- How To Uninstall Python Packages
- Open a terminal/command prompt
- Check if pip is installed
- List installed packages
- Uninstall the package
- Verify that the package is uninstalled
- Uninstalling python packages and dependencies
- Verify the package is uninstalled
- Uninstall dependencies
- Uninstall packages in a Python virtual environment
- Activate the virtual environment
- Uninstall the package
- Verify the package is uninstalled
- Deactivate the virtual environment
- Uninstall Python Package Dependencies With Pipenv
- Activate the Pipenv environment
- Uninstall the package and its dependencies
- Verify the package and its dependencies are uninstalled
- Deactivate the Pipenv environment
- Uninstall A python Package Installed With Setuptools
- Python delete all packages windows
- # Remove/uninstall all packages installed by pip in Python
- # Remove/uninstall all packages installed by pip using xargs
- # Recreate your virtual environment
- # Additional Resources
How To Uninstall Python Packages
Uninstalling Python packages and their dependencies can be done using the pip package manager. The pip package manager is a built-in tool for Python that can be used to install, upgrade, and uninstall packages.
Following is a step-by-step explanation of how to uninstall a package in Python using pip:
- Open a terminal/command prompt
- Check if pip is installed
- List installed packages
- Uninstall the package
- Verify that the package is uninstalled
Open a terminal/command prompt
Open a terminal/command prompt on your system.
Check if pip is installed
Check if pip is installed on your system by running the following command:
If pip is installed, you will see its version number in the output. If not, you will see an error message.
List installed packages
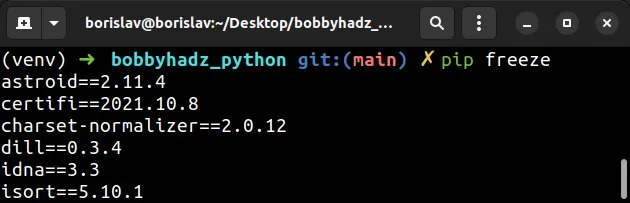
List all the packages that are currently installed on your system using the following command:
Above command command will display a list of all the packages installed on your system along with their version numbers.
Uninstall the package
To uninstall a package, use the following command:
Replace package_name with the name of the package you want to uninstall.
If the package has any dependencies that are no longer required, pip will also prompt you to uninstall them. You can choose whether or not to uninstall them by typing y or n.
Verify that the package is uninstalled
After the package is uninstalled, verify that it is no longer installed on your system by running the pip list command again.
If the package is no longer listed, then it has been successfully uninstalled.
Now you have successfully uninstalled a package in Python using pip.
Uninstalling python packages and dependencies
If the package has dependencies that are no longer required, pip will prompt you to uninstall them as well. You can choose to uninstall the dependencies by typing y or to keep them by typing n.
Verify the package is uninstalled
To verify that the package has been successfully uninstalled, run the pip list command again:
If the package is no longer listed, then it has been successfully uninstalled.
Uninstall dependencies
If you have uninstalled a package and want to remove its dependencies, you can use the pip autoremove command:
Above command will remove any packages that are no longer needed by your system.
It’s important to note that, be careful when using the pip autoremove command as it may remove packages that are still being used by other packages. It’s always a good idea to verify which packages will be removed before running this command.
Now you have successfully uninstalled a Python package and its dependencies using pip.
Uninstall packages in a Python virtual environment
Uninstalling packages in a Python virtual environment is similar to uninstalling packages in a standard Python environment. However, it is important to activate the virtual environment before running the uninstallation command.
Following are the steps to uninstall packages in a Python virtual environment:
Activate the virtual environment
Navigate to the directory where the virtual environment is installed and activate it. The activation command depends on the operating system and the shell you are using.
On Windows using Command Prompt, you can activate the virtual environment by running the following command:
On macOS or Linux using bash shell, you can activate the virtual environment by running the following command:
Uninstall the package
Once the virtual environment is activated, you can use the pip uninstall command to uninstall the package. Replace package_name with the name of the package you want to uninstall:
Verify the package is uninstalled
To verify that the package has been successfully uninstalled, run the following command:
Above command will display a list of all installed packages in the virtual environment. If the package you just uninstalled is not listed, then it has been successfully uninstalled.
Deactivate the virtual environment
After you have uninstalled the package, you can deactivate the virtual environment by running the following command:
Above command will return your command prompt to the standard shell environment.
Now you have successfully uninstalled a package in a Python virtual environment.
Uninstall Python Package Dependencies With Pipenv
Pipenv is a tool for managing Python environments and packages. It provides a way to install packages in a virtual environment, along with their dependencies. To uninstall a package and its dependencies using Pipenv, follow these steps:
Activate the Pipenv environment
Open your command line interface and navigate to the directory where your Pipenv environment is located. Activate the environment by running the following command:
Above command will activate the virtual environment and set the environment variables needed to use Pipenv.
Uninstall the package and its dependencies
To uninstall a package and its dependencies, use the following command:
Replace package_name with the name of the package you want to uninstall.
For example, if you want to uninstall the numpy package and its dependencies, you can type:
Above command will remove the numpy package and its dependencies from your virtual environment.
Verify the package and its dependencies are uninstalled
To verify that the package and its dependencies have been successfully uninstalled, use the pipenv graph command to list all the packages installed in the virtual environment:
Above command will display a list of all the packages installed in the virtual environment, along with their dependencies. If the package and its dependencies are no longer listed, then they have been successfully uninstalled.
Deactivate the Pipenv environment
After you have uninstalled the package and its dependencies, you can deactivate the virtual environment by running the following command:
Above command will return your command prompt to the standard shell environment.
Now you have successfully uninstalled a package and its dependencies using Pipenv.
Uninstall A python Package Installed With Setuptools
Uninstalling a Python package installed with Setuptools is similar to uninstalling a package installed with pip.
- Python Datatype conversion
- Python Mathematical Function
- Basic String Operations in Python
- Python Substring examples
- How to check if Python string contains another string
- Check if multiple strings exist in another string : Python
- Memory Management in Python
- Python Identity Operators
- What is a None value in Python?
- How to Install a Package in Python using PIP
- How to update/upgrade a package using pip?
- How to call a system command from Python
- How to use f-string in Python
- Python Decorators (With Simple Examples)
- Python Timestamp Examples
Python delete all packages windows
Last updated: Feb 20, 2023
Reading time · 4 min
# Remove/uninstall all packages installed by pip in Python
The command uses pip freeze to get a list of the installed packages and uninstalls them without asking for confirmation.
Copied!# 👇️ optionally save the packages that are to be removed pip freeze > to_remove.txt # 👇️ remove/uninstall all packages installed by pip pip uninstall -y -r (pip freeze)
The command uses pip freeze to get a list of the installed packages in requirements format and uninstalls the packages.
The -y option is short for -yes and means that pip should not ask for confirmation when uninstalling.
The -r option is short for —requirement and uninstalls all the packages in the given requirements file.
If you need to install the packages again, use the pip install -r command.
Copied!pip install -r to_remove.txt
If you get an error message that setuptools is not installed, e.g. No module named ‘pkg_resources’, run the following command.
Copied!# 👇️ for Linux or MacOS python -m pip install --upgrade pip setuptools wheel python3 -m pip install --upgrade pip setuptools wheel # 👇️ Windows py -m pip install --upgrade pip setuptools wheel # 👇️ try upgrading pip pip install --upgrade pip setuptools pip3 install --upgrade pip setuptools
You can also store the installed packages in a file and uninstall them directly from the file.
Copied!# 👇️ store the installed packages in a file called reqs.txt pip freeze > reqs.txt # 👇️ uninstall packages 1 by 1 pip uninstall -r reqs.txt # 👇️ uninstall all packages without confirmation required pip uninstall -r reqs.txt -y
I used the name reqs.txt because you might not want to override the contents of your existing requirements.txt (if you already have one).
# Remove/uninstall all packages installed by pip using xargs
Alternatively, you can use xargs to remove all packages installed by pip .
Copied!# 👇️ optionally save the packages that are to be removed pip freeze > to_remove.txt # 👇️ remove/uninstall all packages installed by pip pip freeze | xargs pip uninstall -y
The command uses pip freeze to get a list of the installed packages and then uses xargs to pass the packages as an argument to the pip uninstall command.
We then used the xargs command to pass the installed packages as an argument to the pip uninstall command.
The -y (yes) option makes it so pip doesn’t ask for confirmation when uninstalling packages.
If you need to install the packages again, use the pip install -r command.
Copied!pip install -r to_remove.txt
You might have to install pip , setuptools and wheel after running the command.
Copied!# 👇️ for Linux or MacOS python -m pip install --upgrade pip setuptools wheel python3 -m pip install --upgrade pip setuptools wheel # 👇️ Windows py -m pip install --upgrade pip setuptools wheel # 👇️ try upgrading pip pip install --upgrade pip setuptools pip3 install --upgrade pip setuptools
# Recreate your virtual environment
Alternatively, you can simply recreate your virtual environment.
- Deactivate your virtual environment.
- Delete the folder of your virtual environment.
- Create a new virtual environment.
- Activate the new virtual environment.
Copied!# 👇️ (optional) store the packages to be removed pip freeze > to_remove.txt # 👇️ deactivate deactivate # 👇️ Remove the old virtual environment folder: macOS and Linux rm -rf venv # 👇️ Remove the old virtual environment folder: Windows rd /s /q "venv" # 👇️ initialize a new virtual environment python -m venv venv # 👇️ activate on Unix or MacOS source venv/bin/activate # 👇️ activate on Windows (cmd.exe) venv\Scripts\activate.bat # 👇️ activate on Windows (PowerShell) venv\Scripts\Activate.ps1 # 👇️ (optional) install the modules in your requirements.txt file pip install -r requirements.txt
If running python -m venv venv doesn’t work, try the following commands:
We used the deactivate command to deactivate the virtual environment, deleted the venv folder and created a new virtual environment.
Your virtual environment will use the version of Python that was used to create it.
Make sure to use the correct activation command depending on your operating system.
You might have to upgrade your pip version in the new virtual environment.
Copied!pip install --upgrade pip
You can use the pip install -r requirements.txt command in the new virtual environment if you need to install any packages from a requirements file.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
I wrote a book in which I share everything I know about how to become a better, more efficient programmer.