- Get the Previous Month or Day in Python
- Getting the first and the last day of any month
- Getting the last day of the previous month
- Getting the day of the week for a given date
- Approach #1 Using date.strftime(format)
- Approach #2 Using date.weekday()
- Smart Dates
- Parsing relative dates using the dateparser library
- Datetime Get Previous Month Python
- How to Get the Datetime of the Previous Month in Python?
- Method 1: Get the Datetime of Previous Month in Python Using “datetime” Module With “replace()” Method
- Example
- Method 2: Get the Datetime of Previous Month in Python Using “datetime” Module With Extension “dd”
- Example
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Maria Naz
Get the Previous Month or Day in Python
This article will discuss best practices for parsing dates and getting a specific month, day, or year in the past or the future.
We will use different Python libraries to manipulate dates and times. Apart from the standard datetime package (documentation), we will leverage other modules like dateparser and dateutil to extract localized dates in strings.
For example, the packages should be able to parse strings like “20 days ago”, “two months and two days ago”, “yesterday”, “445 days ago at noon”, et cetera.
Getting the first and the last day of any month
In this case, the datetime package can do the job. All we need to do is get the date today and then set the day to 1.
If you are only interested in the date and not the time, you can call date.today() in line two, then set the day value to 1.
We can get the last day of the month using an inbuilt package called calendar in Python. Precisely, we will make use of the monthrange() function. This function takes the year and month and returns a tuple of the two values – the weekday of the first day of the given month and the number of days in the month. The weekday is integer coded from 0 being a Monday through 6 being Sunday.
From this example, we can note that February 2024 has 29 days (as expected, being a leap year) and that the first day of the month is 3 (Thursday).
We can then use the calendar.monthrange() function to get the last day of the month as follows:
last_day_of_prev_month = date . today ( ) . replace ( day = calendar . monthrange ( year , month ) [ 1 ] ) — timedelta ( days = 1 )
Note that we have just borrowed the ideas we already know from how we got the month’s first day and used the calendar.monthrange() function to pick the number of days in a month for the last day of the month.
Getting the last day of the previous month
Since we already know how to get the first day of the month, we can use the timedelta() function to subtract one day from that.
Getting the day of the week for a given date
Let us discuss two approaches here:
Approach #1 Using date.strftime(format)
The function strftime() returns a string representation of the given date. An explicit format string controls it. To get the weekday, we will use the %A directive as follows (For a complete list of formatting directives, you can read the documentation of strftime)
Today is Tuesday, based on the first line and November 11, 2021, was on Sunday.
Approach #2 Using date.weekday()
This function returns the day of the week as an integer, where Monday is 0 and Sunday is 6. We can proceed to convert the integer into the full name accordingly if we choose to. We can use a dictionary to do this conversion or calendar.day_name[].
Smart Dates
This section will discuss the parsing of localized dates found in string formats that may not fit the string format required by datetime.strftime(), which we discussed in the previous section.
We will be parsing relative dates like “tomorrow”, “in 20 days”, “2 years and 2 weeks ago”, “yesterday”, etc. Let’s now discuss the two packages we can use to parse relative dates
Used case: Parsing of relative dates is crucial when dealing with dates that have been recorded in different formats.
Parsing relative dates using the dateparser library
The parse() function in dateparser can parse relative dates by factoring features like time zones, language, lookup dates in long strings, and even supporting different calendar systems. The general syntax for the parser is
Datetime Get Previous Month Python
While programming in Python, you may want to get the previous month’s date and time. Python provides multiple modules and functions to get it quickly and efficiently. The “datetime” module is one of them that is commonly utilized to work with date and time. This module is included by default in Python, so we are not required to install it separately.
This post will discuss getting the previous month’s date and time in Python.
How to Get the Datetime of the Previous Month in Python?
To get the datetime of the previous month in Python, the following techniques are used:
Method 1: Get the Datetime of Previous Month in Python Using “datetime” Module With “replace()” Method
To get the datetime of the previous month in Python, the “datetime” module with the “replace()” method can be used. The “datetime” module is the built-in package of Python that contains classes for handling dates and times.
Example
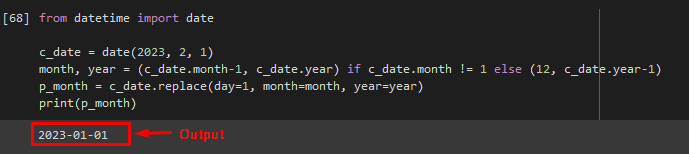
At first, import the “date” module from the “datetime” library:
Now, create a variable that stores the current date, month, and year with the “date” method:
Use the “if” condition with month and years to check if the provided condition is equal to the “1”. If not, then subtract the “1” from the year and current date and store them to the “month” and “year”:
month , year = ( c_date. month — 1 , c_date. year ) if c_date. month != 1 else ( 12 , c_date. year — 1 )
Now, call the “replace()” method with day, month, and year values as arguments and store them to the p_month“ variable:
Use the print statement to view the previous month’s date:
Method 2: Get the Datetime of Previous Month in Python Using “datetime” Module With Extension “dd”
To get the datetime of the previous month in Python, the “datetime” module can be used by importing the “dd” extension. Now, check the provided example for a more understanding.
Example
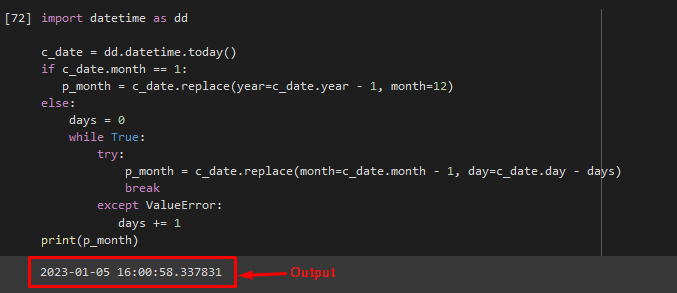
Initially, Import the “datetime” module by utilizing the “dd” extension:
Now, get the current time and date, and call the “dd.datetime.today()” method:
Call the “replace()” method inside the “if” condition, if the current month is “1”, then replace it with the “c_date” as “dd.datetime.year – 1”. Otherwise, set the “days” variable to “0”. You also use the “try” and “catch” blocks. If any exception occurs and print the previous month date and time:
ifc_date. month == 1 :
p_month = c_date. replace ( year = c_date. year — 1 , month = 12 )
else :
days = 0
while True :
try :
p_month = c_date. replace ( month = c_date. month — 1 , day = c_date. day — days )
break
except ValueError :
days + = 1
print ( p_month )
As you can see, the below-given output contains the previous month date and time:
That’s it! We have elaborated how to get the previous month datetime in Python.
Conclusion
To get the previous month’s datetime in Python, the “datetime” module with the “replace()” method and the “datetime” module using the extension “dd” techniques are used. The “datetime” module contains classes for handling dates and times. It can be utilized by importing the “dd” extension. The “replace()” method checks the provided condition and replaces the value according to user desire. This post elaborated on the ways of getting the previous month datetime in Python.
About the author
Maria Naz
I hold a master’s degree in computer science. I am passionate about my work, exploring new technologies, learning programming languages, and I love to share my knowledge with the world.