path. For example, the basename of Desktop/folder/myfile.txt is myfile.txt .
As we want to get filename from the file path, the basename can be extracted using the path.basename() method and filename using path.splitext() . The code example below demonstrates to get filename from the file path using path.basename() and path.splitext() methods.
import os file_path = "Desktop/folder/myfile.txt" basename = os.path.basename(file_path) file_name = os.path.splitext(basename)[0] print(file_name) In case the file has a name like myfile.tar.gz , all the methods explained above will return myfile.tar as the filename.
Suppose we need to get filename without the part after . like myfile instead of myfile.tar from the path Desktop/folder/myfile.tar.gz , the string.index() method can be used to extract only myfile from myfile.tar . But the drawback of this method is if the . is part of the file name like my.file.tar.gz , it will return my as the file name.
The code example below how we can use string.index() to remove .tar from the output myfile.tar of methods explained above:
file_name = "myfile.tar" index = file_name.index('.') file_name = file_name[:index] print(file_name) file_name = "my.file.tar" index = file_name.index('.') file_name = file_name[:index] print(file_name)