- Read Excel XLS with Python Pandas
- Step 1: Install Pandas and odfpy
- Step 2: Read the one sheet of Excel(XLS) file
- Step 3: Read the second sheet of Excel file by name
- Step 4: Python read excel file — specify columns and rows
- Python read excel file select rows
- Python read excel file select columns
- Python read excel file specify columns and rows
- Step 5. Read multiple sheets from Excel file
- Read All Sheets
- Step 6. Pandas read excel data with conversion, NA values and parsing
- Resources
- Read multiple Excel sheets with Python pandas
- pd.read_excel() method
- pd.ExcelFile()
- Moving on…
- How to Use Pandas to Read Excel Files in Python
- The Quick Answer: Use Pandas read_excel to Read Excel Files
- Understanding the Pandas read_excel Function
- How to Read Multiple Sheets in an Excel File in Pandas
- How to Read Only n Lines When Reading Excel Files in Pandas
- Conclusion
- Additional Resources
Read Excel XLS with Python Pandas
In this post you can learn how to read Excel files (ext xls, xlsx etc) with Python and Pandas. We will import one or several sheets from an Excel file to a Pandas DataFrame.
The list of the supported file extensions:
Step 1: Install Pandas and odfpy
Python offers many different modules for reading and manipulating Excel files. In this guide we are going to use pandas and odfpy :
pip install pandas pip install odfpy Step 2: Read the one sheet of Excel(XLS) file
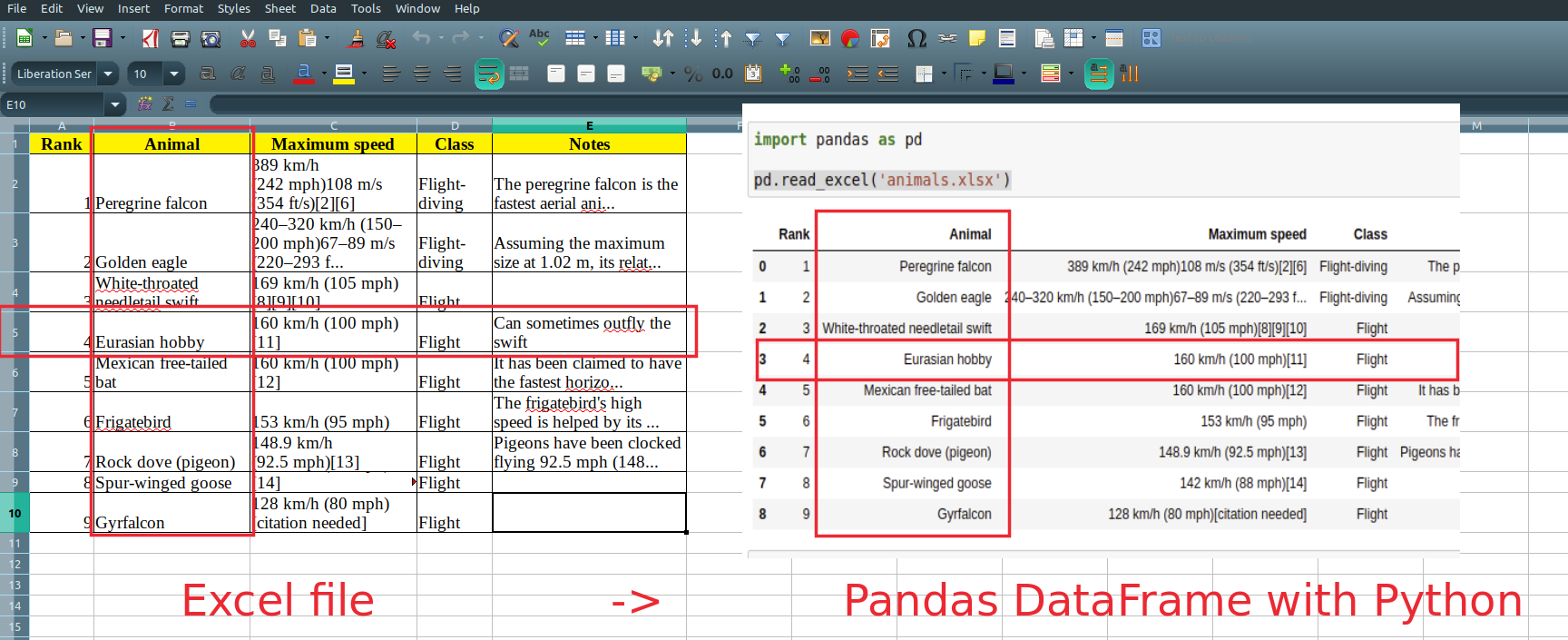
Pandas offers a powerful method for reading any type of Excel files read_excel() . It’s pretty easy to be used and requires only the file path:
import pandas as pd pd.read_excel('animals.xls') It will read and return all non empty cells from the Excel file:
| Rank | Animal | Maximum speed | Class | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | Peregrine falcon | 389 km/h (242 mph)108 m/s (354 ft/s)[2][6] | Flight-diving | The peregrine falcon is the fastest aerial ani. |
| 1 | 2 | Golden eagle | 240–320 km/h (150–200 mph)67–89 m/s (220–293 f. | Flight-diving | Assuming the maximum size at 1.02 m, its relat. |
| 2 | 3 | White-throated needletail swift | 169 km/h (105 mph)[8][9][10] | Flight | NaN |
| 3 | 4 | Eurasian hobby | 160 km/h (100 mph)[11] | Flight | Can sometimes outfly the swift |
| 4 | 5 | Mexican free-tailed bat | 160 km/h (100 mph)[12] | Flight | It has been claimed to have the fastest horizo. |
| 5 | 6 | Frigatebird | 153 km/h (95 mph) | Flight | The frigatebird’s high speed is helped by its . |
| 6 | 7 | Rock dove (pigeon) | 148.9 km/h (92.5 mph)[13] | Flight | Pigeons have been clocked flying 92.5 mph (148. |
| 7 | 8 | Spur-winged goose | 142 km/h (88 mph)[14] | Flight | NaN |
| 8 | 9 | Gyrfalcon | 128 km/h (80 mph)[citation needed] | Flight | NaN |
Step 3: Read the second sheet of Excel file by name
If you like to read data from a specific sheet — for example Sheet 2 then you can specify the name as a parameter — sheet_name :
pd.read_excel('animals.xlsx', sheet_name="Sheet2") | Blackbuck | Unnamed: 1 | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | NaN | NaN |
| 1 | Male blackbuck | Male blackbuck |
| 2 | NaN | NaN |
| 3 | Female with young at the National Zoological Park Delhi | Female with young at the National Zoological P. |
| 4 | Conservation status | Conservation status |
| 5 | Least Concern (IUCN 3.1)[1] | Least Concern (IUCN 3.1)[1] |
| 6 | Scientific classification | Scientific classification |
Step 4: Python read excel file — specify columns and rows
If you like to read a range of data and not the whole sheet — read_excel offers several very useful parameters.
Python read excel file select rows
Next code example will show you how to read 3 rows skipping the first two rows. In this way Pandas will read only some rows from the whole sheet:
pd.read_excel('animals.xlsx', skiprows=2, nrows=3) | 2 | Golden eagle | 240–320 km/h (150–200 mph)67–89 m/s (220–293 f. | Flight-diving | Assuming the maximum size at 1.02 m, its relat. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 3 | White-throated needletail swift | 169 km/h (105 mph)[8][9][10] | Flight | NaN |
| 1 | 4 | Eurasian hobby | 160 km/h (100 mph)[11] | Flight | Can sometimes outfly the swift |
| 2 | 5 | Mexican free-tailed bat | 160 km/h (100 mph)[12] | Flight | It has been claimed to have the fastest horizo. |
Python read excel file select columns
If you like to** work with few columns** and not the whole sheet — then parameter use_cols can be used as shown:
pd.read_excel('animals.xlsx', usecols='C:D') Python read excel file specify columns and rows
Finally if you like to select a range from specific columns and rows than you can use:
| 240–320 km/h (150–200 mph)67–89 m/s (220–293 f. | Flight-diving | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 169 km/h (105 mph)[8][9][10] | Flight |
| 1 | 160 km/h (100 mph)[11] | Flight |
| 2 | 160 km/h (100 mph)[12] | Flight |
Step 5. Read multiple sheets from Excel file
What if you like to read with Pandas multiple sheets from Excel. It’s possible with pd.read_excel by providing a list of all sheets to be read as follows:
pd.read_excel('animals.xlsx', sheet_name=["Sheet1", "Sheet2"]) Note that a dictionary of
In order to access data you can access it by a sheet name as:
pd.read_excel('animals.xlsx', sheet_name=["Sheet1", "Sheet2"]).get('Sheet1') which will return the data for Sheet1 as a DataFrame.
Read All Sheets
For loading all sheets from Excel file use sheet_name=None :
pd.read_excel('animals.xlsx', sheet_name=None) Step 6. Pandas read excel data with conversion, NA values and parsing
Finally let’s check what we can do if we need to convert data, drop or fill missing values, parse dates and numbers.
Pandas offers several parameters for this purpose:
- converters — dict of functions for converting values in certain columns
- keep_default_na — whether or not to include the default NaN values
- parse_dates
- ate_parser — converting a sequence of string columns to an array of datetime instances.
- thousands
- convert_float
You can check the Notebook in the resources for more examples of the above.
Resources
By using DataScientYst — Data Science Simplified, you agree to our Cookie Policy.
Read multiple Excel sheets with Python pandas
In the previous post, we touched on how to read an Excel file into Python. Here we’ll attempt to read multiple Excel sheets (from the same file) with Python pandas. We can do this in two ways: use pd.read_excel() method, with the optional argument sheet_name ; the alternative is to create a pd.ExcelFile object, then parse data from that object.
pd.read_excel() method
- Select sheets to read by index: sheet_name = [0,1,2] means the first three sheets.
- Select sheets to read by name: sheet_name = [‘User_info’, ‘compound’] . This method requires you to know the sheet names in advance.
- Select all sheets: sheet_name = None.
We will read all sheets from the sample Excel file, then use that dataframe for the examples going forward.
The df returns a dictionary of dataframes. The keys of the dictionary contain sheet names, and values of the dictionary contain sheet content.
>> df.values() dict_values([ User Name Country City Gender Age 0 Forrest Gump USA New York M 50 1 Mary Jane CANADA Tornoto F 30 2 Harry Porter UK London M 20 3 Jean Grey CHINA Shanghai F 30, ID Customer purchase Date 0 101 Forrest Gump Dragon Ball 2020-08-12 1 102 Mary Jane Evangelion 2020-01-01 2 103 Harry Porter Kill la Kill 2020-08-01 3 104 Jean Grey Dragon Ball 1999-01-01 4 105 Mary Jane Evangelion 2019-12-31 5 106 Harry Porter Ghost in the Shell 2020-01-01 6 107 Jean Grey Evangelion 2018-04-01, . ]To obtain data from a specific sheet, simply reference the key in the dictionary. For example, df[‘header_row5’] returns the sheet in which data starts from row 5.
pd.ExcelFile()
With this approach, we create a pd.ExcelFile object to represent the Excel file. We do not need to specify which sheets to read when using this method. Note that the previous read_excel() method returns a dataframe or a dictionary of dataframes; whereas pd.ExcelFile( ) returns a reference object to the Excel file.
To get sheet names, we can all the sheet_names attribute from the ExcelFile object, which returns a list of the sheet names (string).
To get data from a sheet, we can use the parse() method, and provide the sheet name.
One thing to note is that the pd.ExcelFile.parse() method is equivalent to the pd.read_excel() method, so that means you can pass in the same arguments used in read_excel().
Moving on…
We have learned how to read data from Excel or CSV files, next we’ll cover how to save a dataframe back into an Excel (or CSV) file.
How to Use Pandas to Read Excel Files in Python
In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to use Python and Pandas to read Excel files using the Pandas read_excel function. Excel files are everywhere – and while they may not be the ideal data type for many data scientists, knowing how to work with them is an essential skill.
By the end of this tutorial, you’ll have learned:
- How to use the Pandas read_excel function to read an Excel file
- How to read specify an Excel sheet name to read into Pandas
- How to read multiple Excel sheets or files
- How to certain columns from an Excel file in Pandas
- How to skip rows when reading Excel files in Pandas
- And more
The Quick Answer: Use Pandas read_excel to Read Excel Files
To read Excel files in Python’s Pandas, use the read_excel() function. You can specify the path to the file and a sheet name to read, as shown below:
# Reading an Excel File in Pandas import pandas as pd df = pd.read_excel('/Users/datagy/Desktop/Sales.xlsx') # With a Sheet Name df = pd.read_excel( io='/Users/datagy/Desktop/Sales.xlsx' sheet_name ='North' )In the following sections of this tutorial, you’ll learn more about the Pandas read_excel() function to better understand how to customize reading Excel files.
Understanding the Pandas read_excel Function
The Pandas read_excel() function has a ton of different parameters. In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to use the main parameters available to you that provide incredible flexibility in terms of how you read Excel files in Pandas.
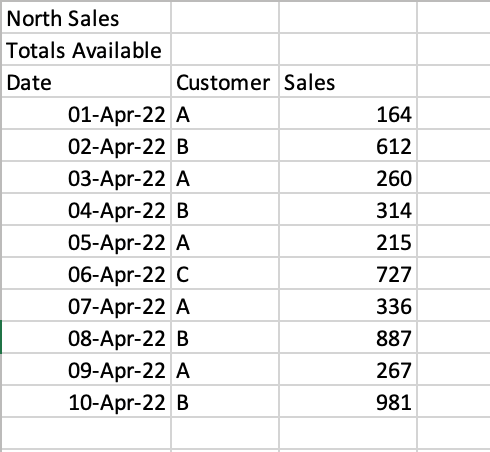
If we were to read the sheet ‘North’ , we would get the following returned:
# Reading a poorly formatted Excel file import pandas as pd df = pd.read_excel( io='https://github.com/datagy/mediumdata/raw/master/Sales.xlsx', sheet_name='North') print(df.head()) # Returns: # North Sales Unnamed: 1 Unnamed: 2 # 0 Totals Available NaN NaN # 1 Date Customer Sales # 2 2022-04-01 00:00:00 A 164 # 3 2022-04-02 00:00:00 B 612 # 4 2022-04-03 00:00:00 A 260Pandas makes it easy to skip a certain number of rows when reading an Excel file. This can be done using the skiprows= parameter. We can see that we need to skip two rows, so we can simply pass in the value 2, as shown below:
# Reading a Poorly Formatted File Correctly import pandas as pd df = pd.read_excel( io='https://github.com/datagy/mediumdata/raw/master/Sales.xlsx', sheet_name='North', skiprows=2) print(df.head()) # Returns: # Date Customer Sales # 0 2022-04-01 A 164 # 1 2022-04-02 B 612 # 2 2022-04-03 A 260 # 3 2022-04-04 B 314 # 4 2022-04-05 A 215This read the file much more accurately! It can be a lifesaver when working with poorly formatted files. In the next section, you’ll learn how to read multiple sheets in an Excel file in Pandas.
How to Read Multiple Sheets in an Excel File in Pandas
Pandas makes it very easy to read multiple sheets at the same time. This can be done using the sheet_name= parameter. In our earlier examples, we passed in only a single string to read a single sheet. However, you can also pass in a list of sheets to read multiple sheets at once.
Let’s see how we can read our first two sheets:
# Reading Multiple Excel Sheets at Once in Pandas import pandas as pd dfs = pd.read_excel( io='https://github.com/datagy/mediumdata/raw/master/Sales.xlsx', sheet_name=['East', 'West']) print(type(dfs)) # Returns:
In the example above, we passed in a list of sheets to read. When we used the type() function to check the type of the returned value, we saw that a dictionary was returned.
Each of the sheets is a key of the dictionary with the DataFrame being the corresponding key’s value. Let’s see how we can access the ‘West’ DataFrame:
# Reading Multiple Excel Sheets in Pandas import pandas as pd dfs = pd.read_excel( io='https://github.com/datagy/mediumdata/raw/master/Sales.xlsx', sheet_name=['East', 'West']) print(dfs.get('West').head()) # Returns: # Date Customer Sales # 0 2022-04-01 A 504 # 1 2022-04-02 B 361 # 2 2022-04-03 A 694 # 3 2022-04-04 B 702 # 4 2022-04-05 A 255You can also read all of the sheets at once by specifying None for the value of sheet_name= . Similarly, this returns a dictionary of all sheets:
# Reading Multiple Excel Sheets in Pandas import pandas as pd dfs = pd.read_excel( io='https://github.com/datagy/mediumdata/raw/master/Sales.xlsx', sheet_name=None)In the next section, you’ll learn how to read multiple Excel files in Pandas.
How to Read Only n Lines When Reading Excel Files in Pandas
When working with very large Excel files, it can be helpful to only sample a small subset of the data first. This allows you to quickly load the file to better be able to explore the different columns and data types.
This can be done using the nrows= parameter, which accepts an integer value of the number of rows you want to read into your DataFrame. Let’s see how we can read the first five rows of the Excel sheet:
# Reading n Number of Rows of an Excel Sheet import pandas as pd df = pd.read_excel( io='https://github.com/datagy/mediumdata/raw/master/Sales.xlsx', nrows=5) print(df) # Returns: # Date Customer Sales # 0 2022-04-01 A 191 # 1 2022-04-02 B 727 # 2 2022-04-03 A 782 # 3 2022-04-04 B 561 # 4 2022-04-05 A 969Conclusion
In this tutorial, you learned how to use Python and Pandas to read Excel files into a DataFrame using the .read_excel() function. You learned how to use the function to read an Excel, specify sheet names, read only particular columns, and specify data types. You then learned how skip rows, read only a set number of rows, and read multiple sheets.
Additional Resources
To learn more about related topics, check out the tutorials below: