- Create a List of numbers from 1 to N in Python
- Introduction
- Method 1: Using range() function
- Frequently Asked:
- Example 1: With step size 1
- Example 2: With step size 2
- Method 2: Using numpy.arange() function
- Example 1: With step size 1
- Example 2: With step size 2
- Method 3: Using while loop
- Method 4: Using List Comprehension
- Summary
- Related posts:
- Share your love
- Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
- Terms of Use
- Disclaimer
- Python create list number
- # Table of Contents
- # Create a list of numbers from 1 to N in Python
- # Create a list of numbers from 1 to N using a list comprehension
- # Using a floating-point number for the step with numpy
- # Create a list of numbers from 1 to N using a list comprehension
- # Create a list of numbers from 1 to N using a for loop
- # Create a list of numbers from 1 to N using a while loop
- # Additional Resources
Create a List of numbers from 1 to N in Python
In this article, we will discuss how to create a Python List of numbers from 1 to N.
Table Of Contents
Introduction
Suppose value of N is 15, then the list should contain numbers from 1 to 15. Like this,
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 ,7, 8, 19, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15]
There are different ways to create a list containing numbers from 1 to N. Let’s dicuss them one by one,
Method 1: Using range() function
The range() function in Python, accepts three arguments i.e. start, stop and step. It returns a sequence of integers from start (inclusive) to stop (exclusive) by given step.
Frequently Asked:
To create a list of numbers from 1 to N, we will pass start as 1, and stop as N + 1. Default value of step size is 1. Therefore, it will return a sequence of numbers from 1 to N. Then we can cast that sequence to a list.
Example 1: With step size 1
In this example, we will create a sequence of numbers from 1 to 15.
N = 15 # Get a list of numbers from 1 to N (including N) numbers = list(range(1, N + 1)) print(numbers) # Print the type of numbers object print(type(numbers))
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15]
We created a List of numbers from 1 to N, where N is 15.
Example 2: With step size 2
In this example, we will create a sequence of numbers from 1 to 15, with step size 2. It will keep every alternate number from 1 to 15.
N = 15 # Get a list of every alternate numbers from 1 to N (including N) numbers = list(range(1, N + 1, 2)) print(numbers)
We creates a list of numbers from 1 to 15, but with step size 2. It means, list contains every alternate number from 1 to 15.
Method 2: Using numpy.arange() function
The arange() function of NumPy module, accepts three arguments i.e. start, stop and step. It returns a numpy array of integers from start (inclusive) to stop (exclusive) by the given step size.
To create a list of numbers from 1 to N, we will pass start as 1, and stop as N + 1. Default value of step size is 1. Therefore, it will return an array of numbers from 1 to N. Then we can call the tolist() function of array, to convert it to a list of numbers.
Example 1: With step size 1
In this example, we will create a sequence of numbers from 1 to 15.
import numpy as np N = 15 # Get a list of numbers from 1 to N (including N) numbers = np.arange(1, N+1).tolist() print(numbers)
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15]
We created a List of numbers from 1 to N, where N is 15.
Example 2: With step size 2
In this example, we will create a sequence of numbers from 1 to 15, with step size 2. It will keep every alternate number from 1 to 15.
import numpy as np N = 15 # Get a list of every alternate numbers from 1 to N (including N) numbers = np.arange(1, N+1, 2).tolist() print(numbers)
We creates a list of numbers from 1 to 15, but with step size 2. It means, list contains every alternate number from 1 to 15.
Method 3: Using while loop
Create an empty list. Then use the while loop to iterate from 1 till N, and for each ith number in loop, append number i to the list. This way our list will have numbers from 1 till N.
Let’s see an example, in which we will create a sequence of numbers from 1 to 15.
# Create an empty list numbers = [] N = 15 i = 1 # Iterate from 1 till N while iWe creates a list of numbers from 1 to 15.
Method 4: Using List Comprehension
To create a list of numbers from 1 to N. Pass the 1, and N+1 to the range() function. It will give a sequence of numbers from 1 to N. Then create a list from them, using List Comprehension. Let’s see an example,
N = 15 # Create a list of numbers from 1 to N numbers = [i for i in range(1, N+1)] print(numbers)We creates a list of numbers from 1 to 15.
Summary
We learned about four different ways to create a list of numbers from 1 till N. Thanks.
Related posts:
Share your love
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed.
Terms of Use
Disclaimer
Copyright © 2023 thisPointer
To provide the best experiences, we and our partners use technologies like cookies to store and/or access device information. Consenting to these technologies will allow us and our partners to process personal data such as browsing behavior or unique IDs on this site and show (non-) personalized ads. Not consenting or withdrawing consent, may adversely affect certain features and functions.
Click below to consent to the above or make granular choices. Your choices will be applied to this site only. You can change your settings at any time, including withdrawing your consent, by using the toggles on the Cookie Policy, or by clicking on the manage consent button at the bottom of the screen.
The technical storage or access is strictly necessary for the legitimate purpose of enabling the use of a specific service explicitly requested by the subscriber or user, or for the sole purpose of carrying out the transmission of a communication over an electronic communications network.
The technical storage or access is necessary for the legitimate purpose of storing preferences that are not requested by the subscriber or user.
The technical storage or access that is used exclusively for statistical purposes. The technical storage or access that is used exclusively for anonymous statistical purposes. Without a subpoena, voluntary compliance on the part of your Internet Service Provider, or additional records from a third party, information stored or retrieved for this purpose alone cannot usually be used to identify you.
The technical storage or access is required to create user profiles to send advertising, or to track the user on a website or across several websites for similar marketing purposes.
Python create list number
Last updated: Feb 22, 2023
Reading time · 5 min
# Table of Contents
# Create a list of numbers from 1 to N in Python
To create a list of numbers from 1 to N:
- Use the range() class to create a range object from 1 to N.
- Use the list() class to convert the range object to a list.
- The new list will contain the numbers in the specified range.
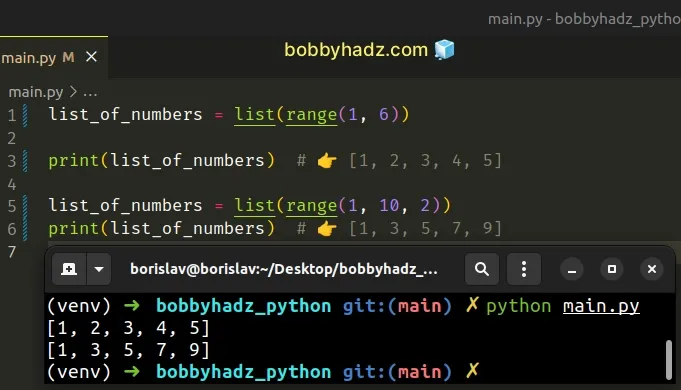
Copied!list_of_numbers = list(range(1, 6)) print(list_of_numbers) # 👉️ [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] list_of_numbers = list(range(1, 10, 2)) print(list_of_numbers) # 👉️ [1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
The range class is commonly used for looping a specific number of times in for loops and takes the following arguments:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| start | An integer representing the start of the range (defaults to 0 ) |
| stop | Go up to, but not including the provided integer |
| step | Range will consist of every N numbers from start to stop (defaults to 1 ) |
If you only pass a single argument to the range() constructor, it is considered to be the value for the stop parameter.
Copied!list_of_numbers = list(range(5)) # 👇️ [0, 1, 2, 3, 4] print(list_of_numbers)
The example shows that if the start argument is omitted, it defaults to 0 and if the step argument is omitted, it defaults to 1 .
If values for the start and stop parameters are provided, the start value is inclusive, whereas the stop value is exclusive.
Copied!list_of_numbers = list(range(1, 5)) # 👇️ [1, 2, 3, 4] print(list_of_numbers)
If you need to specify a step, pass a third argument to the range() class.
Copied!list_of_numbers = list(range(1, 10, 2)) print(list_of_numbers) # 👉️ [1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
The list contains every second number starting from 1 to 10 .
The step argument can only be set to an integer.
# Create a list of numbers from 1 to N using a list comprehension
You can also use a list comprehension to create a list of numbers from 1 to N.
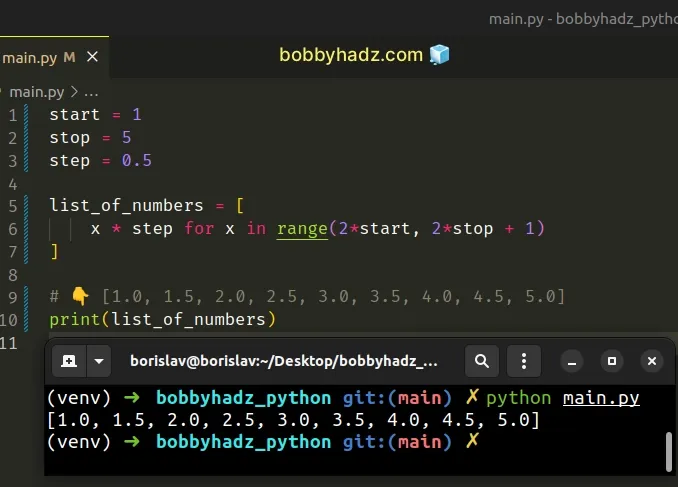
Copied!start = 1 stop = 5 step = 0.5 list_of_numbers = [ x * step for x in range(2*start, 2*stop + 1) ] # 👇️ [1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, 3.5, 4.0, 4.5, 5.0] print(list_of_numbers)
List comprehensions are used to perform some operation for every element or select a subset of elements that meet a condition.
The list in the example starts at 1 and goes to 5 (inclusive) in increments of 0.5 .
You can update the start , stop and setup values.
This approach is useful when you have a step value that is not an integer because the range() class only supports integer values.
# Using a floating-point number for the step with numpy
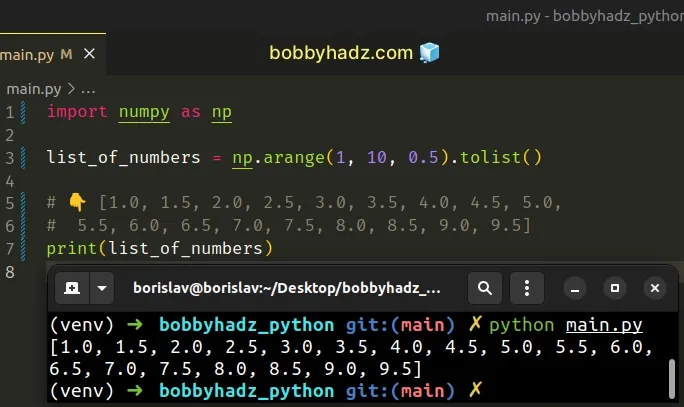
If you need to use a floating-point number for the step , use the numpy.arange() method.
Copied!import numpy as np list_of_numbers = np.arange(1, 10, 0.5).tolist() # 👇️ [1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, 3.5, 4.0, 4.5, 5.0, # 5.5, 6.0, 6.5, 7.0, 7.5, 8.0, 8.5, 9.0, 9.5] print(list_of_numbers)
The numpy.arange method returns an array of evenly spaced values within the given interval.
We used the tolist method to convert the array to a list.
If you need to install the NumPy package, run the following command.
Copied!pip install numpy # 👇️ or pip3 pip3 install numpy
You can omit the step argument to get a list of values from 1 to N in increments of 1.
Copied!import numpy as np list_of_numbers = np.arange(1, 11).tolist() # 👇️ [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10] print(list_of_numbers)
The numpy.arange() method is very similar to the range() class but allows for step values that are floating-point numbers.
# Create a list of numbers from 1 to N using a list comprehension
You can also use a list comprehension to create a list of numbers from 1 to N.
Copied!list_of_numbers = [number for number in range(1, 6)] print(list_of_numbers) # 👉️ [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
List comprehensions are used to perform some operation for every element or select a subset of elements that meet a condition.
On each iteration, we return the current number.
The new list contains the numbers in the range object.
However, this isn't necessary unless you need to perform some operation for every number in the range object.
# Create a list of numbers from 1 to N using a for loop
The same can be achieved using a simple for loop.
Copied!list_of_numbers = [] for number in range(1, 6): list_of_numbers.append(number) print(list_of_numbers) # 👉️ [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
We used a for loop to iterate over the range object.
On each iteration, we use the list.append() method to append the current number to a list.
The list.append() method adds an item to the end of the list.
Copied!my_list = ['bobby', 'hadz'] my_list.append('com') print(my_list) # 👉️ ['bobby', 'hadz', 'com']
Using the list() class to convert the range object to a list should be sufficient unless you have to perform some operation for every number in the range object.
You can also define a reusable function that creates a list of numbers in a for loop.
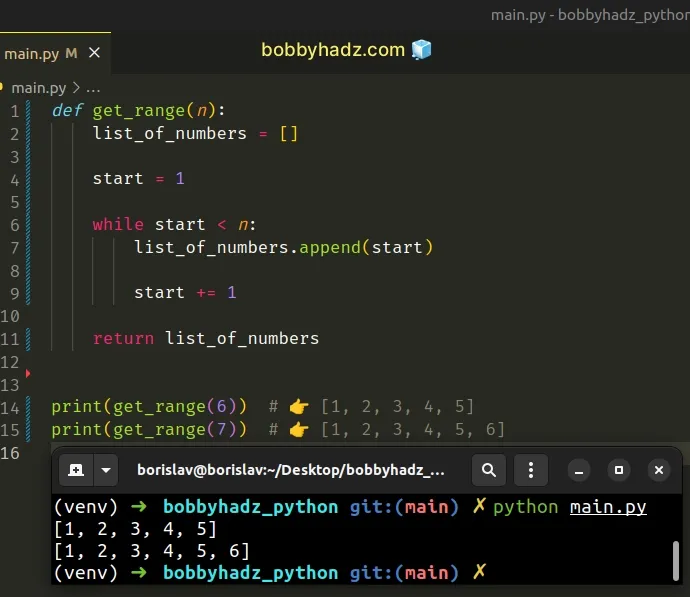
Copied!def get_range(n): list_of_numbers = [] for number in range(1, n + 1): list_of_numbers.append(number) return list_of_numbers print(get_range(6)) # 👉️ [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] print(get_range(7)) # 👉️ [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
The function takes n as a parameter and creates a list of numbers from 1 to n.
# Create a list of numbers from 1 to N using a while loop
You can also use a while loop to create a list of numbers from 1 to N.
Copied!def get_range(n): list_of_numbers = [] start = 1 while start n: list_of_numbers.append(start) start += 1 return list_of_numbers print(get_range(6)) # 👉️ [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] print(get_range(7)) # 👉️ [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
The get_range function takes n as a parameter and creates a list of numbers from 1 to n .
On each iteration, we append the current start value to the list and increment it.
Once the start value is equal to or greater than n , the condition is no longer met and the while loop exits.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
I wrote a book in which I share everything I know about how to become a better, more efficient programmer.