- Python If . Else
- Example
- Indentation
- Example
- Elif
- Example
- Else
- Example
- Example
- Short Hand If
- Example
- Short Hand If . Else
- Example
- Example
- And
- Example
- Or
- Example
- Not
- Example
- Nested If
- Example
- The pass Statement
- Python If Statement explained with examples
- Syntax of If statement in Python
- If statement flow diagram
- Python – If statement Example
- Python if example without boolean variables
- Python If
- Execution Flow Diagram
- Syntax of If Statement
- Examples
- 1. Simple example for If statement
- 2. Python If Statement where Boolean Expression is False
- 3. If statement with compound condition
- 4. If statement with condition evaluating to a number
- 5. If statement with multiple statements in if-block
- 6. Nested If statement
- Summary
Python If . Else
Python supports the usual logical conditions from mathematics:
- Equals: a == b
- Not Equals: a != b
- Less than: a < b
- Less than or equal to: a
- Greater than: a > b
- Greater than or equal to: a >= b
These conditions can be used in several ways, most commonly in «if statements» and loops.
An «if statement» is written by using the if keyword.
Example
In this example we use two variables, a and b , which are used as part of the if statement to test whether b is greater than a . As a is 33 , and b is 200 , we know that 200 is greater than 33, and so we print to screen that «b is greater than a».
Indentation
Python relies on indentation (whitespace at the beginning of a line) to define scope in the code. Other programming languages often use curly-brackets for this purpose.
Example
If statement, without indentation (will raise an error):
Elif
The elif keyword is Python’s way of saying «if the previous conditions were not true, then try this condition».
Example
In this example a is equal to b , so the first condition is not true, but the elif condition is true, so we print to screen that «a and b are equal».
Else
The else keyword catches anything which isn’t caught by the preceding conditions.
Example
a = 200
b = 33
if b > a:
print(«b is greater than a»)
elif a == b:
print(«a and b are equal»)
else:
print(«a is greater than b»)
In this example a is greater than b , so the first condition is not true, also the elif condition is not true, so we go to the else condition and print to screen that «a is greater than b».
You can also have an else without the elif :
Example
Short Hand If
If you have only one statement to execute, you can put it on the same line as the if statement.
Example
Short Hand If . Else
If you have only one statement to execute, one for if, and one for else, you can put it all on the same line:
Example
One line if else statement:
This technique is known as Ternary Operators, or Conditional Expressions.
You can also have multiple else statements on the same line:
Example
One line if else statement, with 3 conditions:
And
The and keyword is a logical operator, and is used to combine conditional statements:
Example
Test if a is greater than b , AND if c is greater than a :
Or
The or keyword is a logical operator, and is used to combine conditional statements:
Example
Test if a is greater than b , OR if a is greater than c :
Not
The not keyword is a logical operator, and is used to reverse the result of the conditional statement:
Example
Test if a is NOT greater than b :
Nested If
You can have if statements inside if statements, this is called nested if statements.
Example
if x > 10:
print(«Above ten,»)
if x > 20:
print(«and also above 20!»)
else:
print(«but not above 20.»)
The pass Statement
if statements cannot be empty, but if you for some reason have an if statement with no content, put in the pass statement to avoid getting an error.
Python If Statement explained with examples
If statements are control flow statements which helps us to run a particular code only when a certain condition is satisfied. For example, you want to print a message on the screen only when a condition is true then you can use if statement to accomplish this in programming. In this guide, we will learn how to use if statements in Python programming with the help of examples.
There are other control flow statements available in Python such as if..else, if..elif..else,
nested if etc. However in this guide, we will only cover the if statements, other control statements are covered in separate tutorials.
Syntax of If statement in Python
The syntax of if statement in Python is pretty simple.
if condition: block_of_code
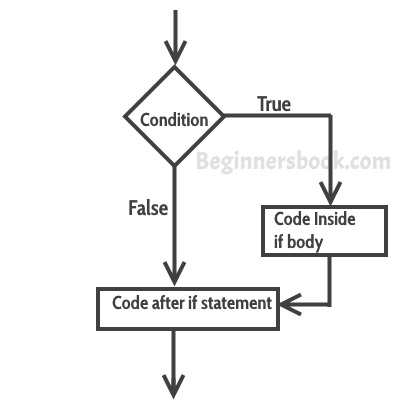
If statement flow diagram
Python – If statement Example
flag = True if flag==True: print("Welcome") print("To") print("BeginnersBook.com") Welcome To BeginnersBook.com
In the above example we are checking the value of flag variable and if the value is True then we are executing few print statements. The important point to note here is that even if we do not compare the value of flag with the ‘True’ and simply put ‘flag’ in place of condition, the code would run just fine so the better way to write the above code would be:
flag = True if flag: print("Welcome") print("To") print("BeginnersBook.com") By seeing this we can understand how if statement works. The output of the condition would either be true or false. If the outcome of condition is true then the statements inside body of ‘if’ executes, however if the outcome of condition is false then the statements inside ‘if’ are skipped. Lets take another example to understand this:
flag = False if flag: print("You Guys") print("are") print("Awesome") The output of this code is none, it does not print anything because the outcome of condition is ‘false’.
Python if example without boolean variables
In the above examples, we have used the boolean variables in place of conditions. However we can use any variables in our conditions. For example:
Python If
Python If statement is a conditional statement wherein a set of statements execute based on the result of a condition.
In this tutorial, you’ll learn about Python If statement, its syntax, and different scenarios where Python If statement can be used.
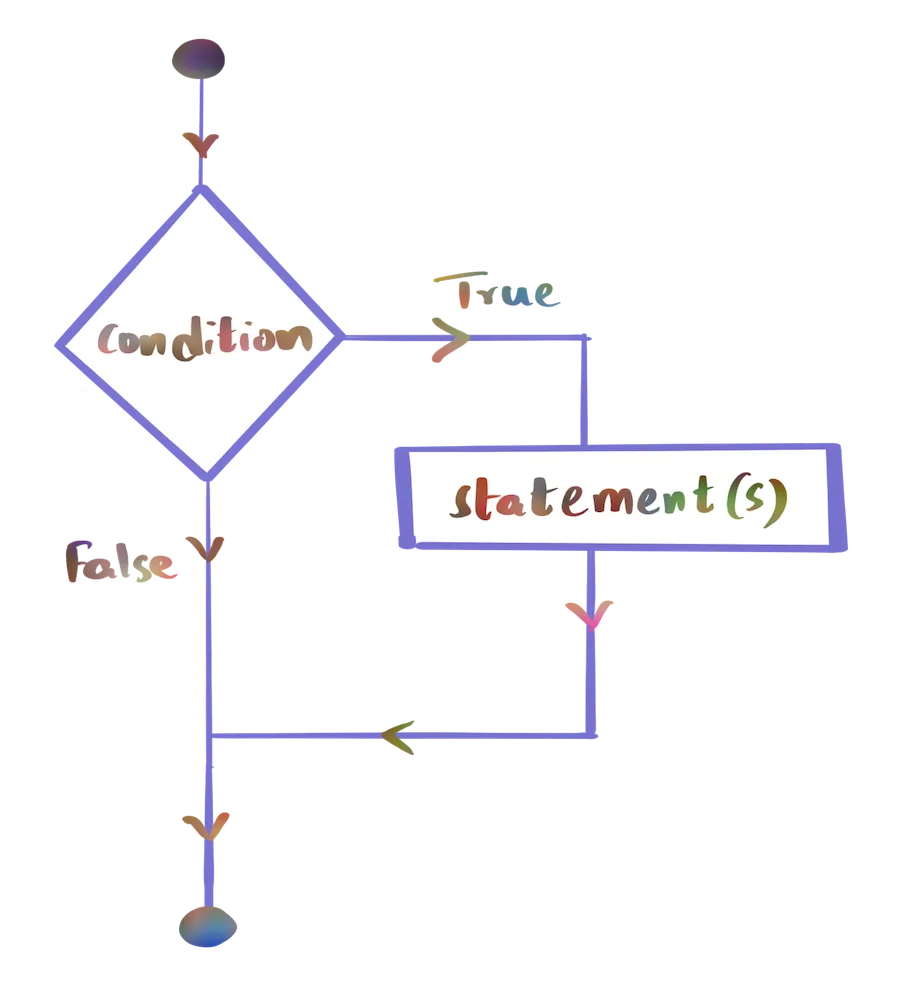
Execution Flow Diagram
Following is a flow diagram of Python if statement. Based on the evaluation of condition, program execution takes one of the paths.
Syntax of If Statement
Following is the syntax of if-statement in Python.
if boolean_expression: statement(s)Observe the indentation provided for statement(s) inside if block and the colon : after boolean expression.
If the boolean expression returns true, the statement(s) of the if block are executed. Else, the statement(s) are not executed, and the program execution continues with the statements after if statement, if there are any.
Following is a flowchart depicting the execution of condition and statements in the if statement.
Examples
1. Simple example for If statement
In this example, we will use a simple boolean expression formed with relational operator, less than, for the if statement condition. The statements(s) inside the if block is just a single print statement.
Python Program
Run the program, and you will see the following output in console.
It is trivial that the condition provided in the above if statement evaluates to true, therefore the statement(s) inside the if block is executed.
2. Python If Statement where Boolean Expression is False
In this example, we will write an if statement where the boolean expression or condition evaluates to false.
Python Program
The condition provided in the If statement evaluates to False, and therefore the statement inside the if-block is not executed.
3. If statement with compound condition
When you need to join multiple conditions in a single boolean expression, use logical operators to join them and create a compound condition as shown in the following program. The logical operators could be: python and, python or or python not.
Python Program
4. If statement with condition evaluating to a number
If the expression in the If statement evaluates to a number, then the statement(s) in if-block are executed if the number is non-zero. zero is considered to be False and non-zero (positive or negative) is considered True.
In this example, we write a Python If statement, where the boolean expression evaluates to a number.
Python Program
a = 2 if a: print(a, 'is not zero')As the value of condition evaluates to 2, which is a non-zero number, the statement(s) inside if block are executed.
5. If statement with multiple statements in if-block
In the syntax section, we already mentioned that there can be multiple statements inside if block.
In this example, we write three statements inside if block. Please note that these statements must have same indentation.
Python Program
a = 10 if a > 2 : print(a, 'is not zero') print('And this is another statement') print('Yet another statement')We have written only print statements in this example inside if block. But you may write a set of any valid python statement(s) inside the if block.
Please note that the statements of if-block have same indentation.
2 is not zero And this is another statement Yet another statement6. Nested If statement
You can write a Python If statement inside another Python If statement. This is called nesting.
In this example, we will write a Nested If statement: an If statement inside another If statement.
Python Program
a = 2 if a!=0: print(a, 'is not zero.') if a>0: print(a, 'is positive.') if a2 is not zero. 2 is positive.As the first/outer condition a!=0 evaluates to true, the execution enters the if block. And the if statements inside this outer if block are considered as yet another Python statements and executed accordingly.
Summary
In this tutorial of Python Examples, we learned what an If statement is, its syntax, its usage, how to write nested If statement.