- How to Remove All Zero/None/Null from Dictionary in Python?
- Program to remove all 0 from dictionary in Python
- Method 1: Using for Loop
- Method 2: Using Python Compression Technique
- Removing None Type Values from Dictionary
- Removing Zero and None Type Values from Dictionary
- Use Case
- Python dict remove none
- # Table of Contents
- # Remove None values from a Dictionary in Python
- # Remove None values from a Dictionary using a for loop
- # Adding the not-None key-value pairs to a new dictionary
- # Remove the None values from a nested Dictionary in Python
- # Replace None values in a Dictionary in Python
- # Replace None values in a Dictionary using dict comprehension
- # Additional Resources
- How to remove None values from a dictionary in Python
- Creating a Dictionary with Keys and Values
- For Loop to remove keys with Value as None
- Complete Code
- How to Remove Null/None Values From a Dictionary in Python
- Given a Python dictionary, remove any term whose value is None
- Challenge
- Solution
- Honorable Mention
How to Remove All Zero/None/Null from Dictionary in Python?
Dictionary is a prominent data structure in Python to store the key and value pair data. Every key in the dictionary has its associated value. That value can be anything legit data structure in python.
Sometimes we need to remove all the dictionary key-value pair having value equals to zero.
Program to remove all 0 from dictionary in Python
Method 1: Using for Loop
We can loop over the dictionary value and can put the check if the value is not equal to zero. In an earlier complete Python dictionary tutorial, we have seen how you can iterate over a complete Python dictionary.
dic_in = dic_out = <> for x, y in dic_in.items(): if y != 0: dic_out[x] = y print(dic_out)
We are doing lot of labor work here. Can we optimize this code using some Python advance concepts?
Method 2: Using Python Compression Technique
There is also the easiest way to do this using the python compression technique.
Here is simple code spinet we can use it to filter out the the dictionary items having values zero.
You can run the complete program here that removes all 0 from the dictionary in Python.
dic_in = dic_out = print(dic_out)
This comprehension runs a loop over the key-value pair of a dictionary item. There is ‘if’ condition that excludes all the dictionary items having value equals to zero.
Similarly, you can write a program to remove all the dictionary elements have negative value by tweaking condition in the code.
Removing None Type Values from Dictionary
Many times, before processing a dictionary, project demands to remove all the dictionary entries having value None or Null.
If you don’t know Python has a None data type which is equivalent to Null data type from many of the other programming languages.
Here is the simple program that removes all the dictionary items having value None.
dic_in = dic_out = print(dic_out)
Removing Zero and None Type Values from Dictionary
You can also combine the above two cases to remove all the entries having values zero or None type.
dic_in = dic_out = print(dic_out)
Here we are using logical ‘and’ operation.
Use Case
One of the best use cases, filtering all the students who scored marks more than 50.
Suppose you have a dictionary that maintains the student’s exam score data where the key is student’s id and value is student’s mark.
Note: Comprehension is a generic technique where you can put any if condition as per the requirement. It filters the dictionary item as per the condition.
Python is known for its simplicity.
Python dict remove none
Last updated: Feb 18, 2023
Reading time · 5 min
# Table of Contents
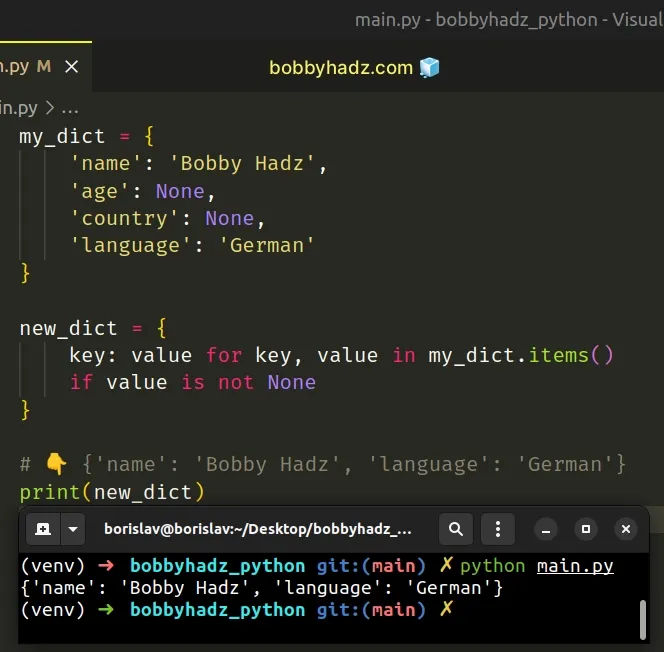
# Remove None values from a Dictionary in Python
Use a dict comprehension to remove None values from a dictionary in Python.
The dict comprehension will get passed each key-value pair in the dictionary where we can check if the value is not None before including it in the final result.
Copied!my_dict = 'name': 'Bobby Hadz', 'age': None, 'country': None, 'language': 'German' > new_dict = key: value for key, value in my_dict.items() if value is not None > # 👇️ print(new_dict)
Dict comprehensions are very similar to list comprehensions.
They perform some operation for every key-value pair in the dictionary or select a subset of key-value pairs that meet a condition.
Note that this approach doesn’t remove the None values from the dictionary in place, it creates a new dictionary that doesn’t contain any None values.
An alternative approach is to use a for loop.
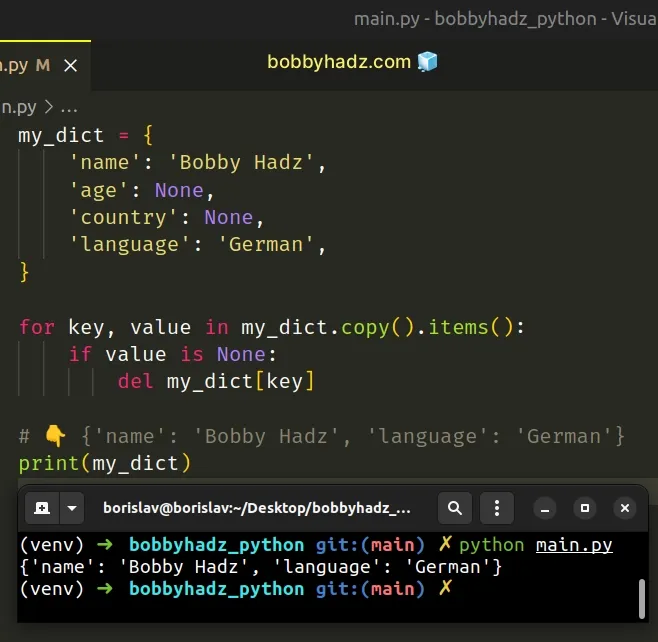
# Remove None values from a Dictionary using a for loop
This is a three-step process:
- Use a for loop to iterate over the dictionary’s items.
- On each iteration, check if the value is None .
- If the value is None , delete the corresponding key.
Copied!my_dict = 'name': 'Bobby Hadz', 'age': None, 'country': None, 'language': 'German', > for key, value in my_dict.copy().items(): if value is None: del my_dict[key] # 👇️ print(my_dict)
We created a copy of the dictionary because it’s not allowed to change the size of a dictionary while iterating over it.
The dict.items method returns a new view of the dictionary’s items ((key, value) pairs).
Copied!my_dict = 'id': 1, 'name': 'Bobby Hadz'> print(my_dict.items()) # 👉️ dict_items([('id', 1), ('name', 'Bobby Hadz')])
On each iteration, we check if the value is None, and if it is, we delete the corresponding key.
This approach mutates the original dictionary.
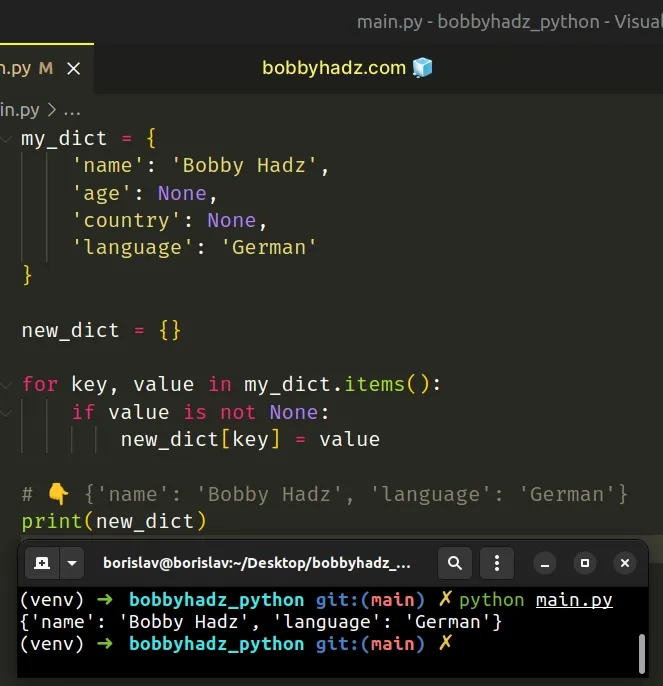
# Adding the not-None key-value pairs to a new dictionary
You can also add not-None key-value pairs to a new dictionary instead of mutating the original one.
Copied!my_dict = 'name': 'Bobby Hadz', 'age': None, 'country': None, 'language': 'German' > new_dict = > for key, value in my_dict.items(): if value is not None: new_dict[key] = value # 👇️ print(new_dict)
On each iteration, we check if the value is not None , and if it isn’t, we add the key-value pair to a new dictionary.
# Remove the None values from a nested Dictionary in Python
If you need to remove the None values from a nested dictionary, use a recursive function.
Copied!def remove_none_from_dict(dictionary): for key, value in list(dictionary.items()): if value is None: del dictionary[key] elif isinstance(value, dict): remove_none_from_dict(value) elif isinstance(value, list): for item in value: if isinstance(item, dict): remove_none_from_dict(item) return dictionary my_dict = 'name': 'Bobby Hadz', 'age': None, 'country': None, 'language': 'German', 'address': 'country': None, 'city': 'Example' > > # # 'address': > print(remove_none_from_dict(my_dict))
The function uses the dict.items() method to iterate over the supplied dictionary.
On each iteration, we check if the current value is None .
Copied!if value is None: del dictionary[key]
If the condition is met, we delete the key from the dictionary.
The first elif statement checks if the value is a dictionary.
Copied!elif isinstance(value, dict): remove_none_from_dict(value)
If the value is a nested dictionary, we pass it to the function, so it removes the direct None values.
The second elif statement checks if the value is a list.
Copied!elif isinstance(value, list): for item in value: if isinstance(item, dict): remove_none_from_dict(item)
If the value is a list, then it might be a list of dictionaries, so we iterate over the list.
On each iteration, we check if the current item is a dictionary.
If the condition is met, we call the function with the dictionary, so it can remove the direct None values.
# Replace None values in a Dictionary in Python
To replace the None values in a dictionary:
- Use the object_pairs_hook keyword argument of the json.loads() method.
- Check if each value the object_pairs_hook function gets called with is None .
- If it is, replace None with the specified replacement value.
Copied!import json person = 'name': None, 'address': 'country': None, 'city': None, 'street': 'abc 123'>, 'language': 'German', > def replace_none_in_dict(items): replacement = '' return k: v if v is not None else replacement for k, v in items> json_str = json.dumps(person) person = json.loads(json_str, object_pairs_hook=replace_none_in_dict) # 👇️ , 'language': 'German'> print(person)
You can update the replacement variable in the replace_none_in_dict function to change the replacement value.
The json module makes things a little more straightforward if you have nested objects that may have None values.
The json.dumps method converts a Python object to a JSON formatted string.
The json.loads method parses a JSON string into a native Python object.
We passed the object_pairs_hook keyword argument to the json.loads() method and set it to a function.
Copied!def replace_none_in_dict(items): replacement = '' return k: v if v is not None else replacement for k, v in items>
The function is going to get called with a list of key-value pair tuples, e.g. [(‘country’, None), (‘city’, None), (‘street’, ‘abc 123’)] .
In our function, we simply check if the value is not None and return it, otherwise, we return a replacement value.
# Replace None values in a Dictionary using dict comprehension
If your dictionary doesn’t contain nested objects, use a dict comprehension.
Copied!person = 'name': None, 'address': None, 'language': 'German', 'country': 'Germany', > # 👇️ change this if you need to update the replacement value replacement = '' employee = key: value if value is not None else replacement for key, value in person.items() > # 👇️ print(employee)
The dict.items method returns a new view of the dictionary’s items ((key, value) pairs).
Copied!my_dict = 'id': 1, 'name': 'Alice'> print(my_dict.items()) # 👉️ dict_items([('id', 1), ('name', 'Alice')])
In our dict comprehension, we check if each value isn’t None and return it, otherwise, we return a replacement.
Note that this approach wouldn’t work if your dictionary has nested dictionaries that have None values. If that’s the case, use the previous approach.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
I wrote a book in which I share everything I know about how to become a better, more efficient programmer.
How to remove None values from a dictionary in Python
In this tutorial, we will be learning the steps to be followed in order to remove None Values from a dictionary in Python. We’ll be using Pycharm IDE to solve this problem. We will be using items() function to detect a None value in the given dictionary.
Creating a Dictionary with Keys and Values
#Create a List keys = ["Name", "Age", "Country","Nothing"] #Convet List Into Keys d = dict.fromkeys(keys) print(d) #Give values to required Keys d['Name']='CodeSpeedy' d['Age']=18 d['Country']='India' print(d)
For Loop to remove keys with Value as None
items() method is used to return the list with all dictionary keys with values.
We will be using a for loop to check if a value from the dictionary d matches with None. If the condition is true, then we simply delete the key that has None as its value.
#Using a for loop to remove keys with Value as None for key, value in dict(d).items(): if value is None: del dPython dict remove none print(d)
Complete Code
Here is the complete Python code to remove None values from a dictionary:
#Create a List keys = ["Name", "Age", "Country","Nothing"] #Convet List Into Keys d = dict.fromkeys(keys) print(d) #Give values to required Keys d['Name']='CodeSpeedy' d['Age']=18 d['Country']='India' print(d) #Using a for loop to remove keys with Value as None for key, value in dict(d).items(): if value is None: del dPython dict remove none print(d)
How to Remove Null/None Values From a Dictionary in Python
Given a Python dictionary, remove any term whose value is None
Challenge
Given a Python dictionary, remove any term whose value is None
The function should accommodate nested dictionaries, which occur when the value of a term is another dictionary.
Solution
To clean the provided dictionary, each key-value pair will be examined. If the data type of the value is a dict , then the function should be recursively called. Otherwise, as long as the value is not equal to None , then it will be added to the clean dictionary, which is returned after iterating over the entire dictionary.
def cleanNullTerms(d):
clean = <> for k, v in d.items():
if isinstance(v, dict):
nested = cleanNullTerms(v)
if len(nested.keys()) > 0:
clean[k] = nested
elif v is not None:
clean[k] = v return clean
To test our function, we’ll use sample data that includes None values in both the top level as well as a nested dictionary.
data = "first_name": "Jonathan",
"middle_name": None,
"last_name": "Hsu",
"family": "mother": "Mary",
"father": "Peter",
"brother": "Charles",
"sister": None
>
>print(cleanNullTerms(data))
"""
'first_name': 'Jonathan',
'last_name': 'Hsu',
'family': 'mother': 'Mary',
'father': 'Peter',
'brother': 'Charles'
>
>
"""
Honorable Mention
If nested dictionaries are not a concern then a one-liner function using dictionary comprehension is sufficient. This function would perform a shallow clean, meaning None values in nested data structures would not be removed.
def cleanNullTerms(d):
return k:v
for k, v in d.items()
if v is not None
>