- Как разделить список на части в Python
- Способ 1: использование метода len()
- Как разбить список на n частей в Python
- Разделение списка на четные части по N элементов в Python
- Способ 2: использование понимания списка
- Python: Split a List (In Half, in Chunks)
- How to Access a Python List by Its Index
- How to Split a Python List in Half
- Split Lists into Chunks Using a For-Loop
- Split Python Lists into Chunks Using a List Comprehension
- Split Lists into Chunks Using NumPy
- Split Lists into Chunks Using Itertools
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
- Additional Resources
Как разделить список на части в Python
Существуют следующие методы разделения списка на части в Python:
- Использование len(): метод len() возвращает длину списка и использует floor деление.
- Использование понимания списка: разбейте список на части и укажите N для понимания списка.
- Использование цикла for: используйте цикл for, чтобы разделить список на разные части.
- Использование numpy array_split() позволяет разбить массив на заданное количество массивов.
Способ 1: использование метода len()
Чтобы разделить список в Python, вы можете использовать метод «len()» с iterable в качестве списка, чтобы найти его длину, а затем разделить длину на 2, используя оператор «//», чтобы найти middle_index списка.
Как видно из вывода, мы разделили список ровно пополам. Мы использовали оператор двоеточия(:) для доступа к первой и второй половине разделенного списка.
Как разбить список на n частей в Python
Чтобы разделить список на n частей в Python, используйте функцию numpy.array_split(). Функция np.split() разбивает массив на несколько подмассивов.
Метод numpy array_split() возвращает список из n массивов Numpy, каждый из которых содержит примерно одинаковое количество элементов из списка.
В этом примере мы разделили список на 3 части.
Разделение списка на четные части по N элементов в Python
Список можно разделить в зависимости от размера определенного фрагмента. Это означает, что мы можем определить размер части. Если подмножество списка не соответствует размеру определенного фрагмента, необходимо вставить заполнители на место держателей пустых элементов.
Поэтому мы будем использовать None в качестве фильтра для заполнения этих пустых держателей элементов.
print ( list ( list_split ( [ 11 , 21 , 31 , 41 , 51 , 61 , 71 , 81 , 91 , 101 , 111 , 112 , 113 ] , 7 ) ) )
Список разбит на равные части по 7 элементов в каждой.
Приведенная выше функция list_split() принимает аргументы: listA для списка и chunk_size для числа, на которое нужно разделить. Затем функция выполняет итерацию по списку с приращением размера фрагмента n.
Ожидается, что каждый фрагмент будет иметь размер, указанный в качестве аргумента. Если элементов недостаточно для разделения одинакового размера, оставшиеся неиспользуемые элементы заполняются None.
Способ 2: использование понимания списка
Используя понимание списка, мы можем разделить «исходный список» и «создать фрагменты». Чтобы разделить список на части, укажите N в синтаксисе «понимания списка», и он создаст новый список с N частями элементов.
Python: Split a List (In Half, in Chunks)
In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to use Python to split a list, including how to split it in half and into n equal-sized chunks. You’ll learn how to split a Python list into chunks of size n , meaning that you’ll return lists that each contain n (or fewer if there are none left) items. Knowing how to work with lists in Python is an important skill to learn.
By the end of this tutorial, you’ll have learned:
- How to split a list in half in Python
- How to split a list into chunks in Python
- How to split a list at a particular index position in Python
- How to use NumPy to split a list in Python
The Quick Answer: Use List Indexing to Split a List in Python
How to Access a Python List by Its Index
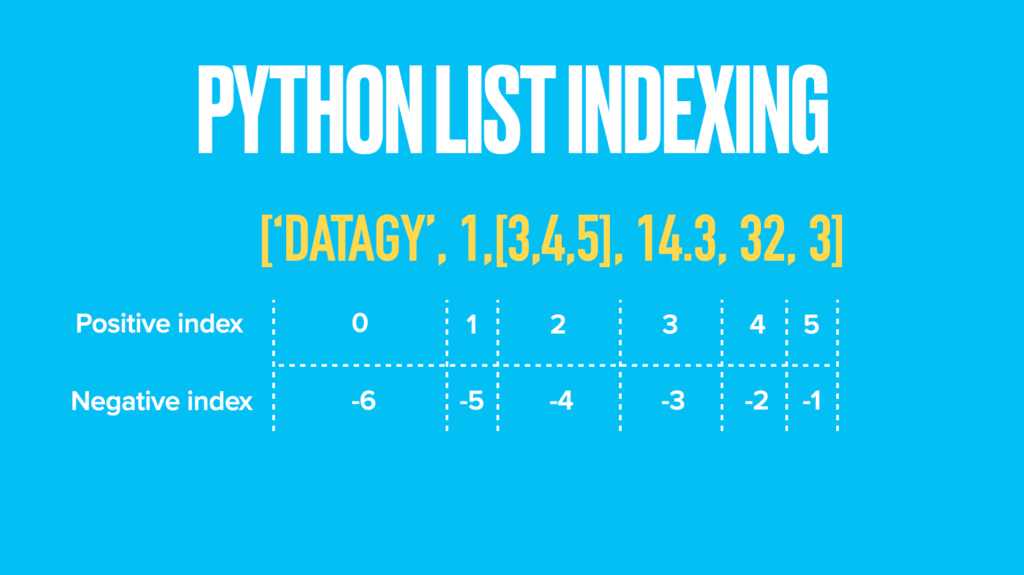
One of the many wonderful properties of lists is that they are ordered. This means that we can access an item, or a range of items, by its index. Let’s see how Python list indices work:
We can see here that Python lists have both a positive index as well as a negative index. A positive index begins at position 0, meaning the first item. A negative list index begins at -1, allowing you to retrieve the last item of a list.
Similarly, you can access ranges of data within a list using list slicing. This can be done by using the : colon character, which allows you to select items from a specific position up to a specific position.
How to Split a Python List in Half
You can easily split a Python list in half using list indexing. As you learned above, you can select multiple items in a list using list slicing. Let’s see how we can use list slicing to split a list in half:
# Split a List in Half with Python List Slicing a_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10] half_length = len(a_list) // 2 first_half, second_half = a_list[:half_length], a_list[half_length:] print(f'') print(f'') # Returns: # first_half=[1, 2, 3, 4, 5] # second_half=[6, 7, 8, 9, 10]Let’s break down what we did in the code above:
- We created a list a_list , which contains ten different items
- We then created an integer variable, half_length , which is the result of dividing the length of the list by two using integer division
- We then assigned variables, first_half and second_half , which sliced the lists up to and from the half variable
In the following section, you’ll learn how to split a list into different sized chunks in Python.
Split Lists into Chunks Using a For-Loop
For-loops in Python are an incredibly useful tool to use. They make a lot of Python methods easy to implement, as well as easy to understand. For this reason, let’s start off by using a for-loop to split our list into different chunks.
One of the ways you can split a list is into n different chunks. Let’s see how we can accomplish this by using a for loop:
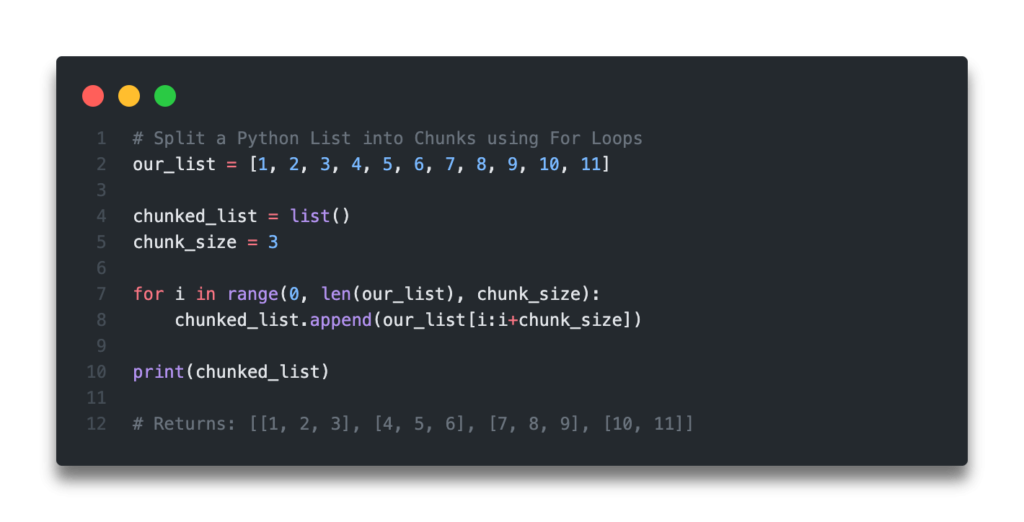
# Split a Python List into Chunks using For Loops a_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11] chunked_list = list() chunk_size = 3 for i in range(0, len(a_list), chunk_size): chunked_list.append(a_list[i:i+chunk_size]) print(chunked_list) # Returns: [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9], [10, 11]]Let’s take a look at what we’ve done here:
- We instantiate two lists: a_list , which contains the items of our original list, and chunked_list , which is empty
- We also declare a variable, chunk_size , which we’ve set to three, to indicate that we want to split our list into chunks of size 3
- We then loop over our list using the range function. What we’ve done here is created items from 0, through to the size of our list, iterating at our chunk size. For example, our range function would read range(0, 11, 3) , meaning that we’d loop over using items 0,3,6,9 .
- We then index our list from i:i+chunk_size , meaning the first loop would be 0:3 , then 3:6 , etc.
- These indexed lists are appended to our list
We can see that this is a fairly straightforward way of breaking a Python list into chunks. Next, you’ll learn how to do accomplish this using Python list comprehensions.
Split Python Lists into Chunks Using a List Comprehension
In many cases, Python for-loops can be rewritten in a more Pythonic way by writing them as one-liners called list comprehensions. List comprehensions in Python have a number of useful benefits over for-loops, including not having to instantiate an empty list first, and not having to break your for-loop over multiple lines.
Let’s see how we can write a Python list comprehension to break a list into chunks:
# Split a Python List into Chunks using list comprehensions our_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11] chunk_size = 3 chunked_list = [our_list[i:i+chunk_size] for i in range(0, len(our_list), chunk_size)] print(chunked_list) # Returns: [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9], [10, 11]]Before we break down this code, let’s see what the basic syntax of a Python list comprehension looks like:
Now let’s break down our code to see how it works:
- We declare a variable chunk_size to determine how big we want our chunked lists to be
- For our list comprehensions expression, we index our list based on the i th to the i+chunk_size th position
- We use this expression to iterate over every item in the output of the range() object that’s created based on range(0, len(our_list), chunk_size , which in this case would be 0,3,6,9
While this approach is a little faster to type, whether or not it is more readable than a for-loop, is up for discussion. Let’s learn how to split our Python lists into chunks using numpy.
Want to learn more? Check out my in-depth tutorial about Python list comprehensions by clicking here!
Split Lists into Chunks Using NumPy
Numpy is an amazing Python library that makes mathematical operations significantly easier. That being said, NumPy also works with a list-like object, called NumPy arrays, that make working with lists much easier. These NumPy arrays come packaged with lots of different methods to manipulate your arrays.
It’s important to note that this method will only work with numeric values.
In this section of the tutorial, we’ll use the NumPy array_split() function to split our Python list into chunks. This function allows you to split an array into a set number of arrays.
Let’s see how we can use NumPy to split our list into 3 separate chunks:
# Split a Python List into Chunks using numpy import numpy as np a_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] our_array = np.array(a_list) chunked_arrays = np.array_split(our_array, 3) chunked_list = [list(array) for array in chunked_arrays] print(chunked_list) # Returns: [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]This is a fairly long way of doing things, and we can definitely cut it down a little bit. Let’s see how that can be done:
chunked_list = [list(array) for array in np.array_split(np.array(our_list), 3)] print(chunked_list) # Returns: [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]Let’s break this down a little bit:
- We turn our list into a Numpy array
- We split our array into n number of arrays using the np.array_split() function
- Finally, we use a list comprehension to turn all the arrays in our list of arrays back into lists.
Want to learn more about division in Python? Check out my tutorial on how to use floored integer division and float division in Python in this tutorial here.
Split Lists into Chunks Using Itertools
Let’s see how we can use itertools library to split a list into chunks. In particular, we can use the zip_longest function to accomplish this.
Let’s see how we can do this:
# Split a Python List into Chunks using itertools from itertools import zip_longest our_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11] chunk_size = 3 chunked_list = list(zip_longest(*[iter(our_list)]*chunk_size, fillvalue='')) print(chunked_list) # Returns: [(1, 2, 3), (4, 5, 6), (7, 8, 9), (10, 11, '')] chunked_list = [list(item) for item in list(zip_longest(*[iter(our_list)]*chunk_size, fillvalue=''))] print(chunked_list) # Returns: [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9], [10, 11]]We can see here that we can have a relatively simple implementation that returns a list of tuples. Notice one of the things that are done here is split the list into chunks of size n, rather than into n chunks.
Frequently Asked Questions
The best way to split a Python list is to use list indexing, as it gives you huge amounts of flexibility.
The NumPy array_split() function allows you to easily split arrays into a given number of arrays. However, the function only works with numeric values (as NumPy arrays can only contain numeric values).
Conclusion
In this post, you learned how to split a Python list into chunks. You learned how to accomplish splitting a Python list into chunks of size n or into n number chunks . You learned how to do this using a for-loop, using list comprehensions, NumPy and itertools.
Additional Resources
To learn more about related topics, check out the tutorials below: